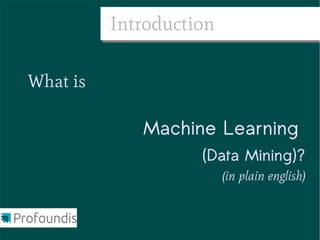
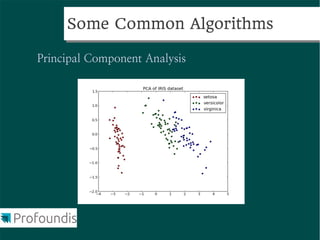
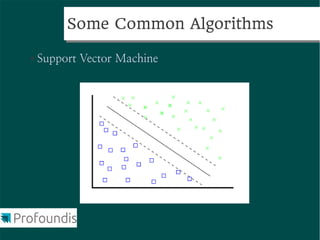
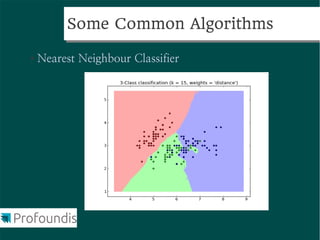
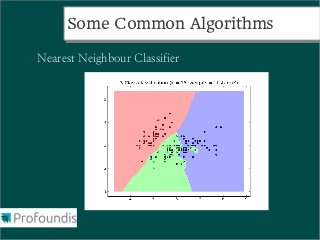
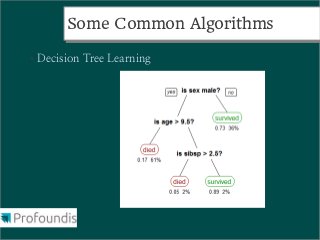
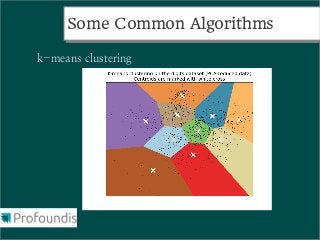
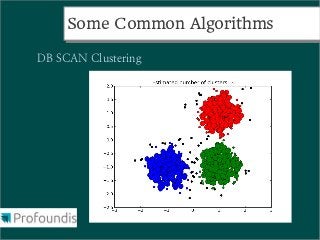
This document provides an introduction to machine learning concepts and the scikit-learn library. It discusses the basics of supervised and unsupervised learning techniques, common machine learning algorithms like k-means clustering and support vector machines, and steps for performing machine learning analysis. Examples of applying machine learning to tasks like log file analysis, outlier detection, and forecasting are also presented. The document encourages exploring scikit-learn's documentation and examples to learn how to apply machine learning to real-world problems.