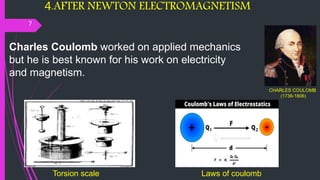
Physics began with early Greek philosophers like Aristotle and Ptolemy. Copernicus initiated the Copernican Revolution by proposing a heliocentric model of the solar system. Galileo and Newton further developed mechanics through experimentation and mathematical formulation. Later, scientists like Maxwell, Hertz and Marconi established electromagnetism as a fundamental force. Pioneers such as Planck, Einstein, Bohr and Heisenberg developed quantum theory and relativity, radically changing views of reality. Today, physicists seek a grand unified theory connecting all fundamental forces.