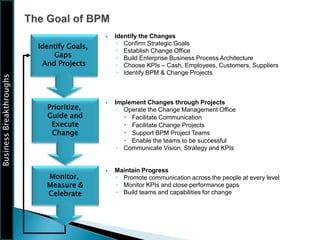
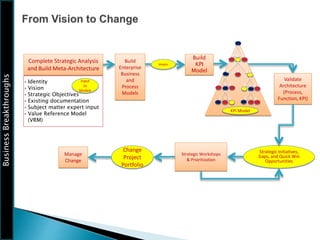
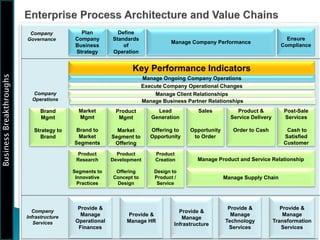
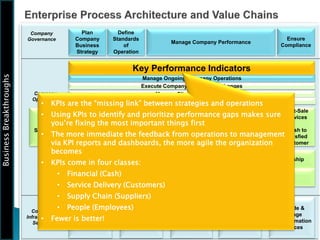
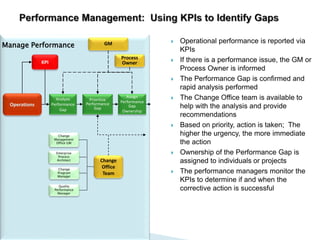
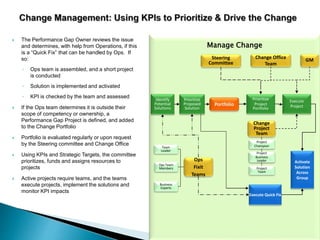
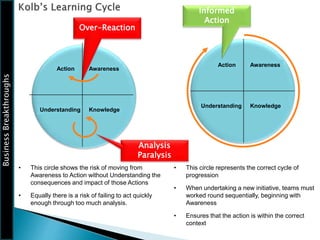
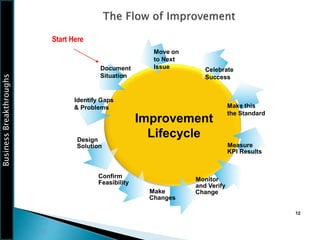
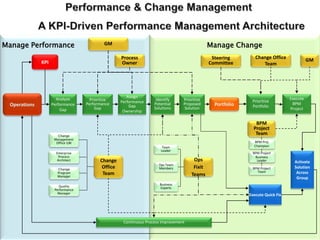
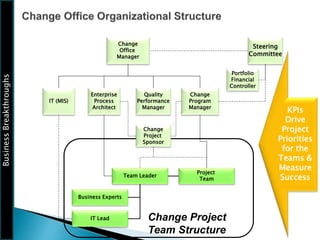
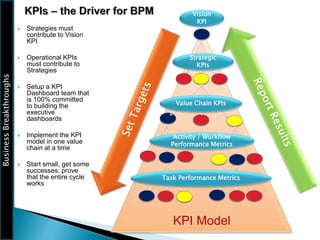
The document outlines the framework for Business Breakthroughs Inc., detailing its enterprise business model, governance, performance management, and change management processes. It emphasizes the importance of Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for identifying strategic gaps and prioritizing performance improvements across various operational areas. The document provides guidance on implementing change initiatives, maintaining progress, and ensuring organizational agility through effective management of KPIs and communication.