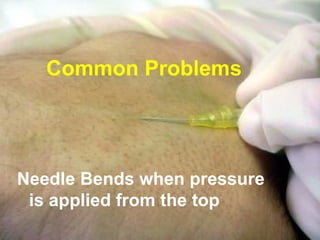
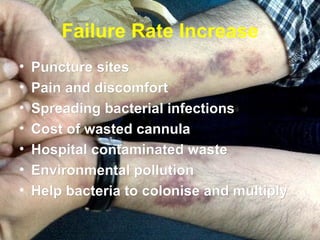
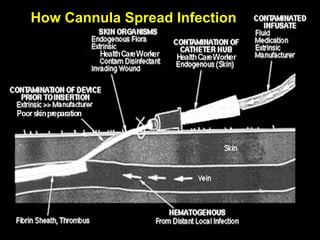
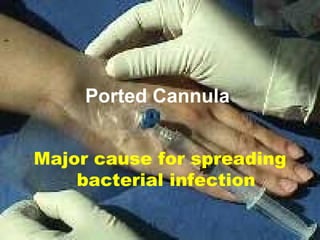
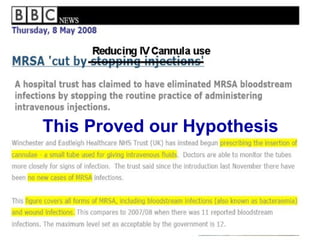
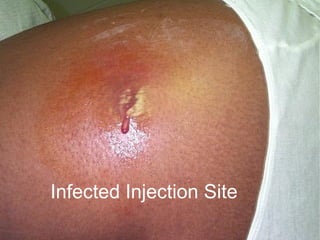
The document discusses the major threat posed by cannulas and ported cannulas in spreading bacterial infections in hospitals. It notes that while cannulas were rapidly accepted by the medical profession when first invented, the technique of insertion was not properly evaluated. This led to an increase in staphylococcal infections that paralleled the rise in cannula use. Various types of cannulas are described but all are noted to do the same job. Common problems with insertion like needle bending and failure rates are also discussed.