1) The document provides instructions for a math lesson assignment on linear functions and solving equations. Students are to complete practice problems from their textbook and sign up for extra credit on an earlier test.
2) The warmup exercises involve solving various equations algebraically. The lesson defines linear functions and their relationship to roots/zeros, discussing how to graphically and algebraically solve linear equations by setting them equal to zero.
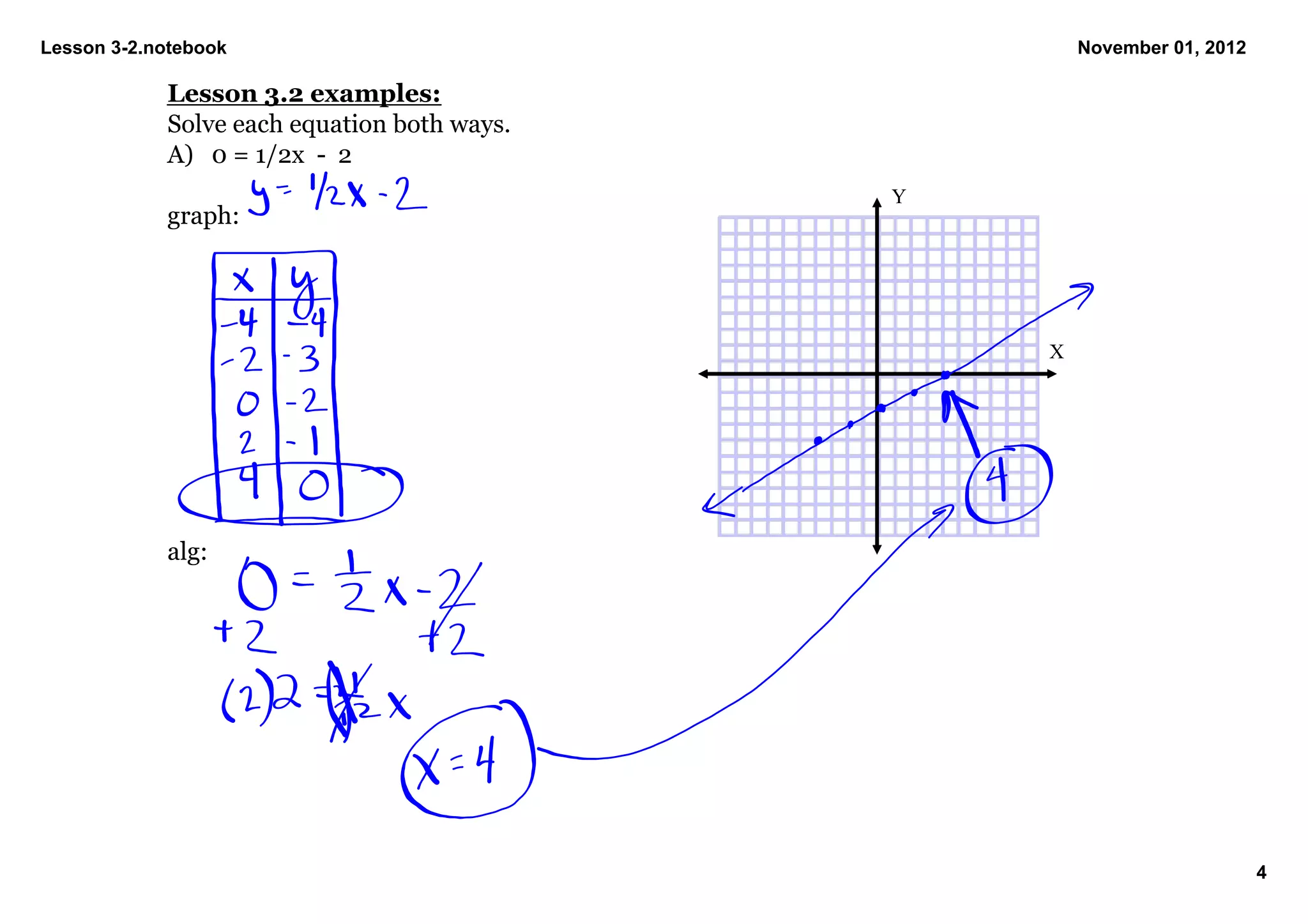
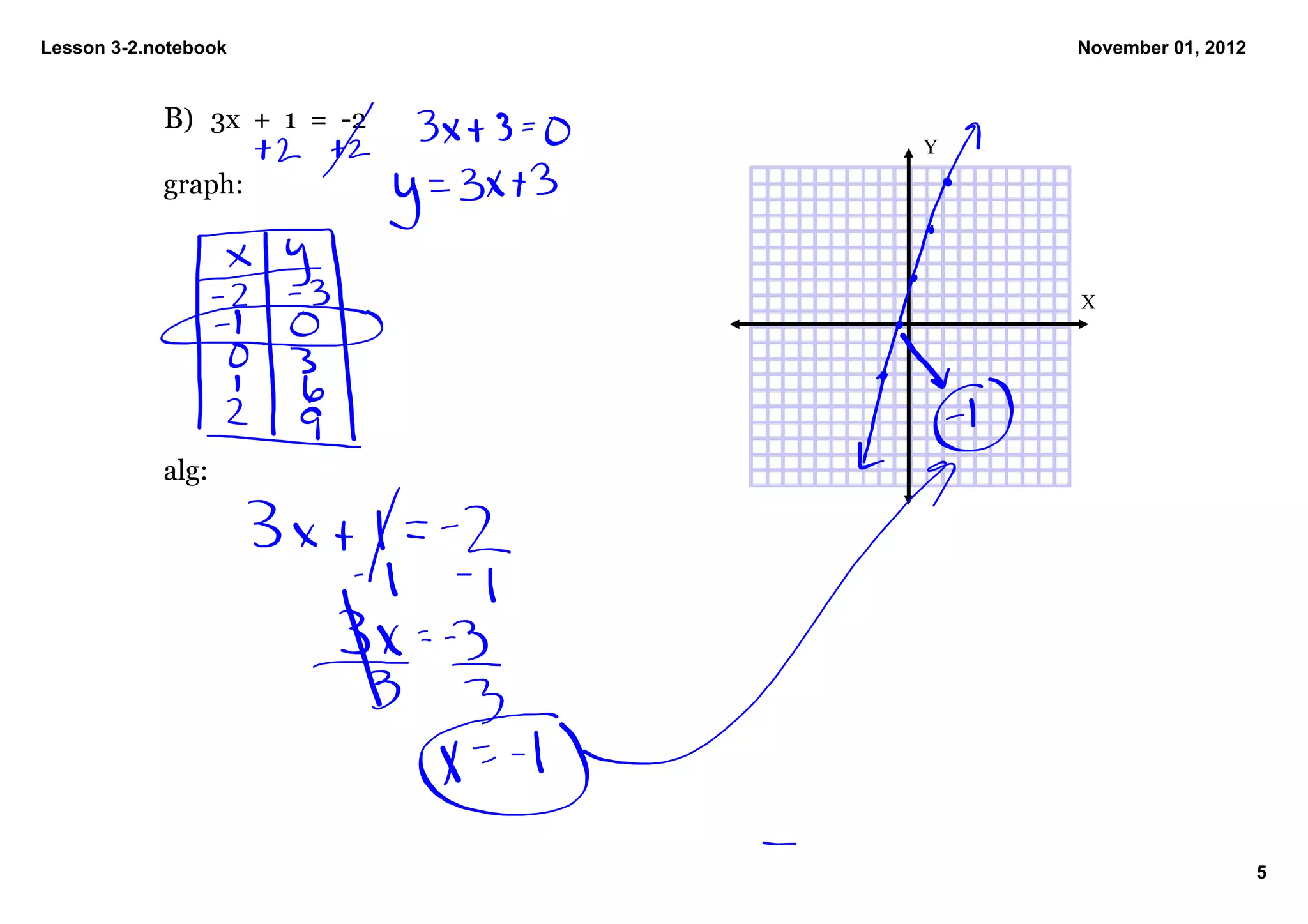
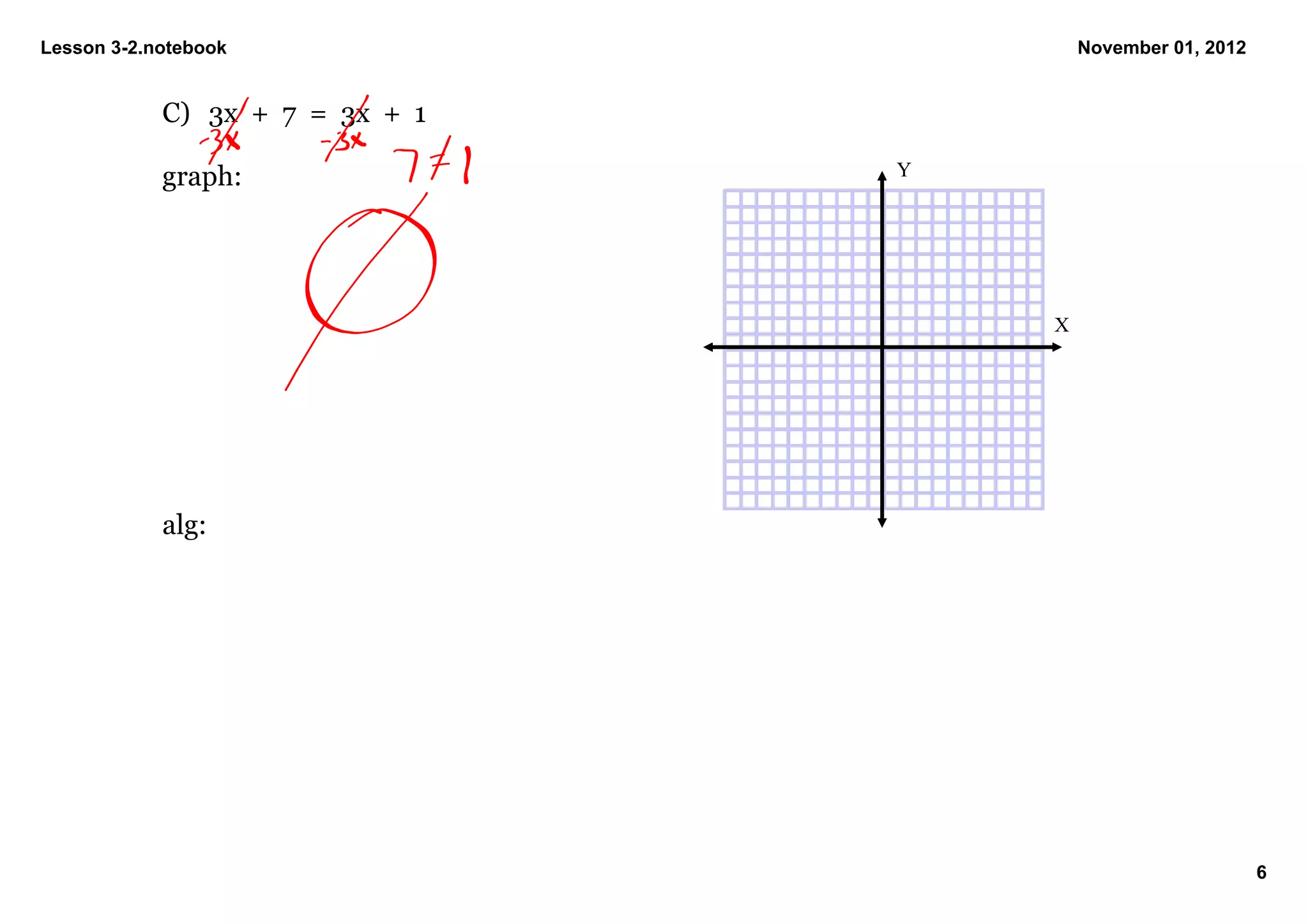
3) Examples are shown of solving equations both graphically by sketching the line and algebraically by isolating the variable, such as solving 0 = 1/2x - 2 for x = 4.


![Lesson 32.notebook November 01, 2012
Lesson 3.2:
*linear function a function for which the graph is a line
*root the solution of an equation [any value that makes the equation
true]
*zeros values of x for which f(x) = 0
...located at the xintercept of the function...or the xvalue when y = 0
***We can solve linear functions 2 ways:
by graphing where it hits the "x" axis
by algebraically isolate the variable
To solve graphically...
set everything equal to zero
plug y in for the zero
graph it
where it his the "x" is the solution
3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/8thalg-l3-2-nov1-121101110838-phpapp02/75/8th-alg-l3-2-nov1-3-2048.jpg)