This document discusses 8 PowerShell commands that every Windows administrator should know:
1. Get-Help provides help and documentation for PowerShell cmdlets.
2. Get-ExecutionPolicy and Set-ExecutionPolicy get and set the PowerShell execution policy which controls script execution.
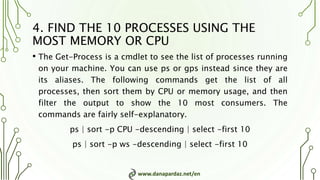
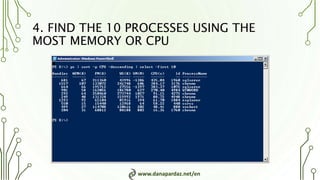
3. Get-Process lists running processes and can be used with Sort and Select to find the top 10 processes by CPU or memory usage.
4. Stop-Process and Start-Service stop and start system services and processes.
5. Export-CSV saves PowerShell output like lists of processes or Active Directory users to CSV files.
6. Get-Service, Stop-Service, and Start-Service get, stop, and