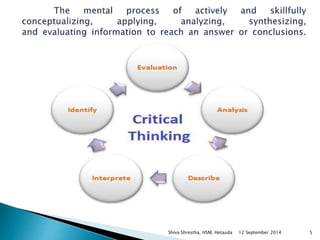
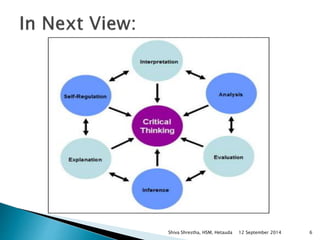
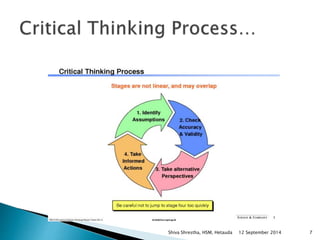
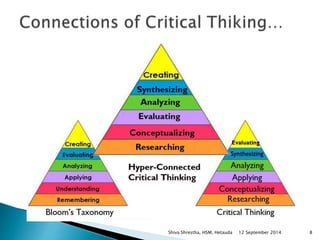
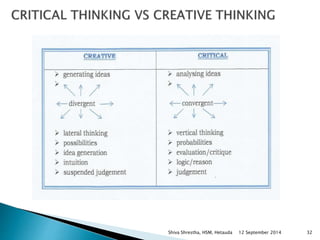
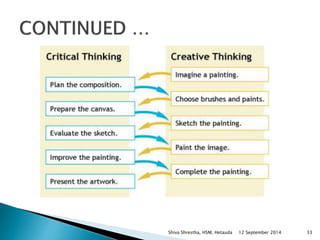
The document is a lecture presentation by Shiva Shrestha of Hetauda School of Management on critical thinking. It defines critical thinking and discusses various viewpoints on it. It also covers the critical thinking process, importance of critical thinking, inquiry skills used in critical thinking, relationship between critical thinking and decision making, costs of fallacious reasoning, and more.