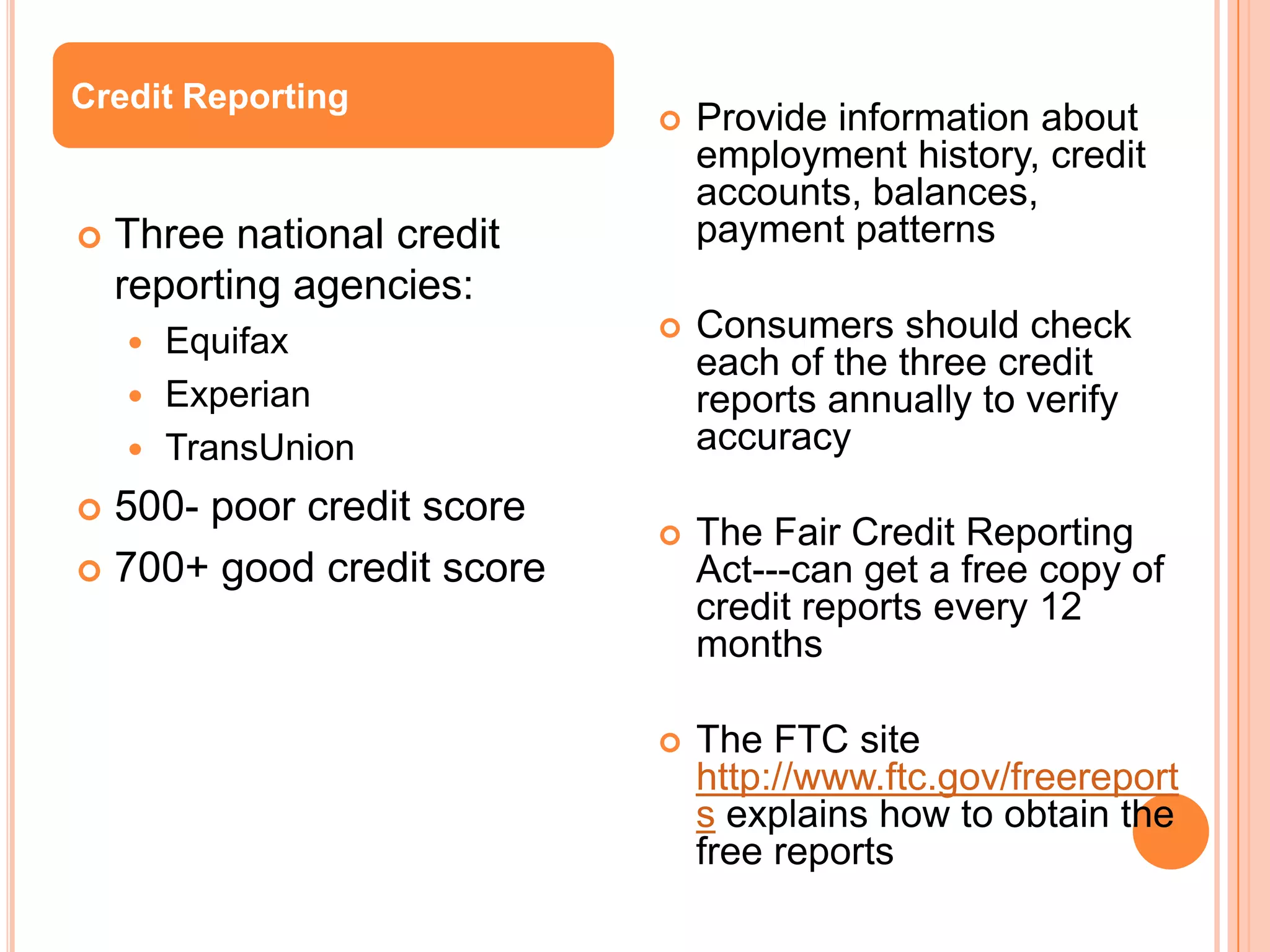
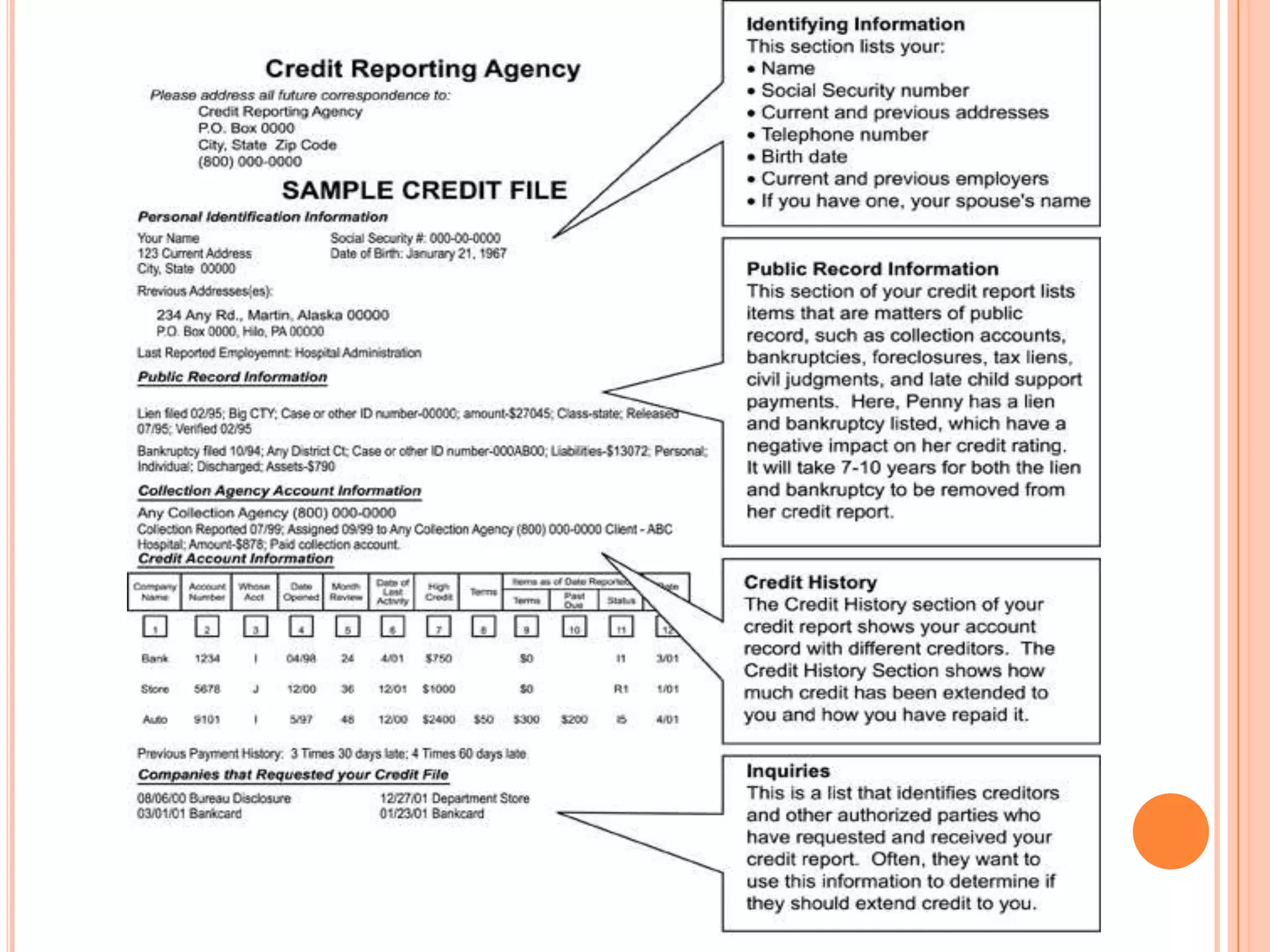
The document provides information on establishing and maintaining good credit. It discusses the importance of creditors evaluating a person's ability and willingness to repay debts through their credit rating and the "3 Cs" of character, capacity, and capital. It offers tips for establishing good credit such as taking out small loans and paying all bills on time. It also covers considerations for choosing credit, types of loan sources, and maintaining good financial habits to protect one's credit rating.