This document contains an agenda for an English language learning class. The objectives are to:
1. Read and discuss Act 2, Scene 5 of a play (likely Romeo and Juliet), answering comprehension questions.
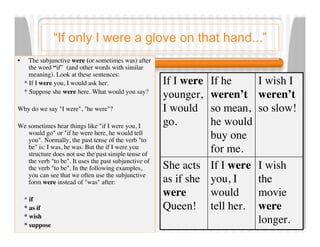
2. Learn about and practice using the subjunctive mood in English.
3. Practice the reading strategy of monitoring and clarifying.
4. Finish reading Act 2 and begin Act 3 of the play, answering more comprehension questions.