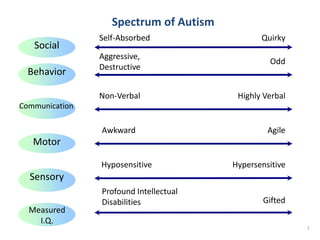
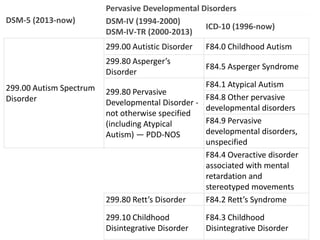
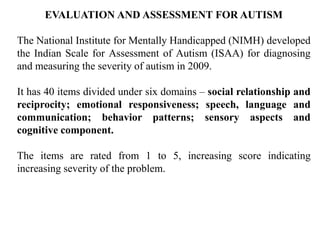
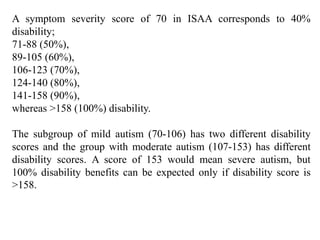
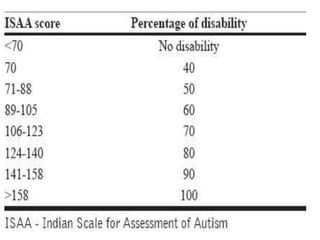
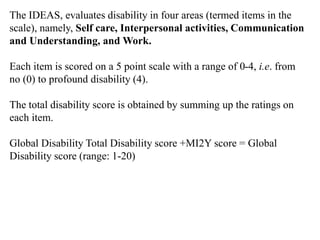
This document discusses disability certification in psychiatry. It provides information on evaluating and assessing autism using the Indian Scale for Assessment of Autism (ISAA). The ISAA rates individuals on a scale from 1 to 5 across six domains to determine the severity of autism as mild, moderate or severe. It also discusses the Indian disability evaluation and assessment scale (IDEAS) for measuring psychiatric disability in conditions like schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, dementia and obsessive compulsive disorder. The IDEAS evaluates disability across four areas and provides a global disability score to determine eligibility for welfare benefits. The document also provides guidance on assessing and determining disability levels for individuals with mental retardation based on their intelligent quotient score.