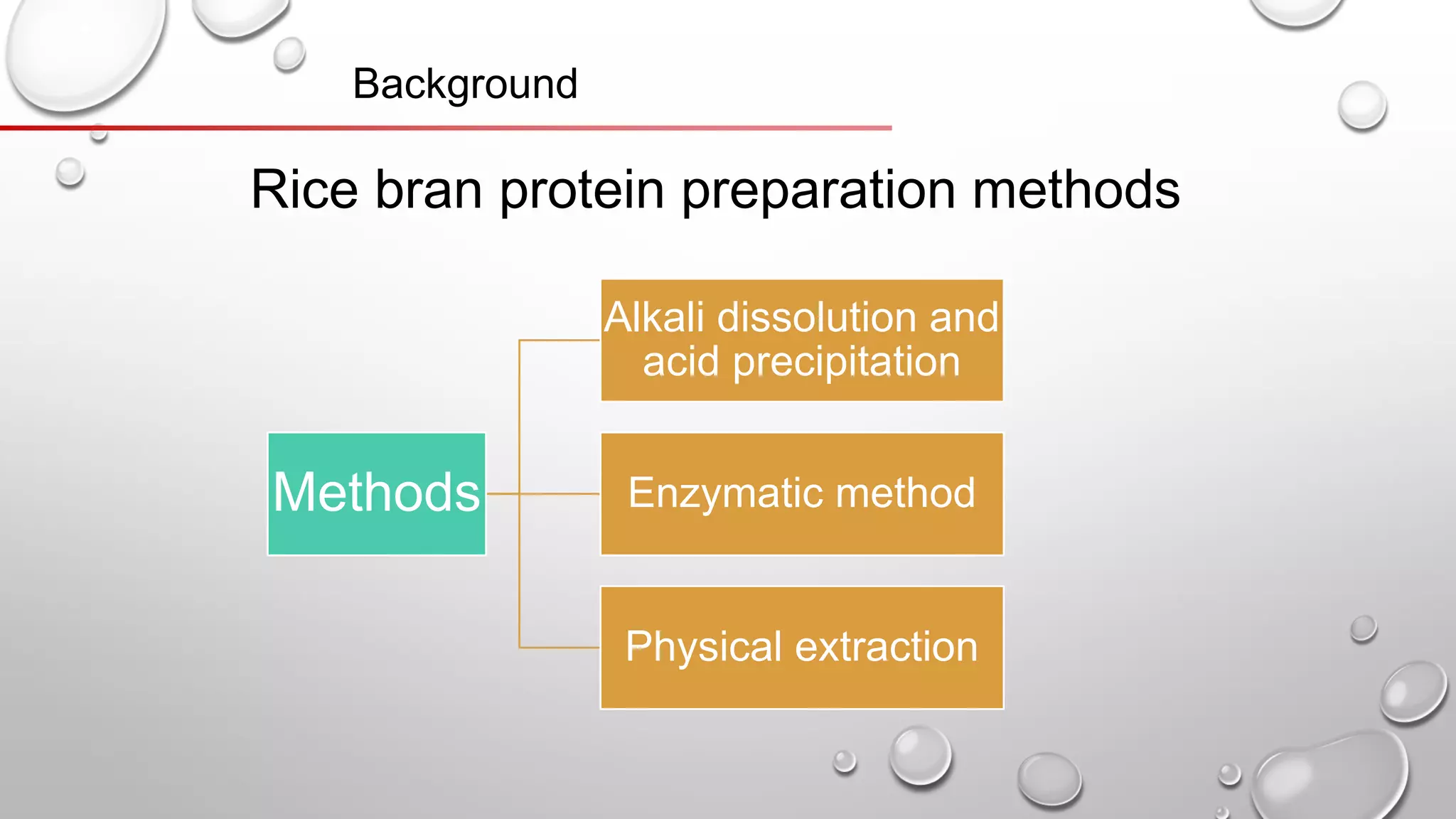
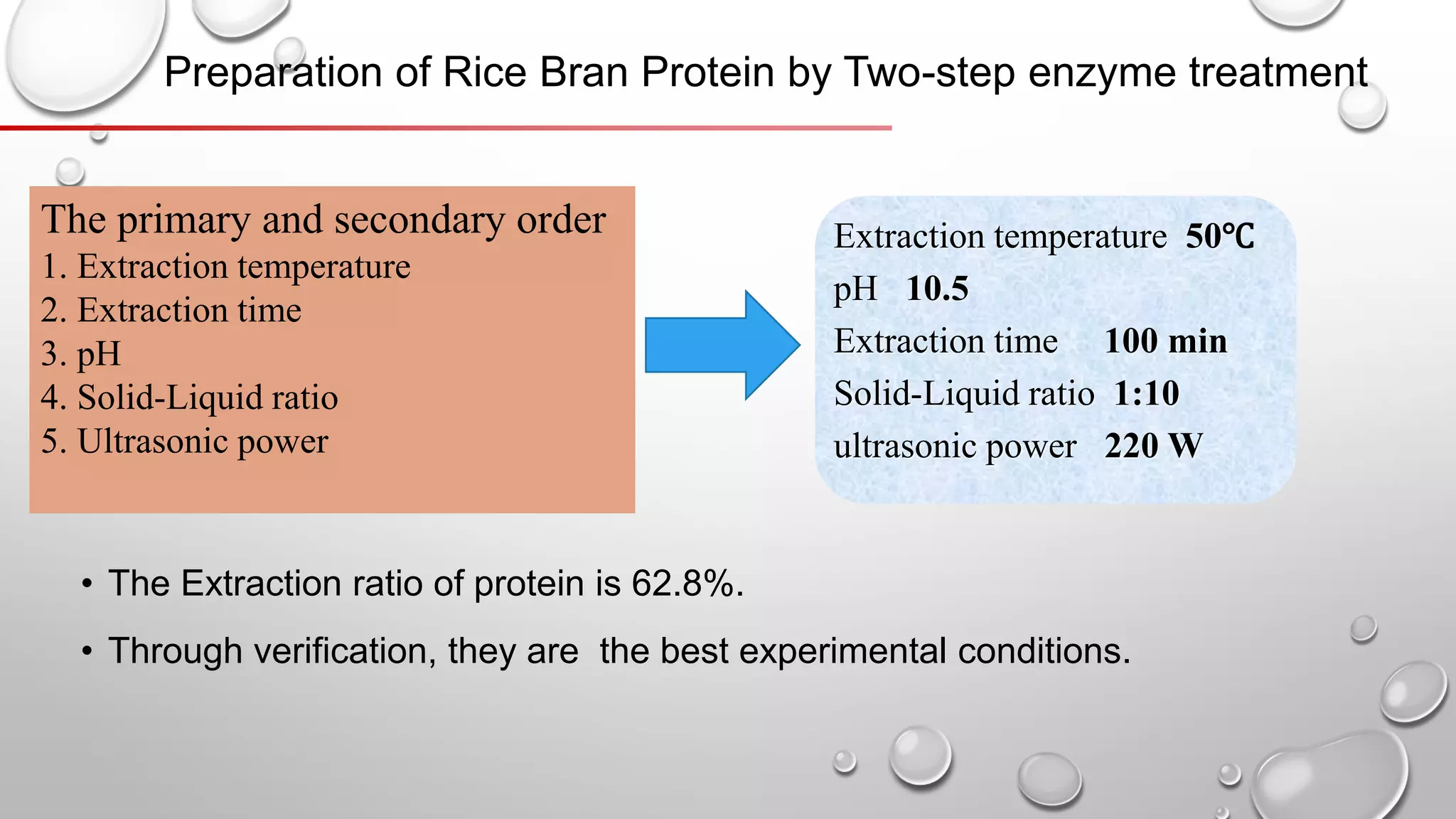
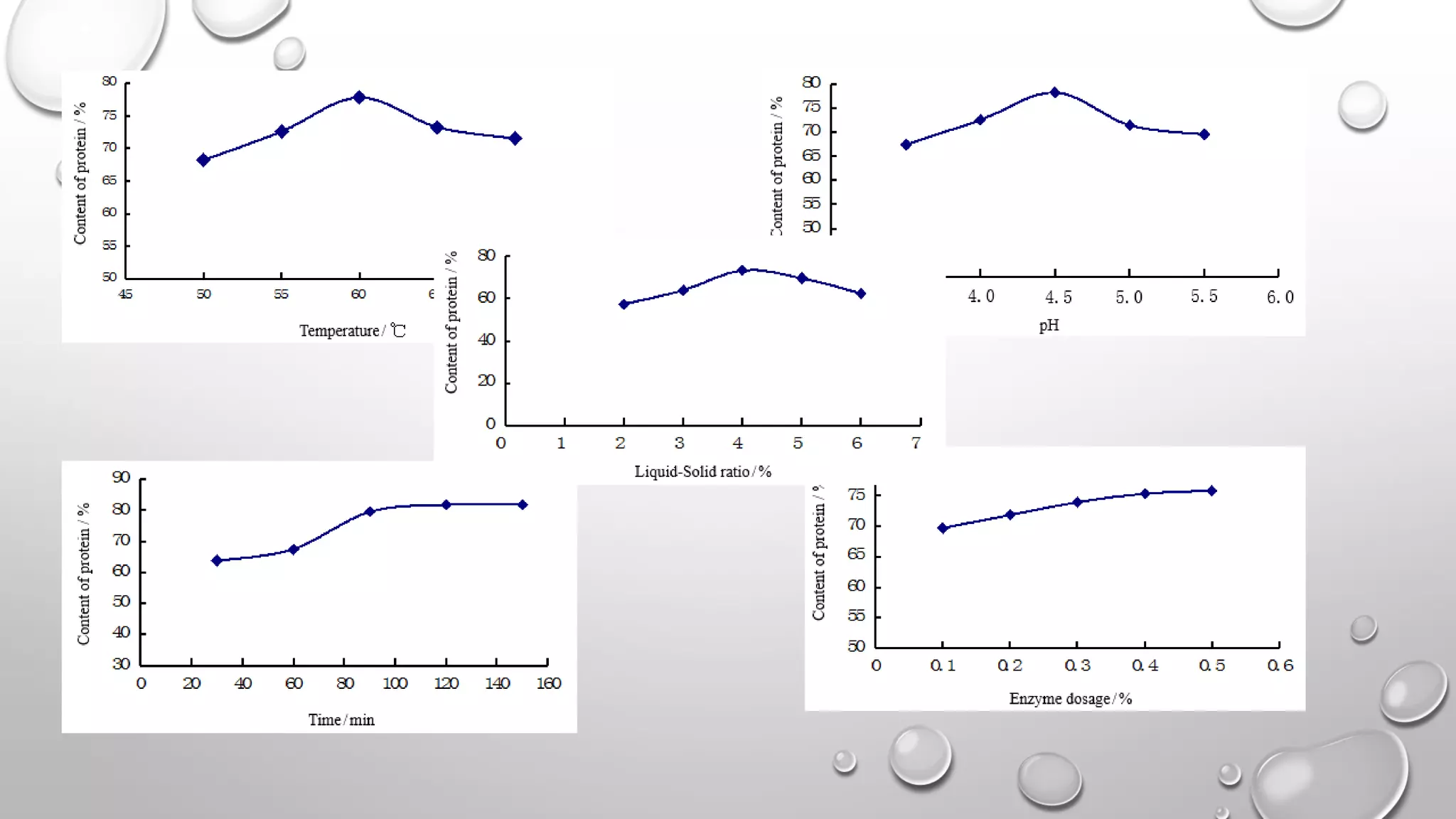
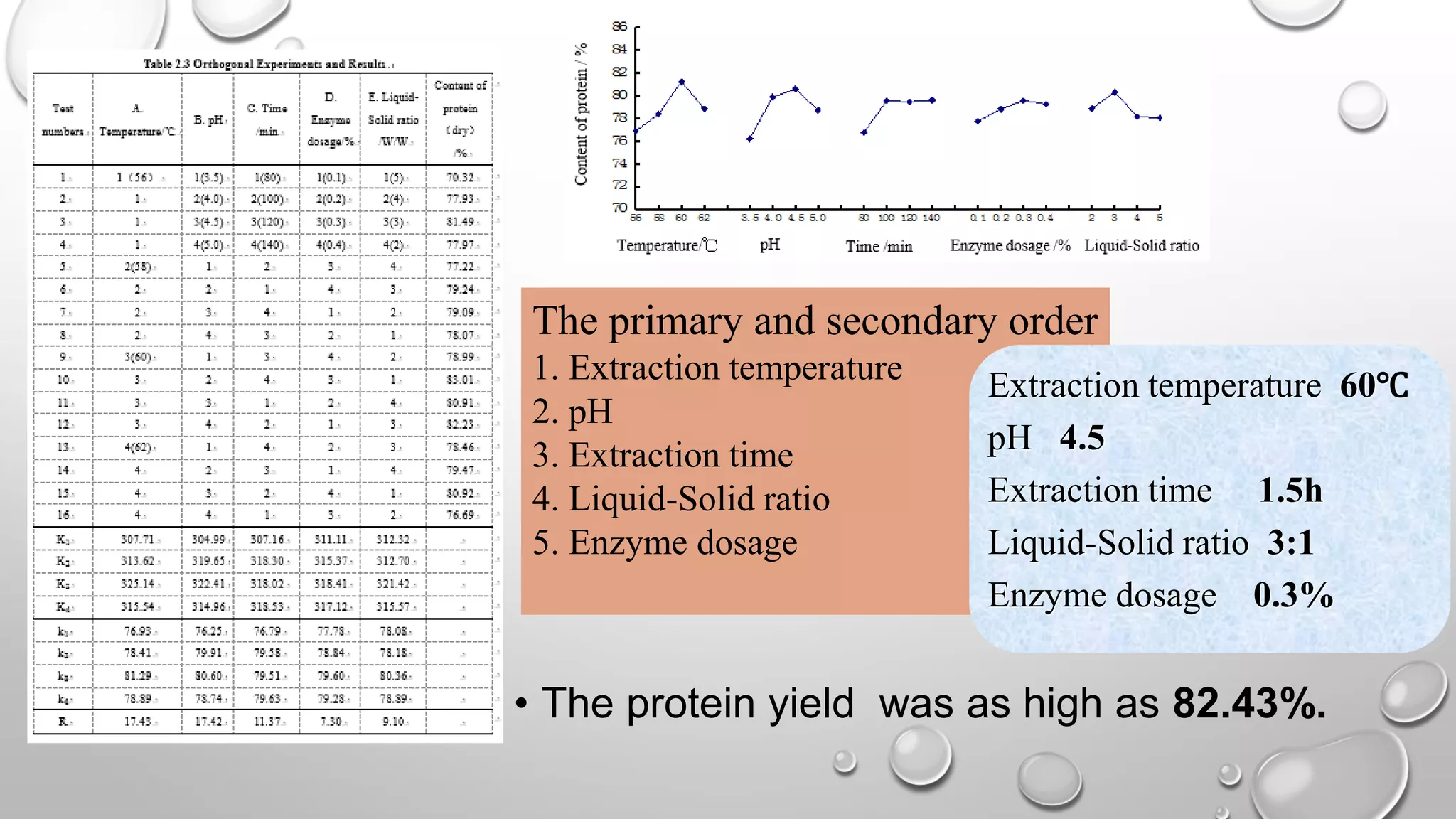
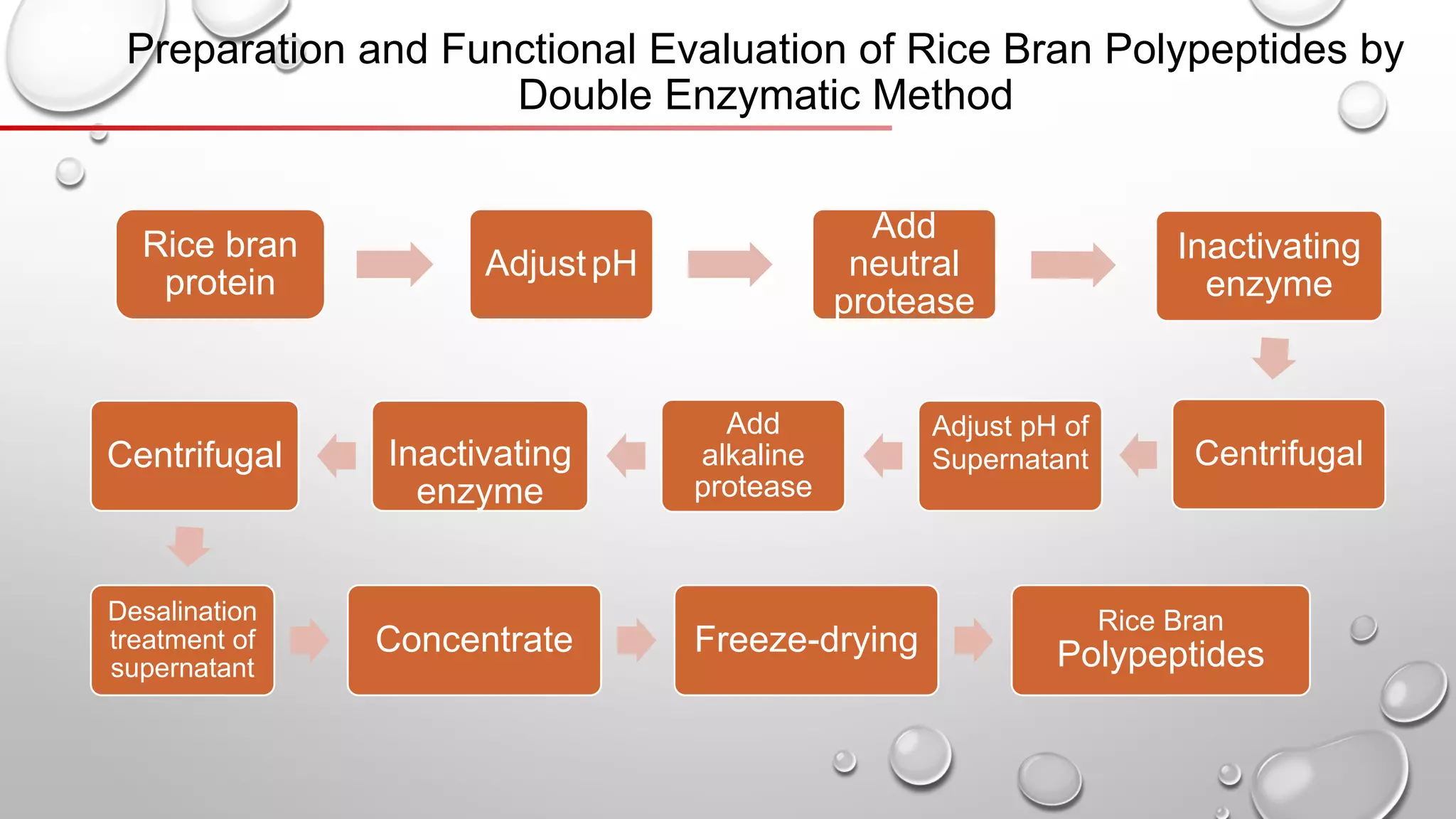
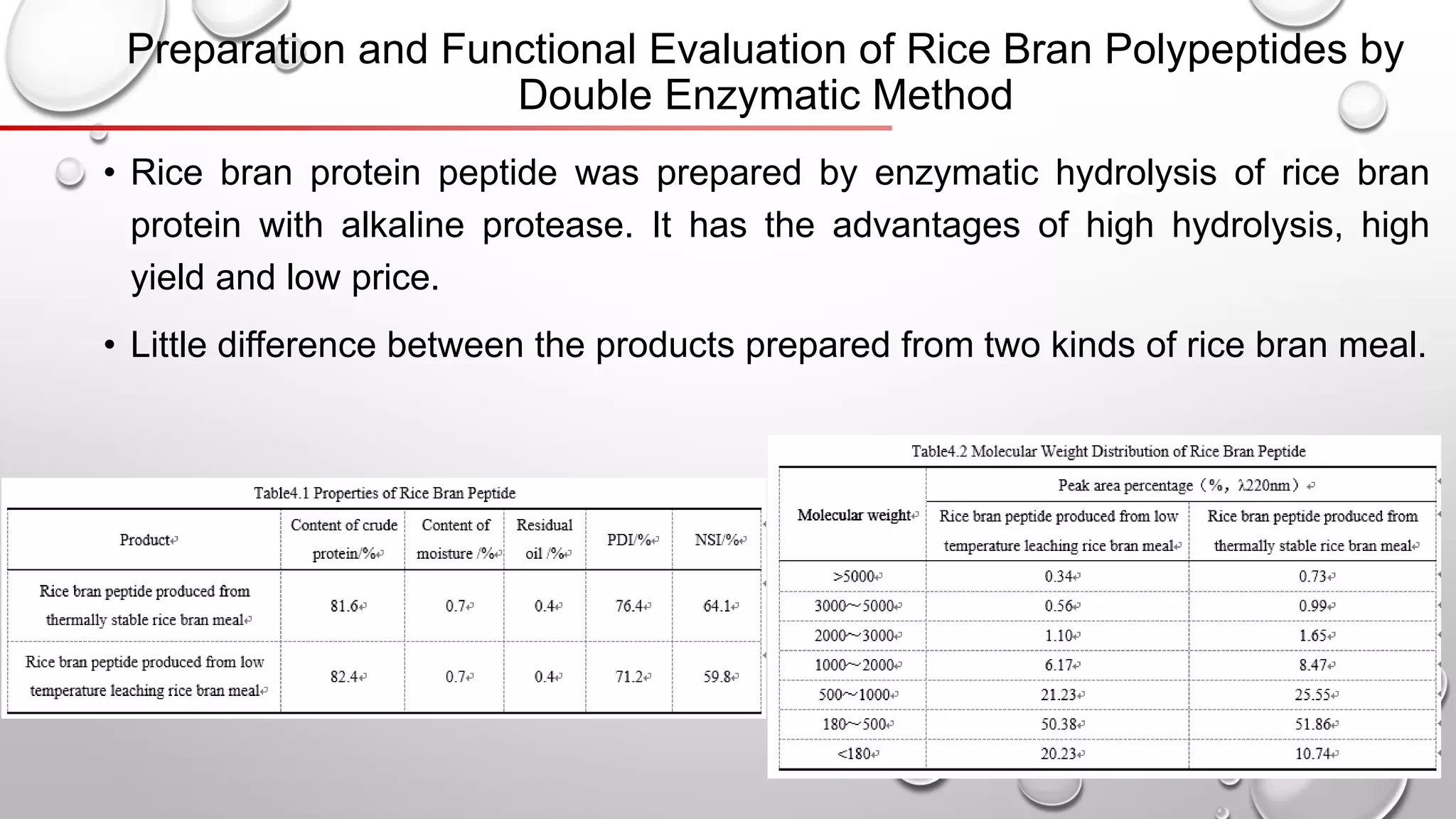
This document discusses methods for extracting protein from rice bran, including a two-step enzymatic hydrolysis method. The two-step method uses alkaline protease and glucoamylase to extract 62.8% of the protein from rice bran meal. Thermally stable rice bran meal and low-temperature leached rice bran meal produce proteins with similar functionality, though thermally stable rice bran yields less. A double enzymatic method using neutral and alkaline proteases produces rice bran polypeptides. While this research increases the extracted protein content to 90%, further study of peptide biological activity and food industry applications is still needed.