This document discusses pre-spinning processes, specifically dust removal in the blowroom. It contains the following key points:
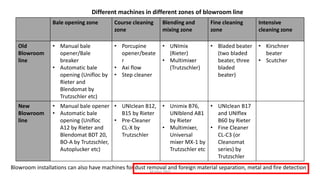
1) Dust is difficult to remove from fibers as the particles are very light and strongly adhere to fiber surfaces. Various blowroom machines use fiber-to-fiber and fiber-to-metal friction to remove dust.
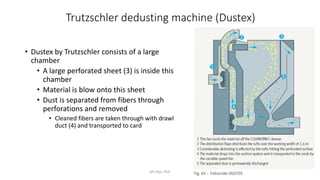
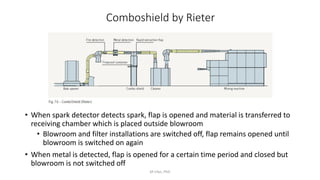
2) Common dust removal machines in the blowroom include the Rieter dedusting chamber within transport ducts and the Trutzschler Dustex machine, which uses a perforated sheet to separate dust from fibers.
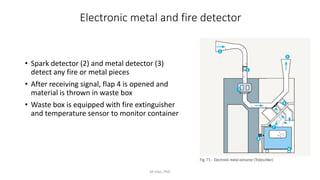
3) The blowroom also contains equipment for metal detection and removal, including magnets, electronic detectors, and safety measures like switching off machines if