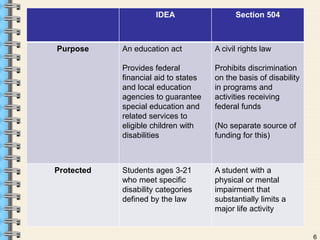
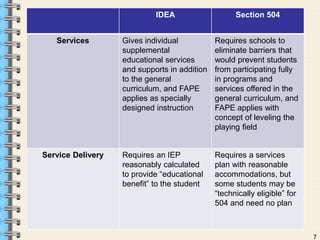
Section 504 is a federal law that prohibits discrimination against individuals with disabilities. It requires schools to provide reasonable accommodations to students with disabilities so they are not denied the opportunity to participate fully in school programs. The number of students qualifying under Section 504 has increased due to changes made by the ADA that expanded the definition of disability. Schools must evaluate students if there is reason to suspect a disability, and for eligible students they must create a services plan outlining appropriate accommodations to meet their needs. Section 504 plans provide protections and accommodations to ensure students with disabilities have equal access to educational opportunities.