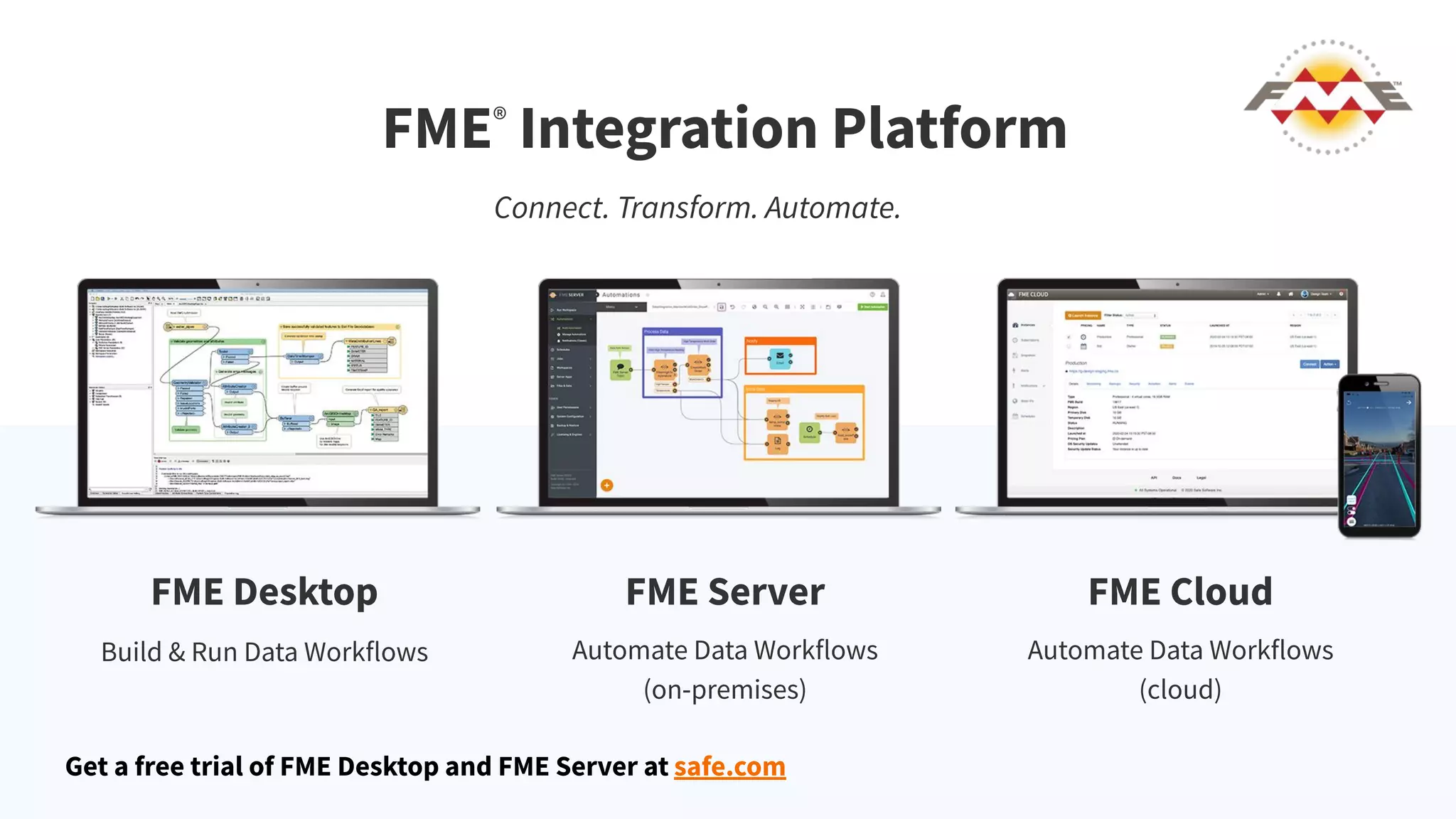
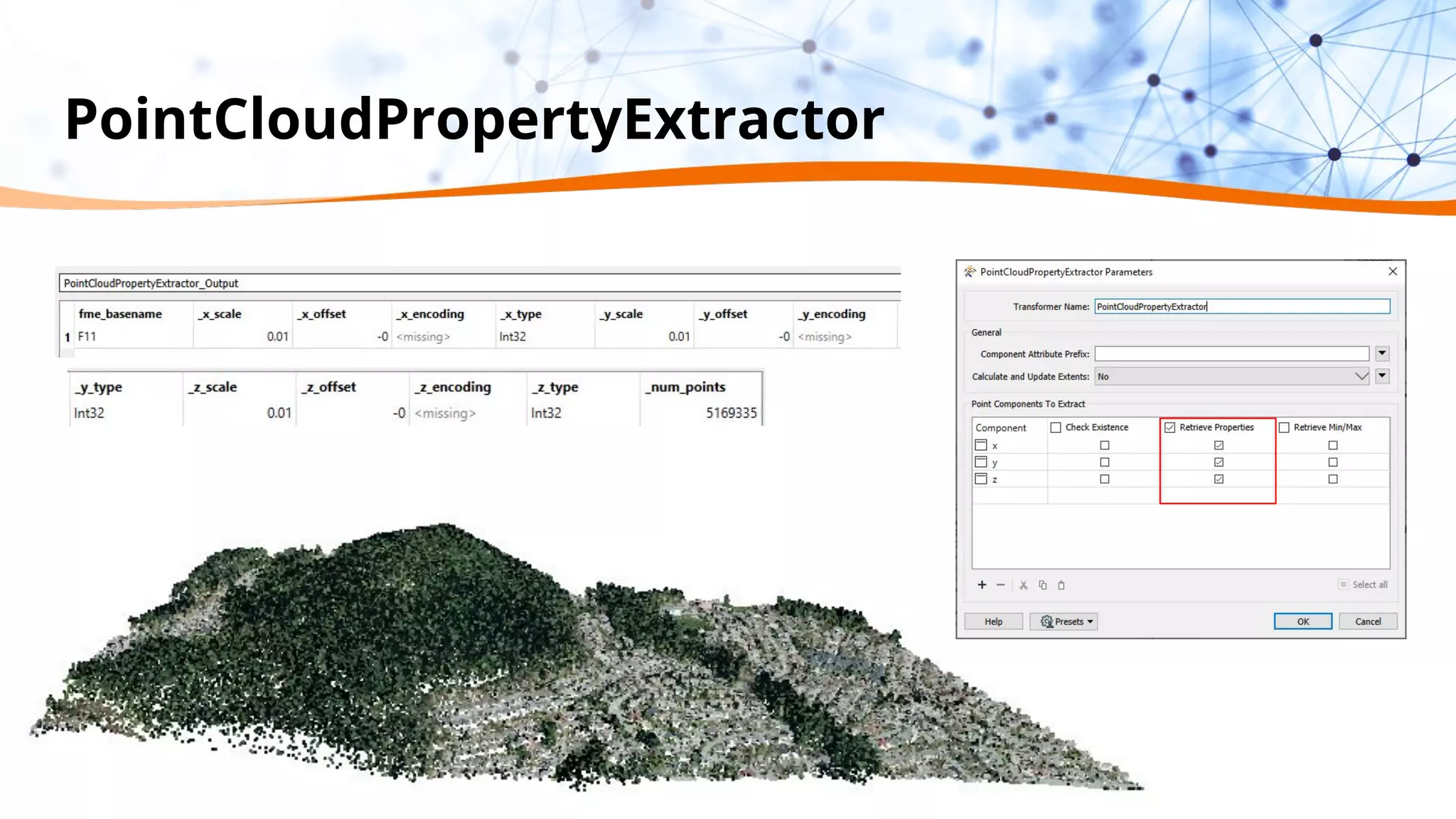
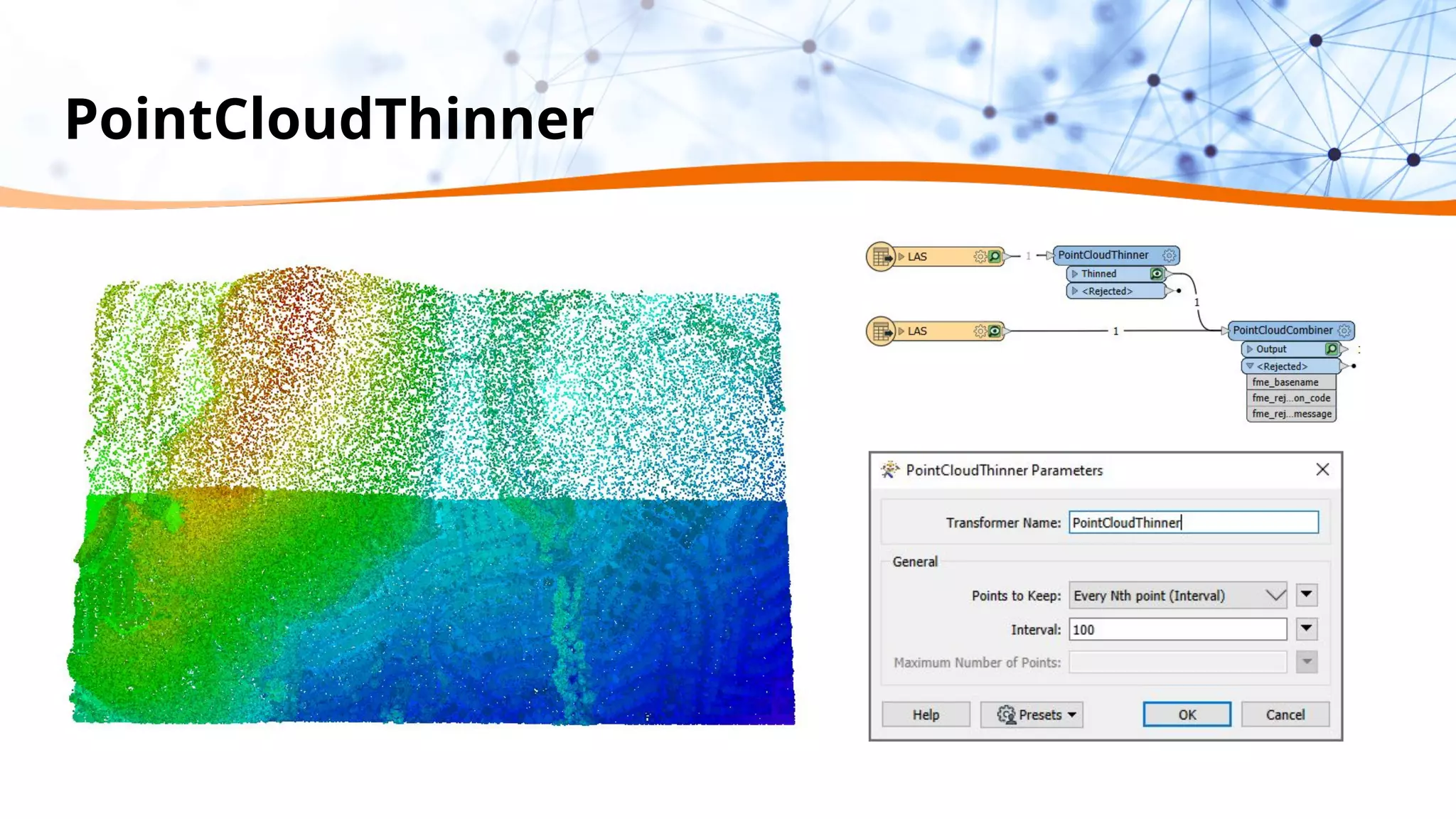
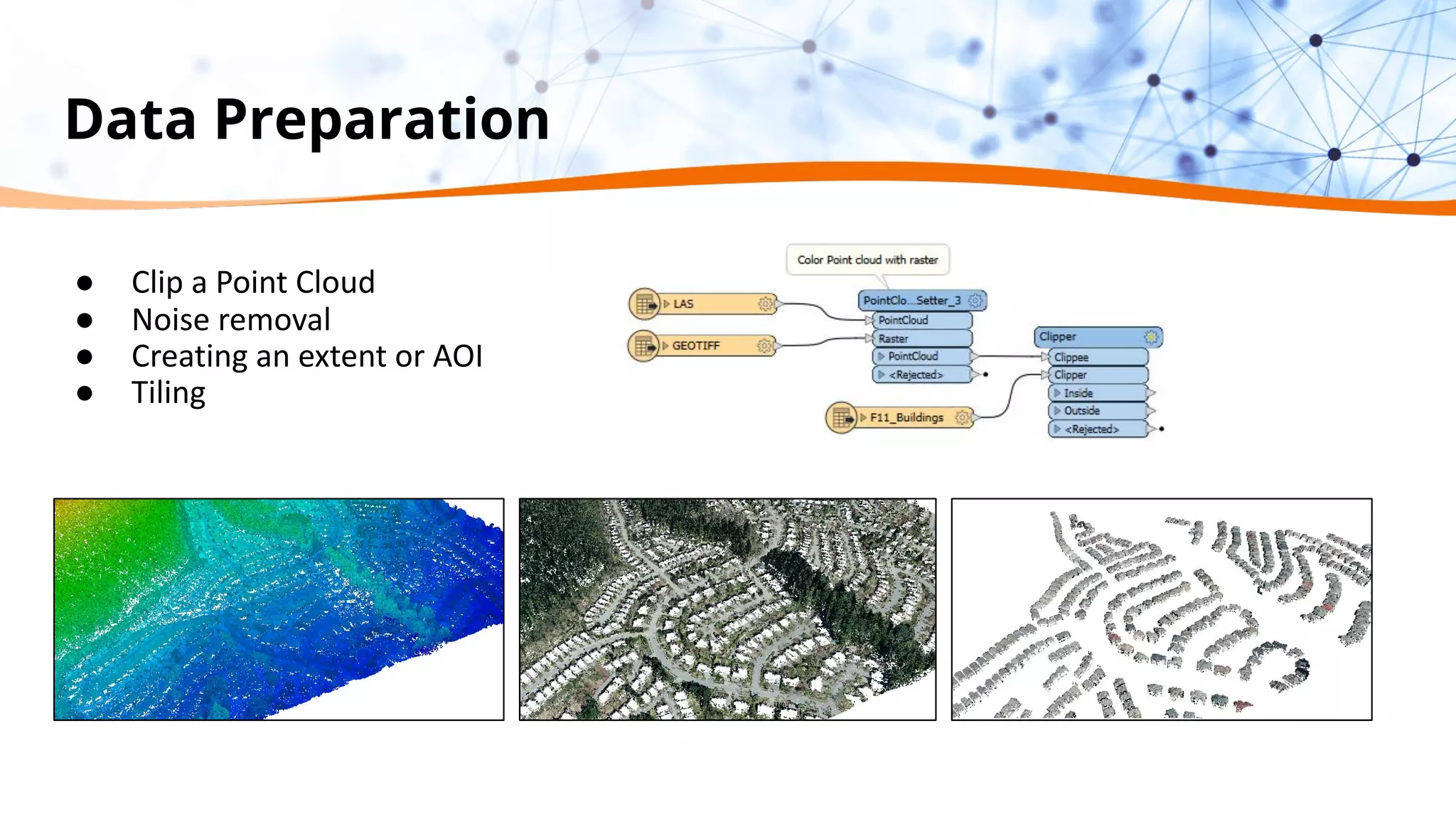
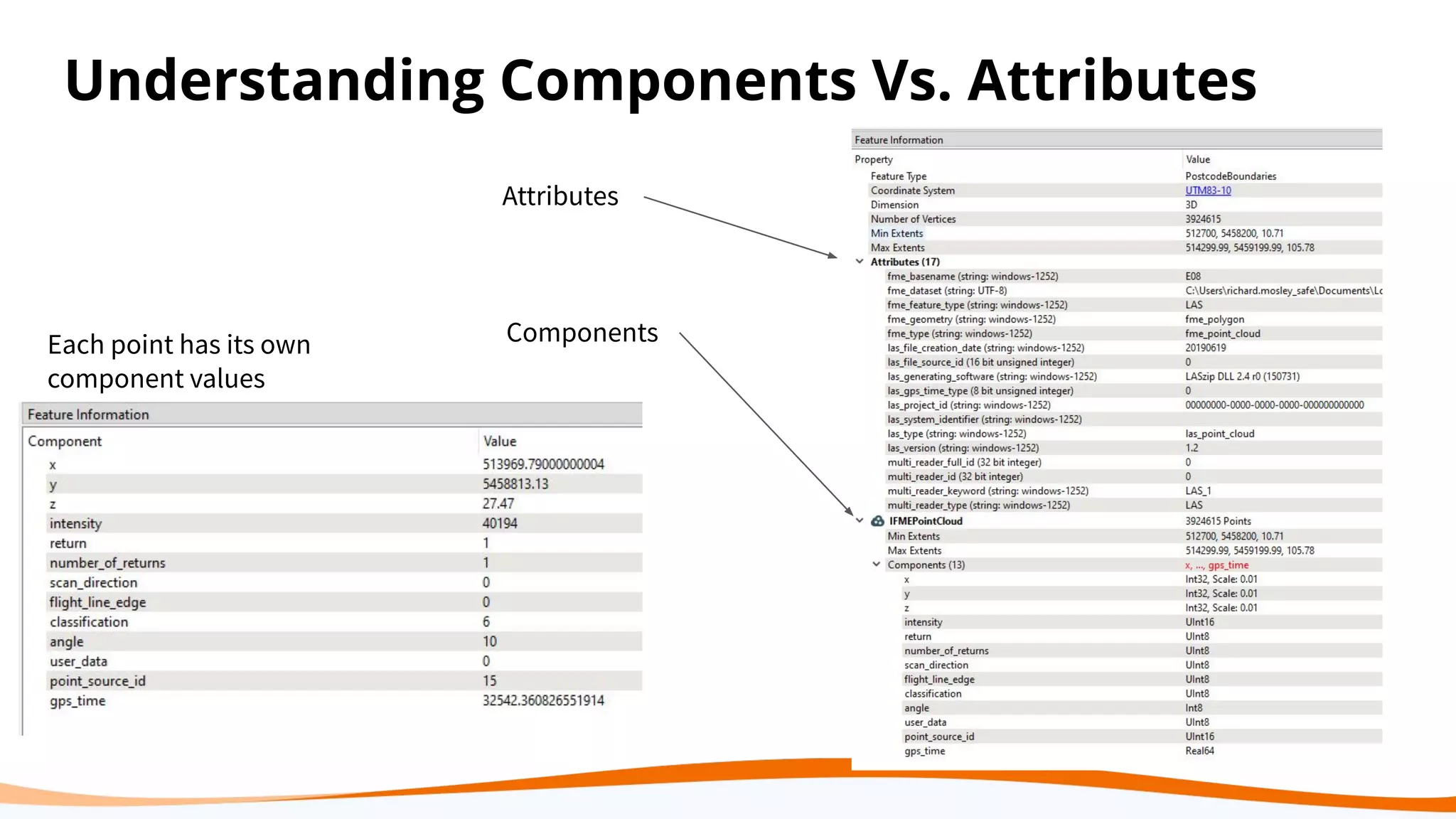
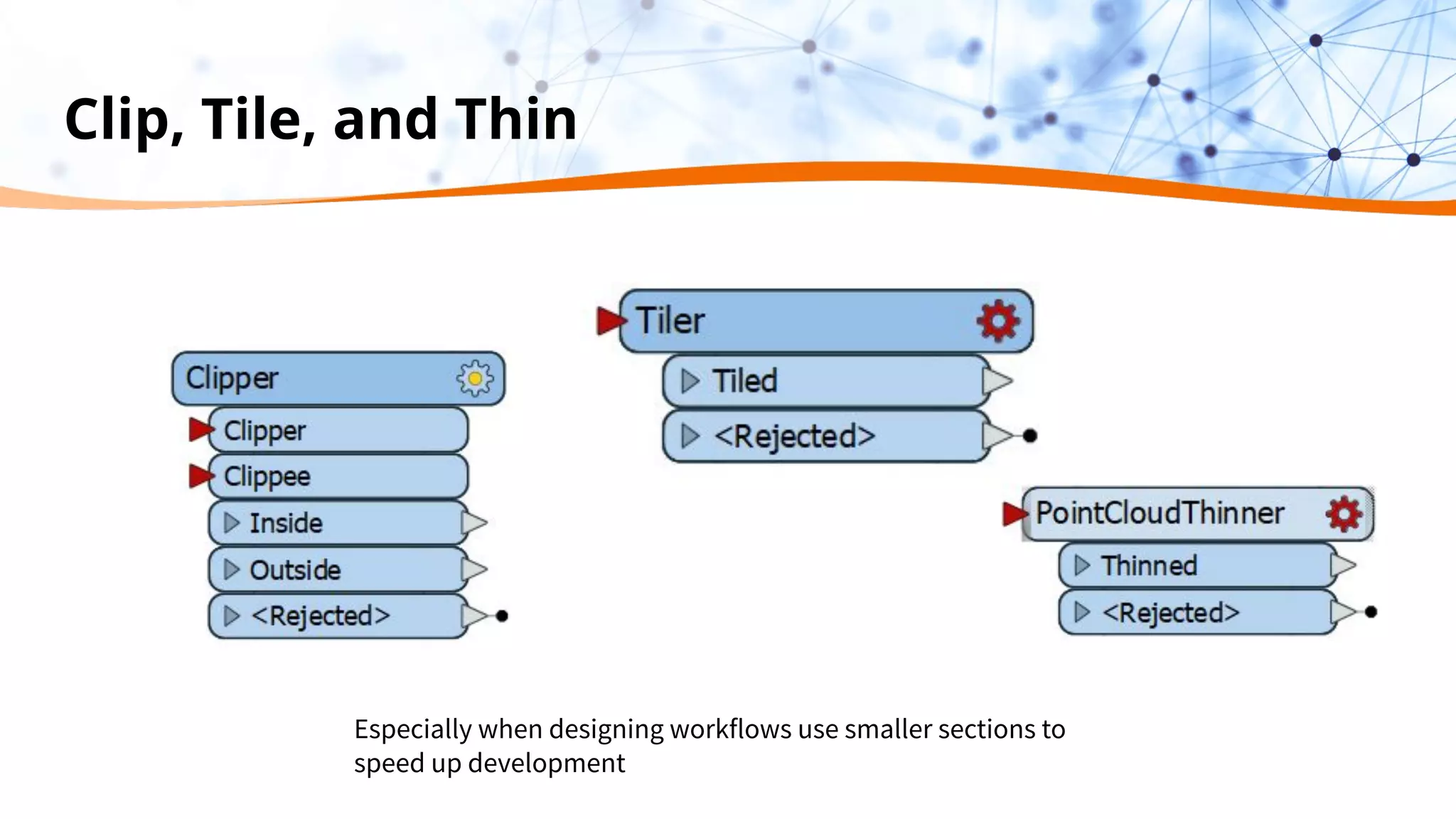
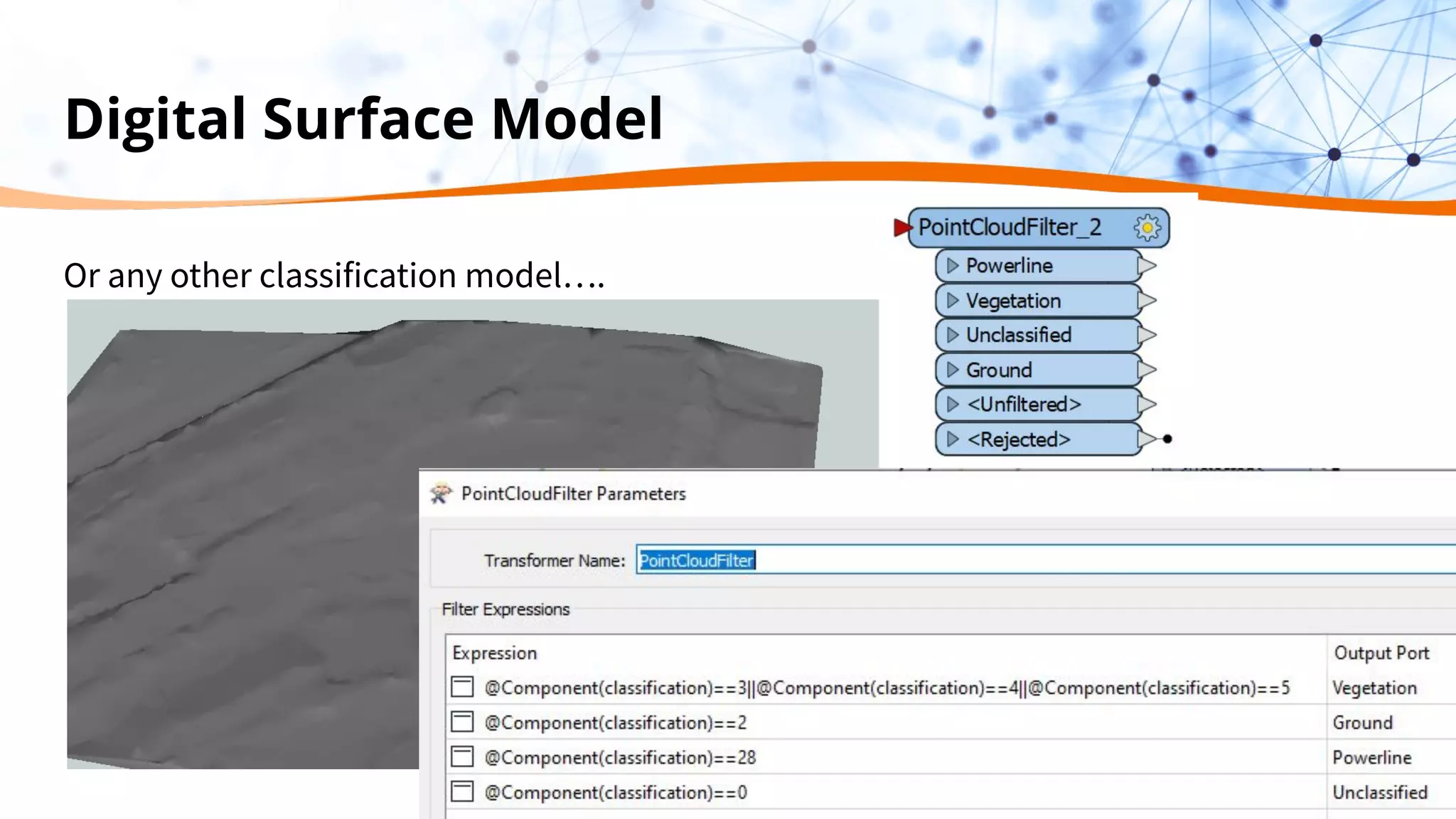
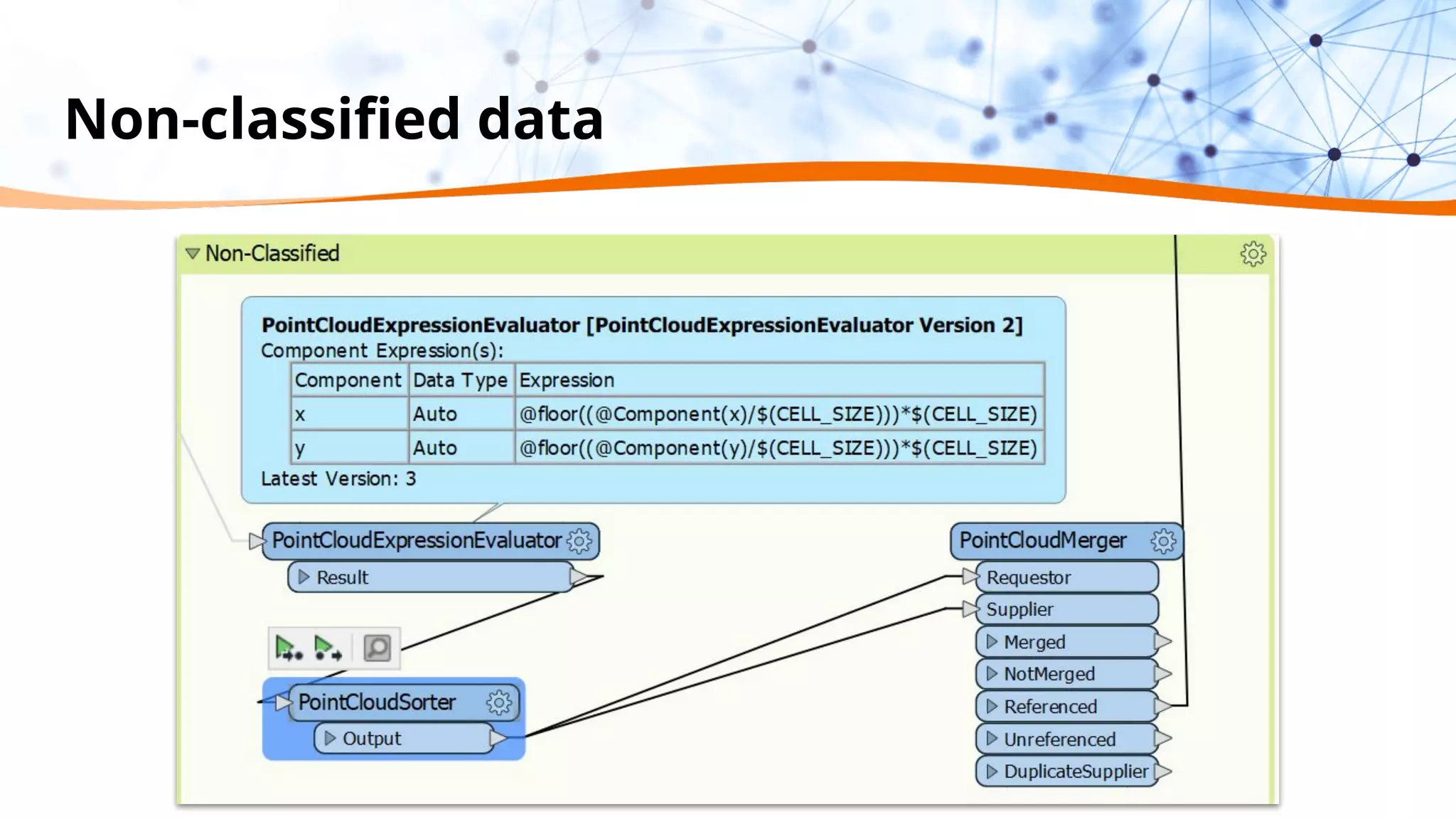
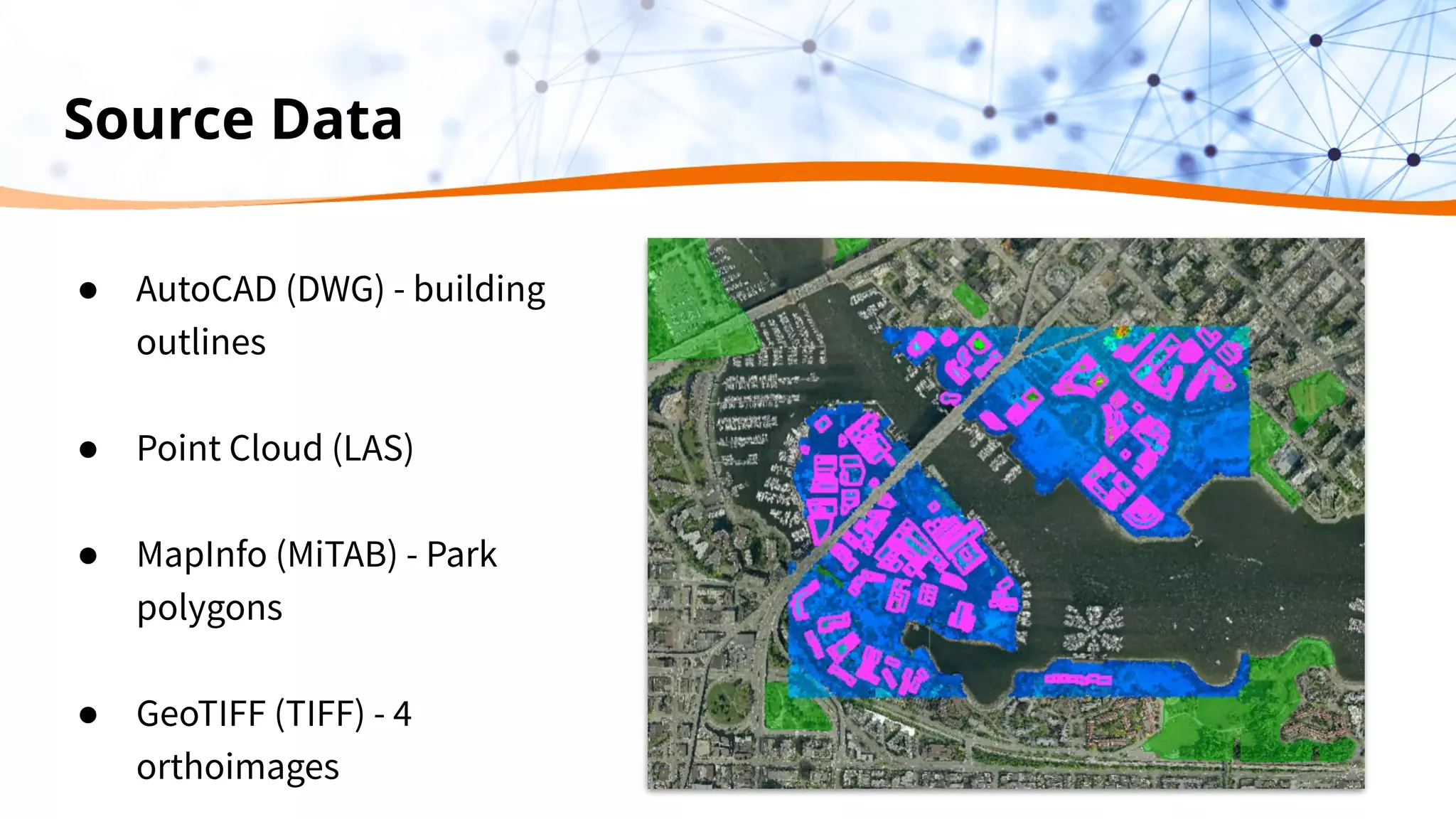
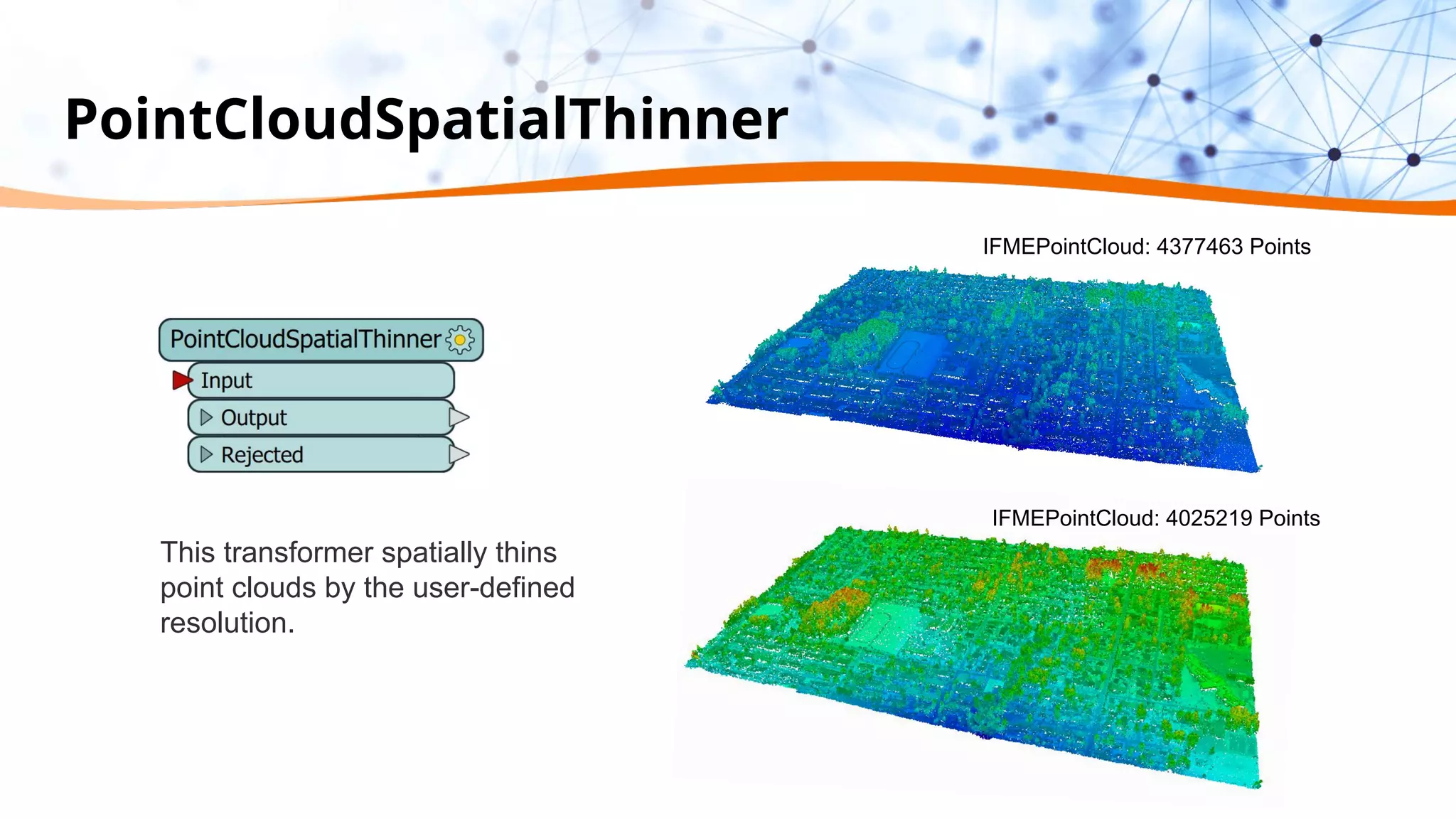
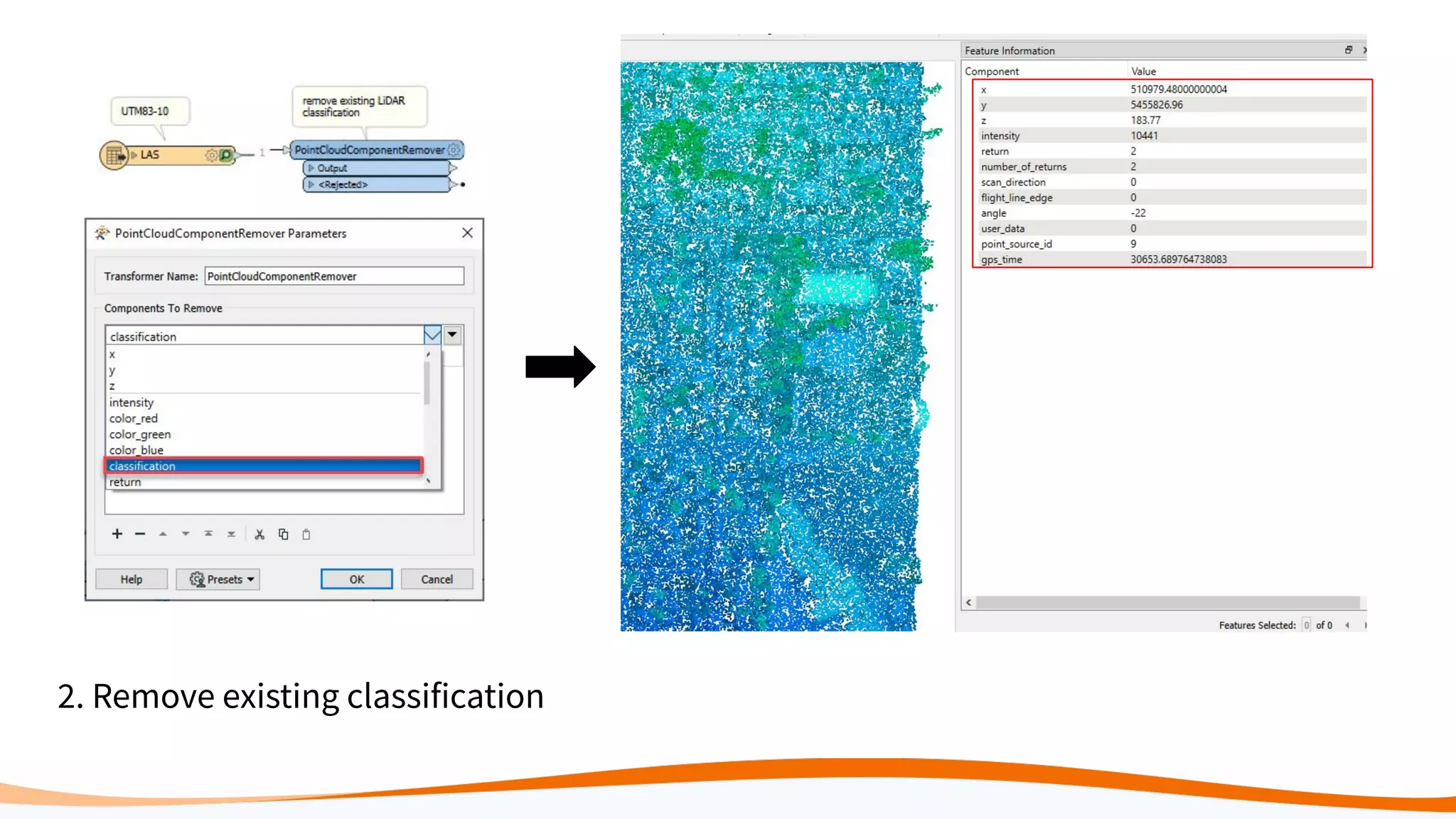
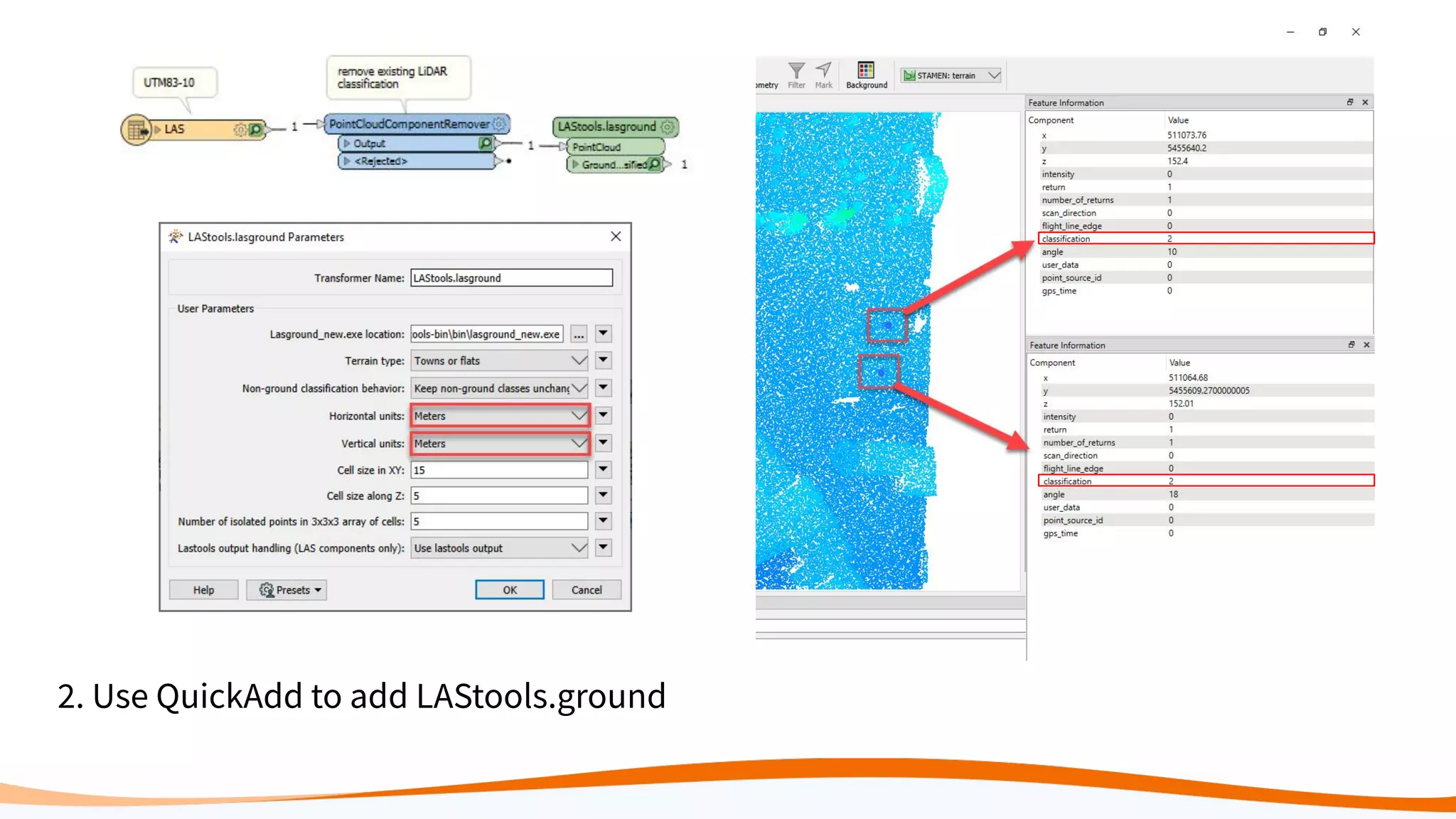
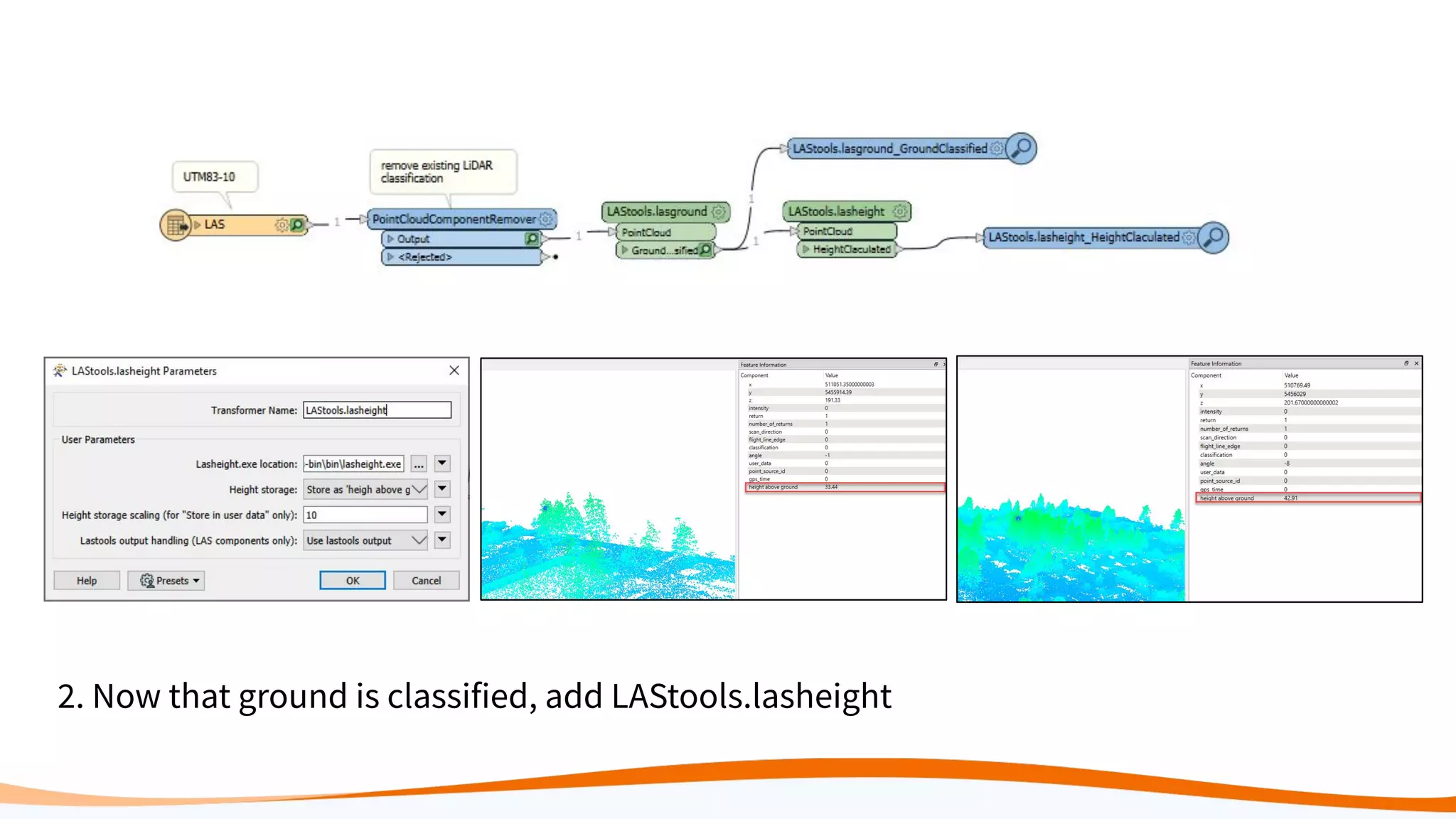
This document discusses 5 ways to improve LiDAR workflows using FME software. It begins with an overview of LiDAR and point clouds before addressing each of the 5 ways: 1) simplifying point cloud transformations with FME transformers, 2) preparing data, 3) automating surface model creation, 4) visualizing solutions through 3D city modeling, and 5) expanding tools with FME Hub and third party tools like LAStools. The presentation concludes by emphasizing how FME can help simplify and scale LiDAR workflows.