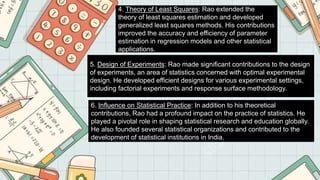
The document highlights the contributions of five prominent Indian mathematicians: Aryabhata, Srinivasa Ramanujan, Brahmagupta, Bhaskara II, and C.R. Rao, detailing their significant achievements in various branches of mathematics. Aryabhata introduced concepts like the decimal numeral system and rules for algebra, while Ramanujan made groundbreaking contributions to number theory and infinite series. Brahmagupta advanced arithmetic operations and quadratic equations, Bhaskara II made strides in calculus and trigonometry, and C.R. Rao significantly impacted statistics with the Rao-Blackwell theorem and multivariate analysis.