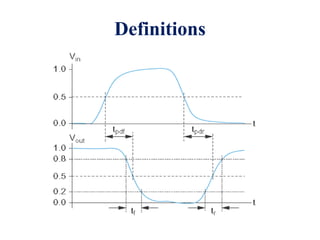
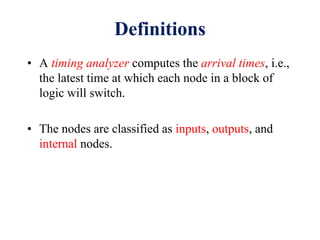
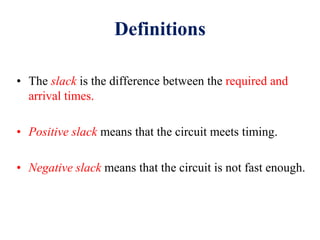
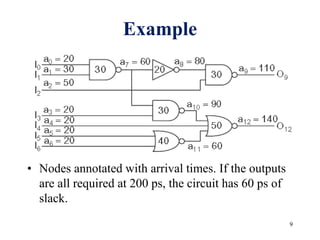
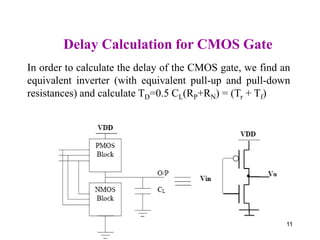
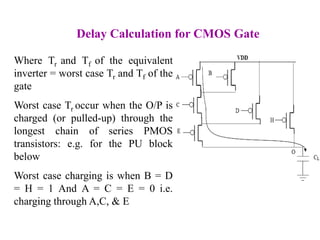
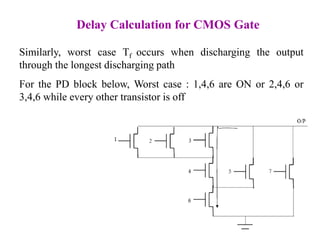
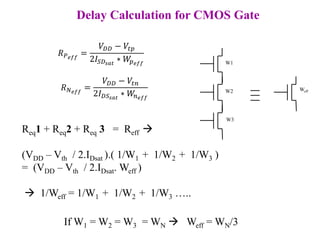
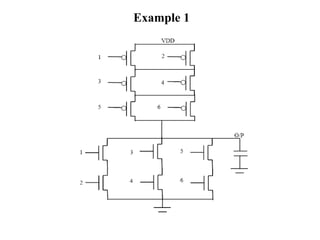
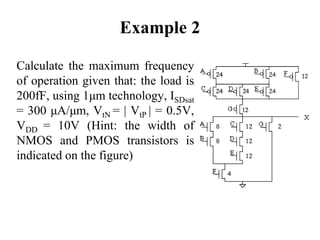
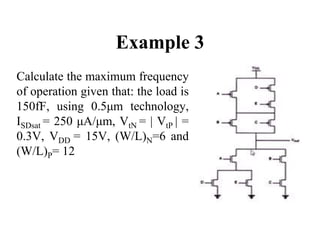
This document defines various delay metrics for CMOS gates including propagation delay, rise time, fall time, and contamination delay. It also discusses how to calculate the equivalent resistance and effective width of PMOS and NMOS transistors to determine the average propagation delay of a CMOS gate. Two examples are then provided to demonstrate calculating the maximum frequency of operation for different CMOS gates given technological parameters.