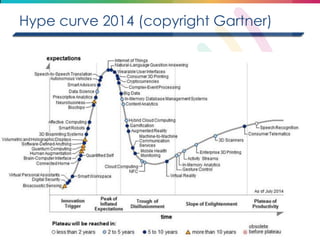
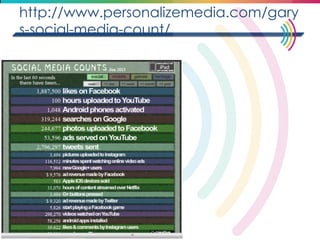
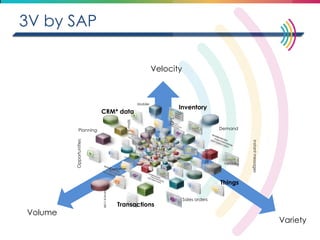
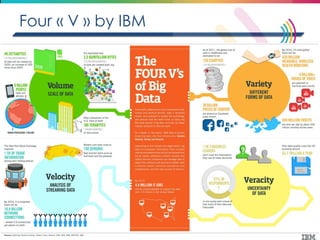
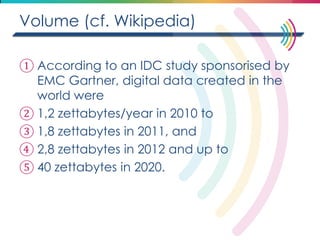
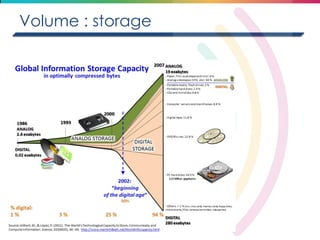
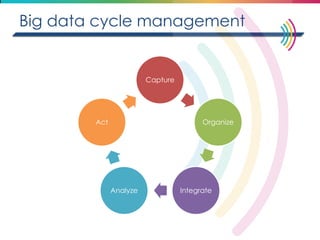
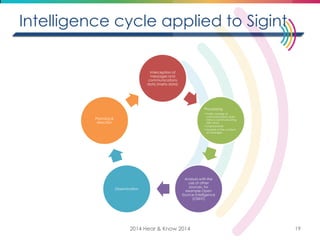
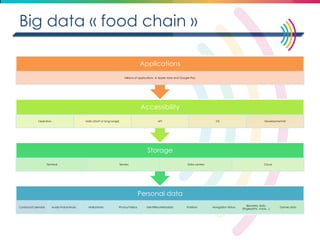
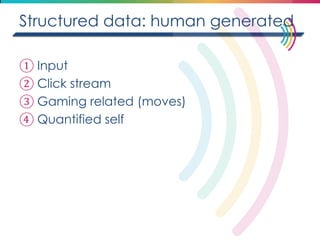
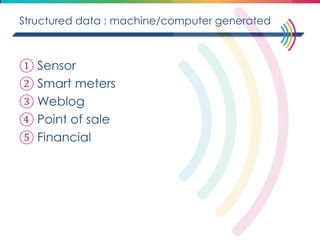
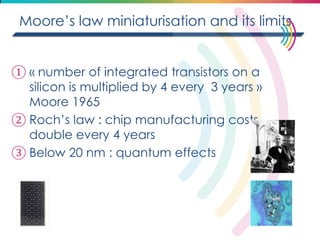
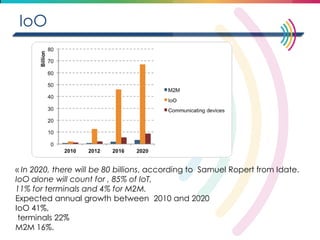
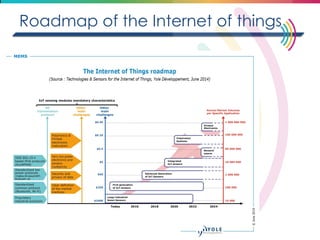
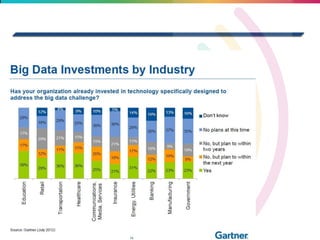
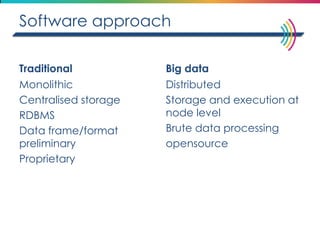
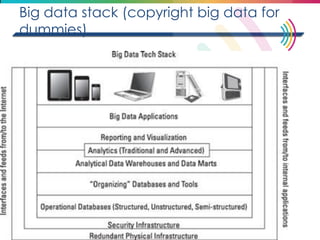
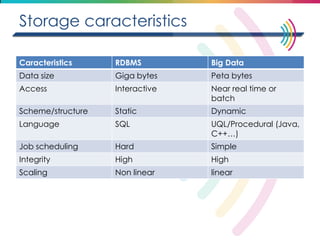
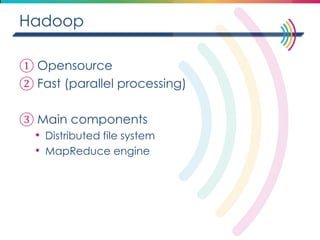
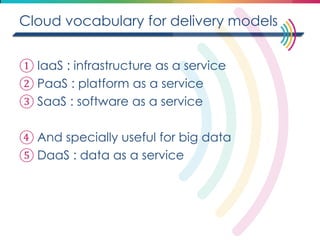
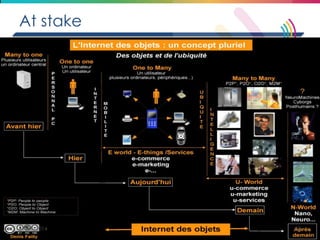
This document discusses big data, including its definition, dimensions, infrastructure, tools, and applications. Big data is characterized by volume, variety, velocity, and veracity. It is generated from a variety of human and machine sources and stored using distributed systems like Hadoop. Tools like MapReduce and R are used to analyze big data and provide insights in domains like marketing, healthcare, transportation and more. Infrastructure must be scalable and flexible to handle the growing size, types and speed of data.