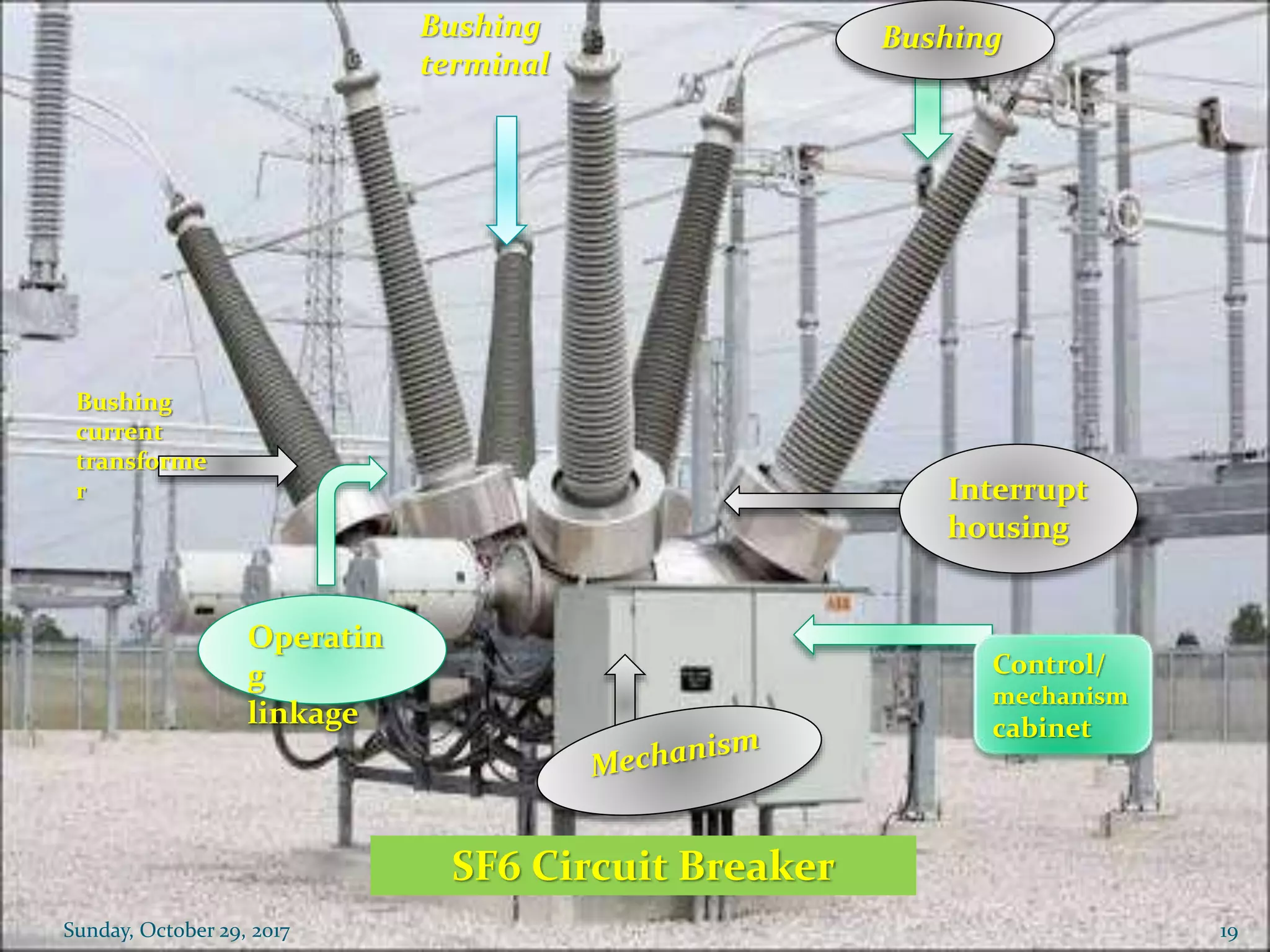
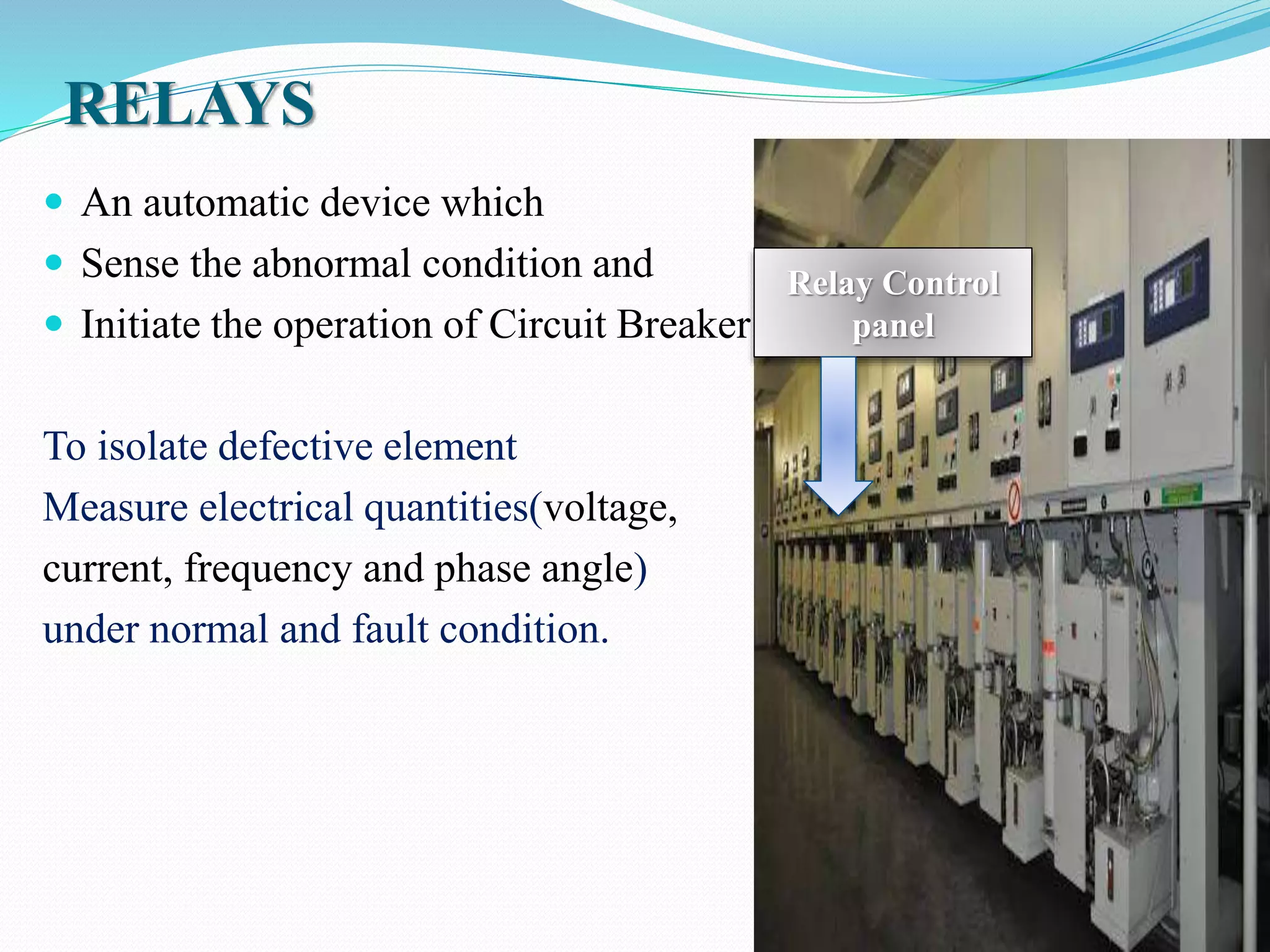
The document presents a detailed overview of a summer practical training program at the 400 kV grid substation in Heerapura, Jaipur, covering various components such as power transformers, conductors, circuit breakers, and control systems. It outlines the specifications and functions of electrical equipment, including transformers, insulators, and relays, along with the setup and arrangement in the substation. The training aimed to enhance practical knowledge and understanding of electrical power systems through direct observation and experience in the field.