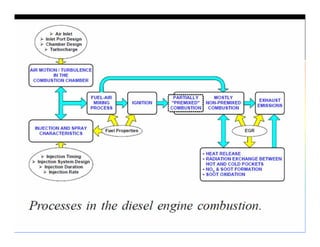
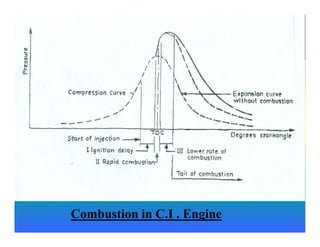
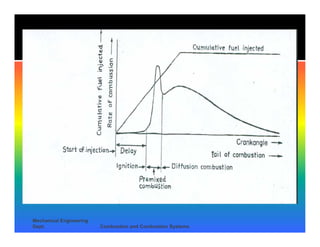
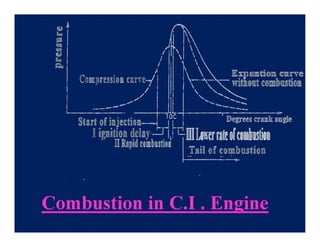
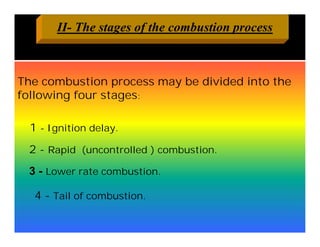
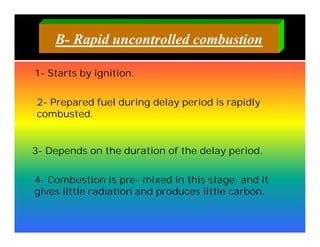
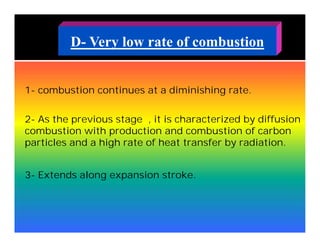
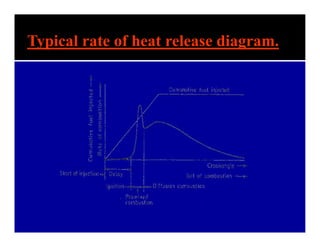
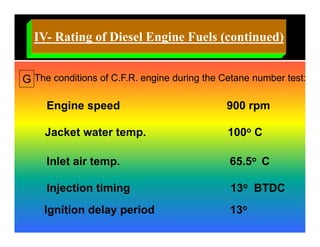
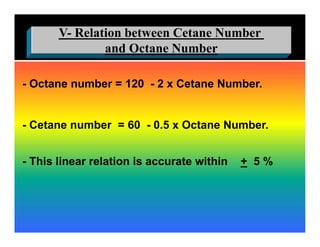
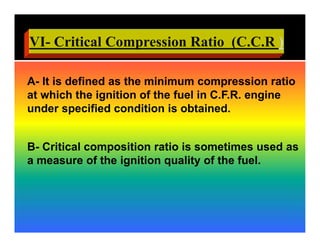
The document discusses the combustion process in diesel engines. It describes the four stages of combustion: 1) ignition delay, 2) rapid uncontrolled combustion, 3) lower rate combustion, and 4) tail of combustion. It also discusses knocking in diesel engines, the rating of diesel fuels using metrics like cetane number and diesel index, and the relationship between cetane number and octane number. The critical compression ratio is defined as the minimum ratio needed for ignition under specified conditions.