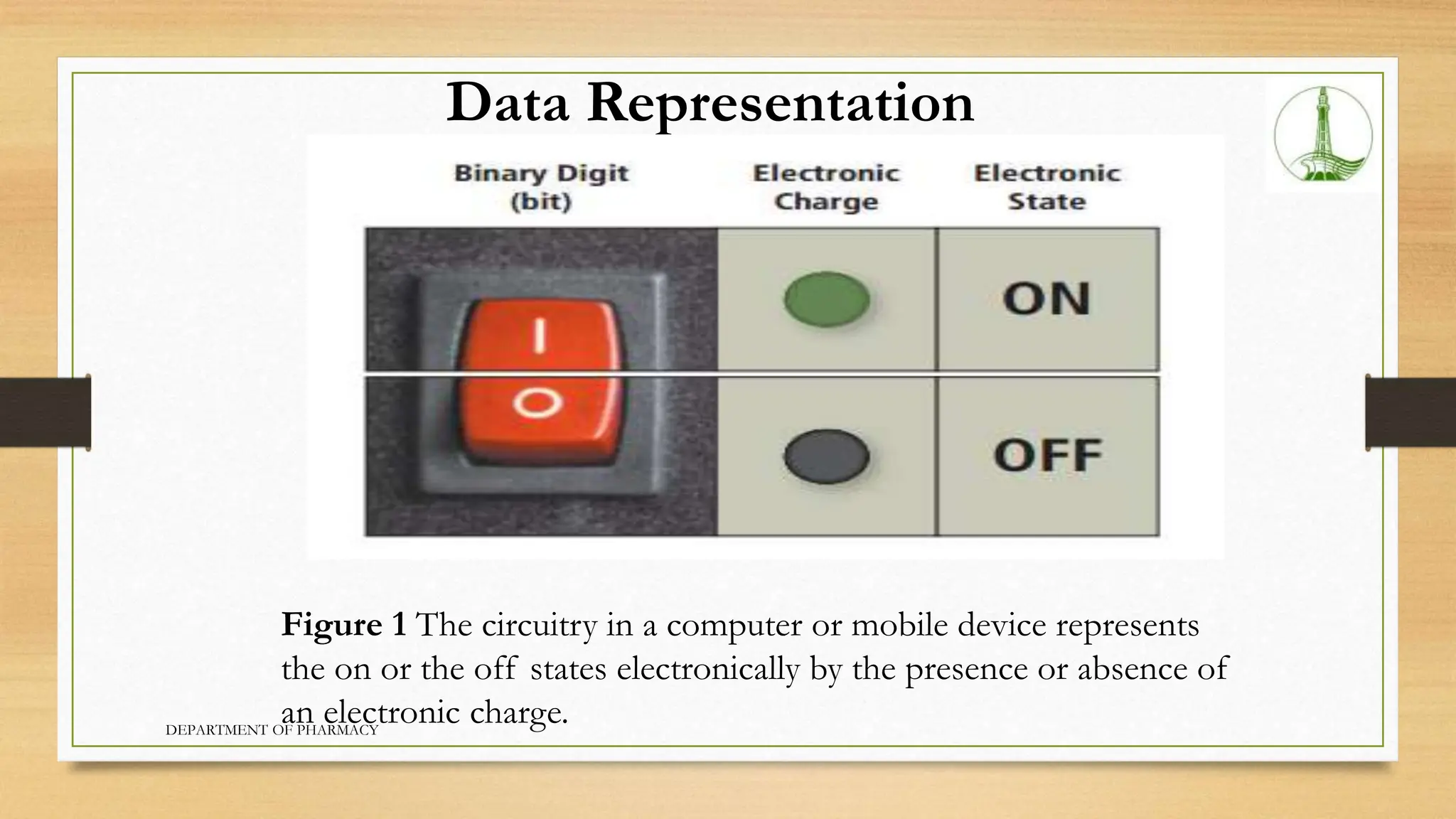
This document provides an overview of fundamentals of computing technology including:
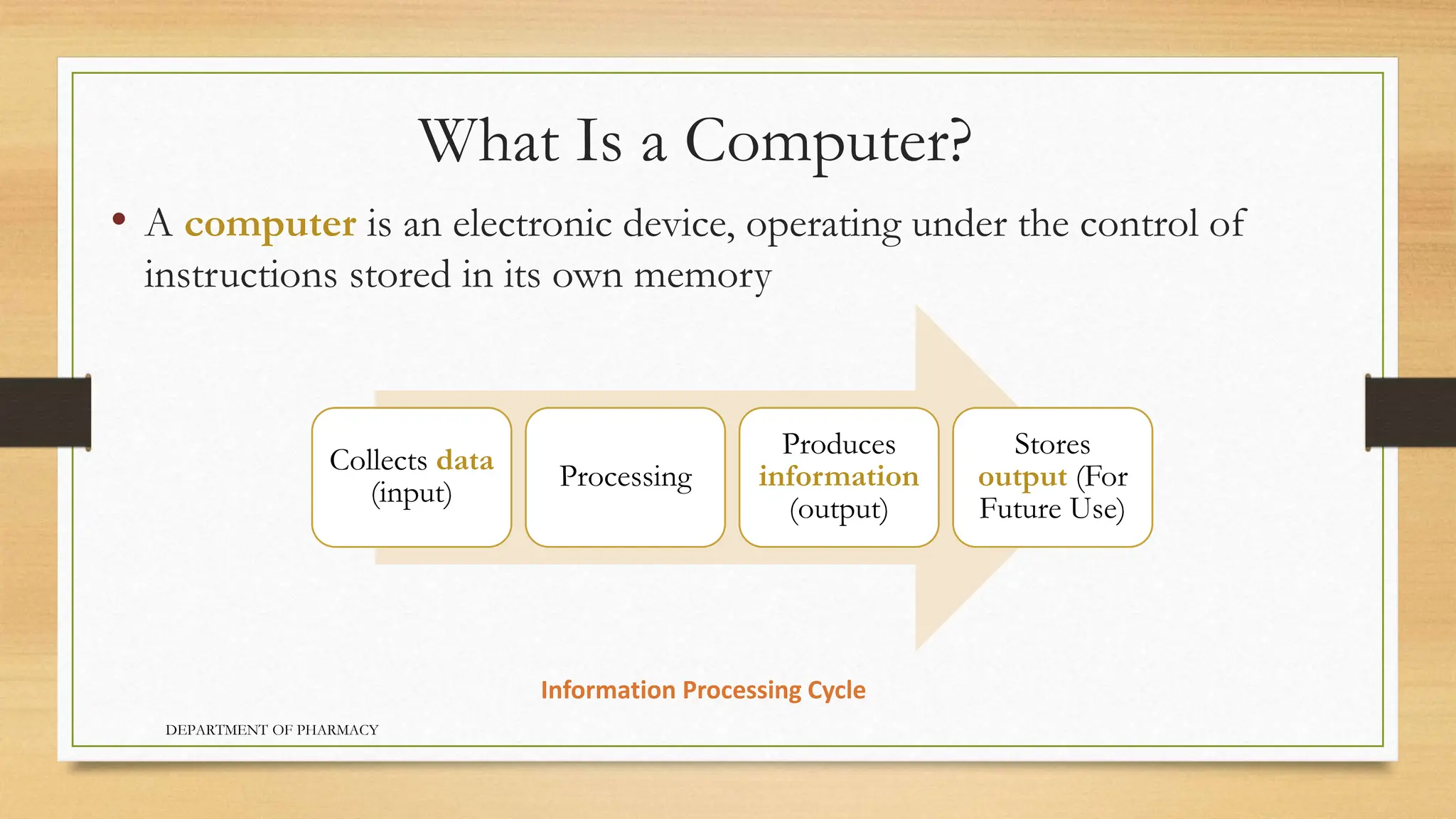
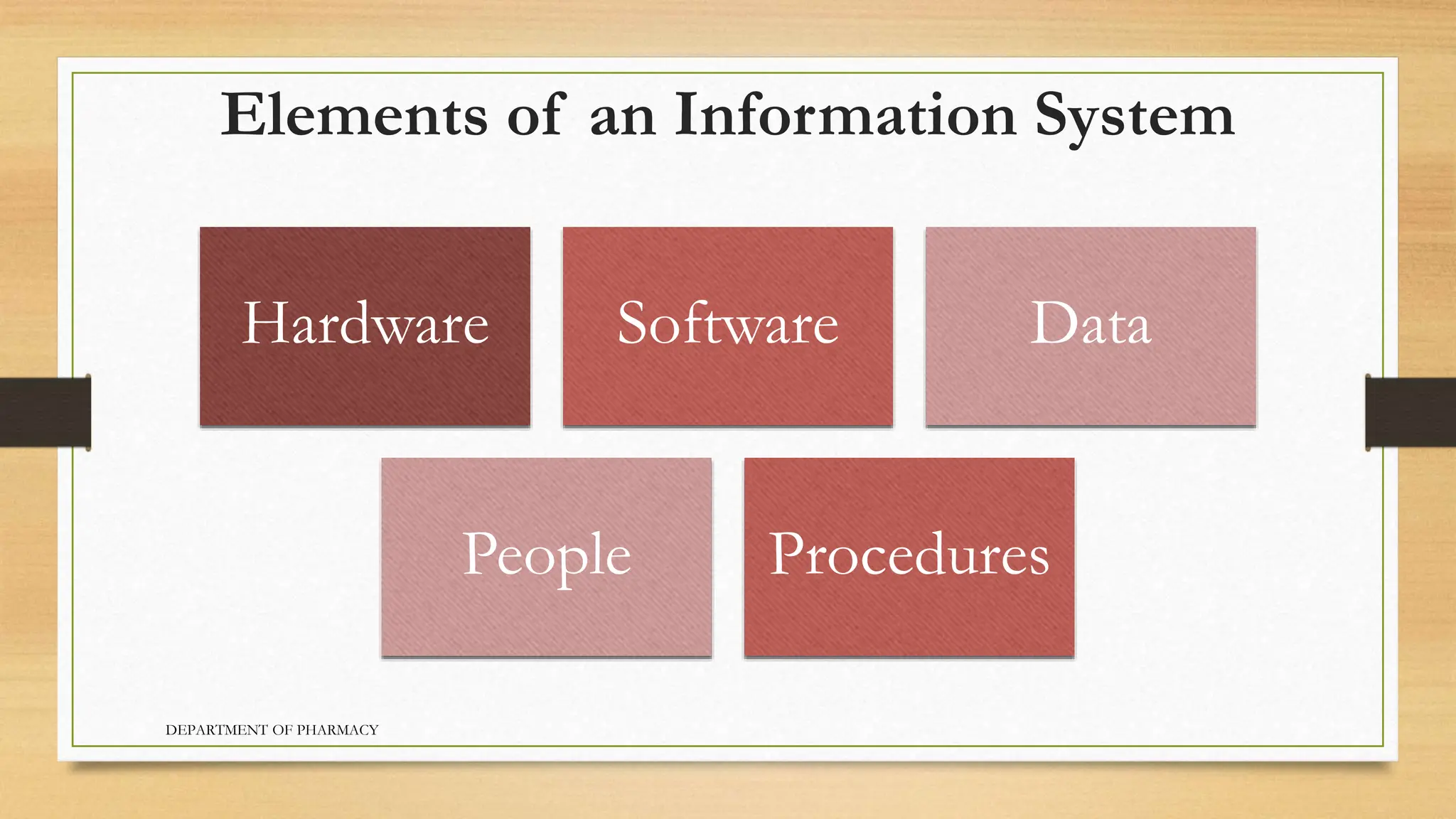
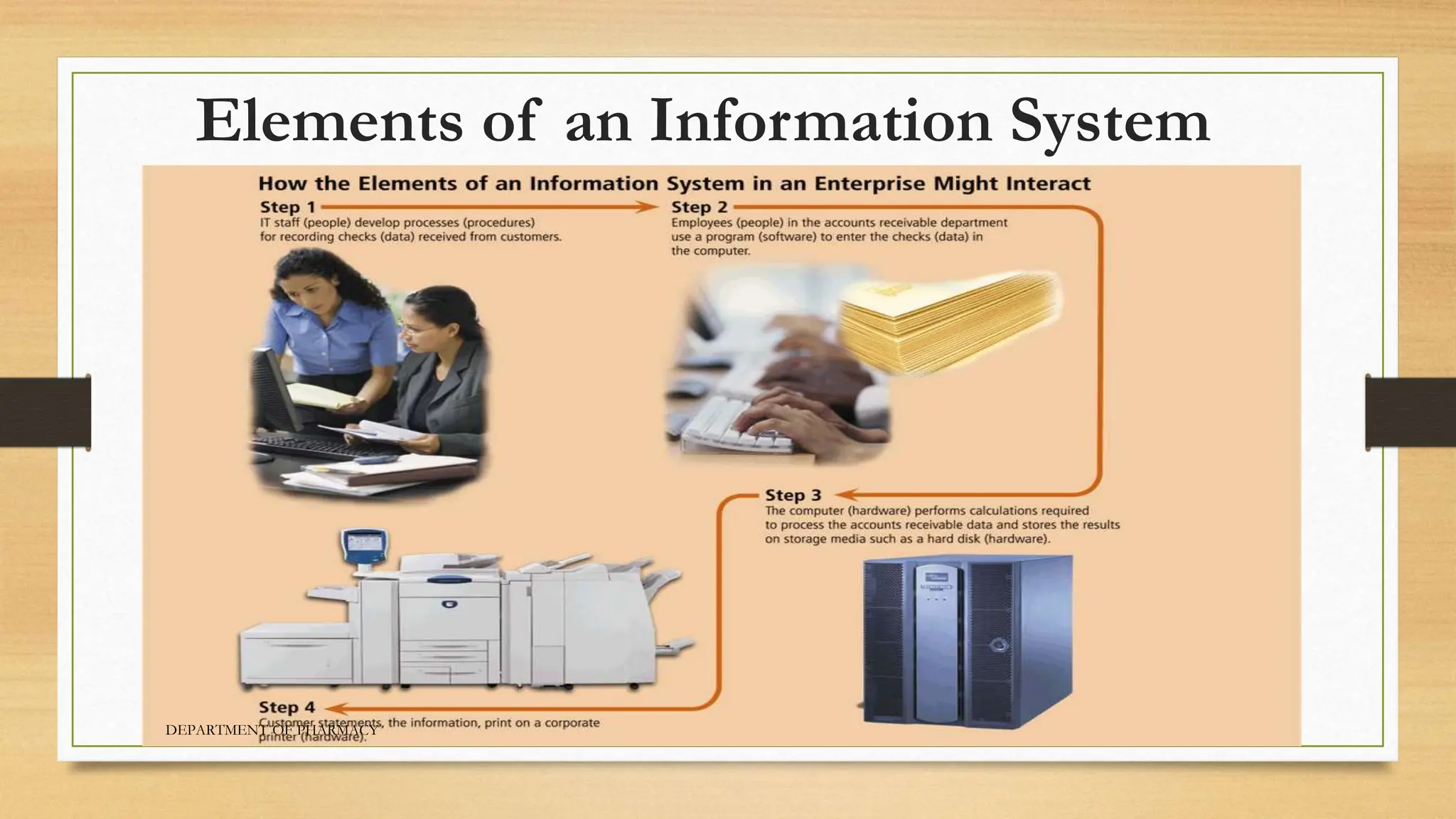
- The main components of a computer are hardware, software, data, people, and procedures. A computer collects input, processes it, stores output for future use, and produces information.
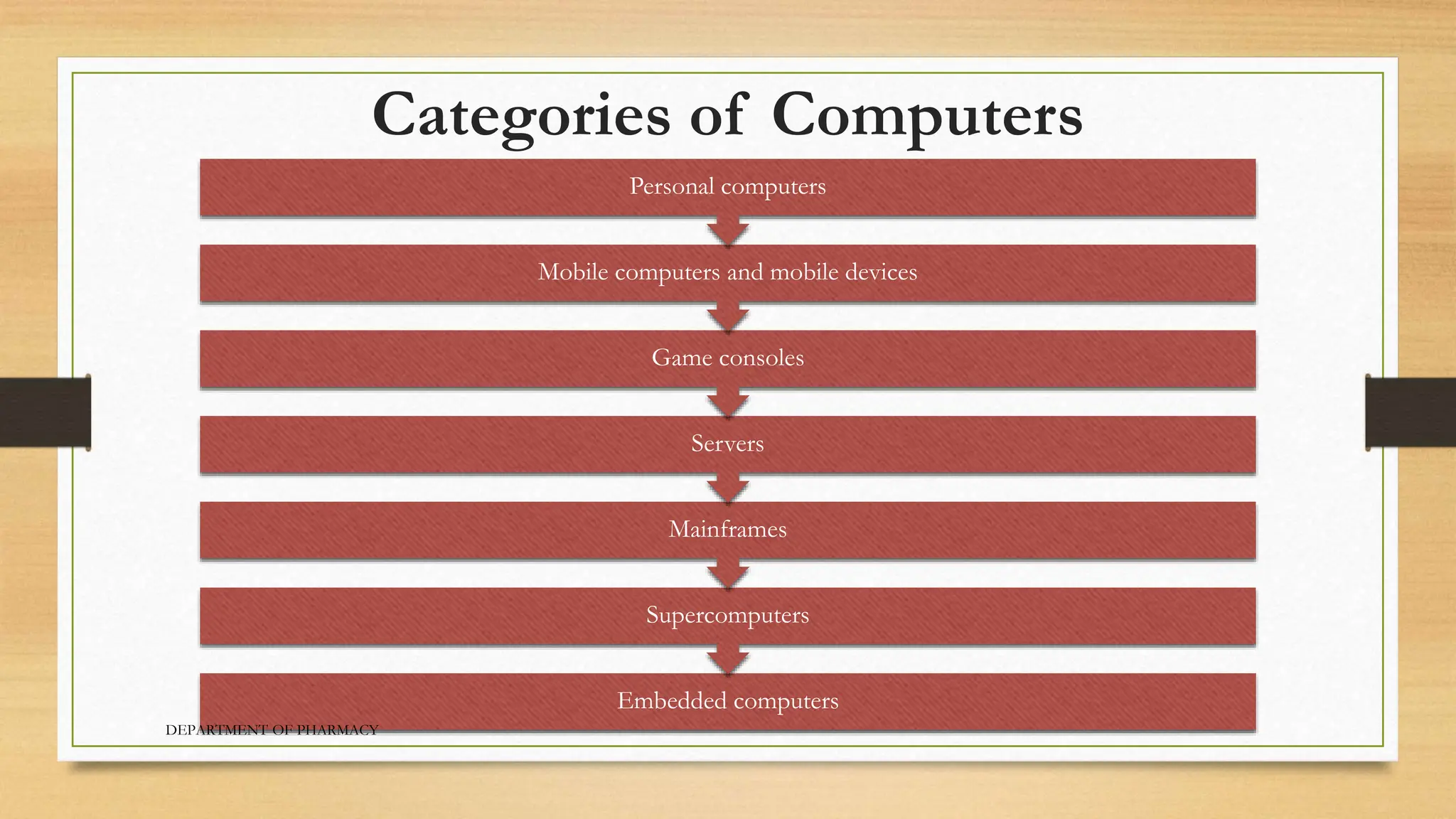
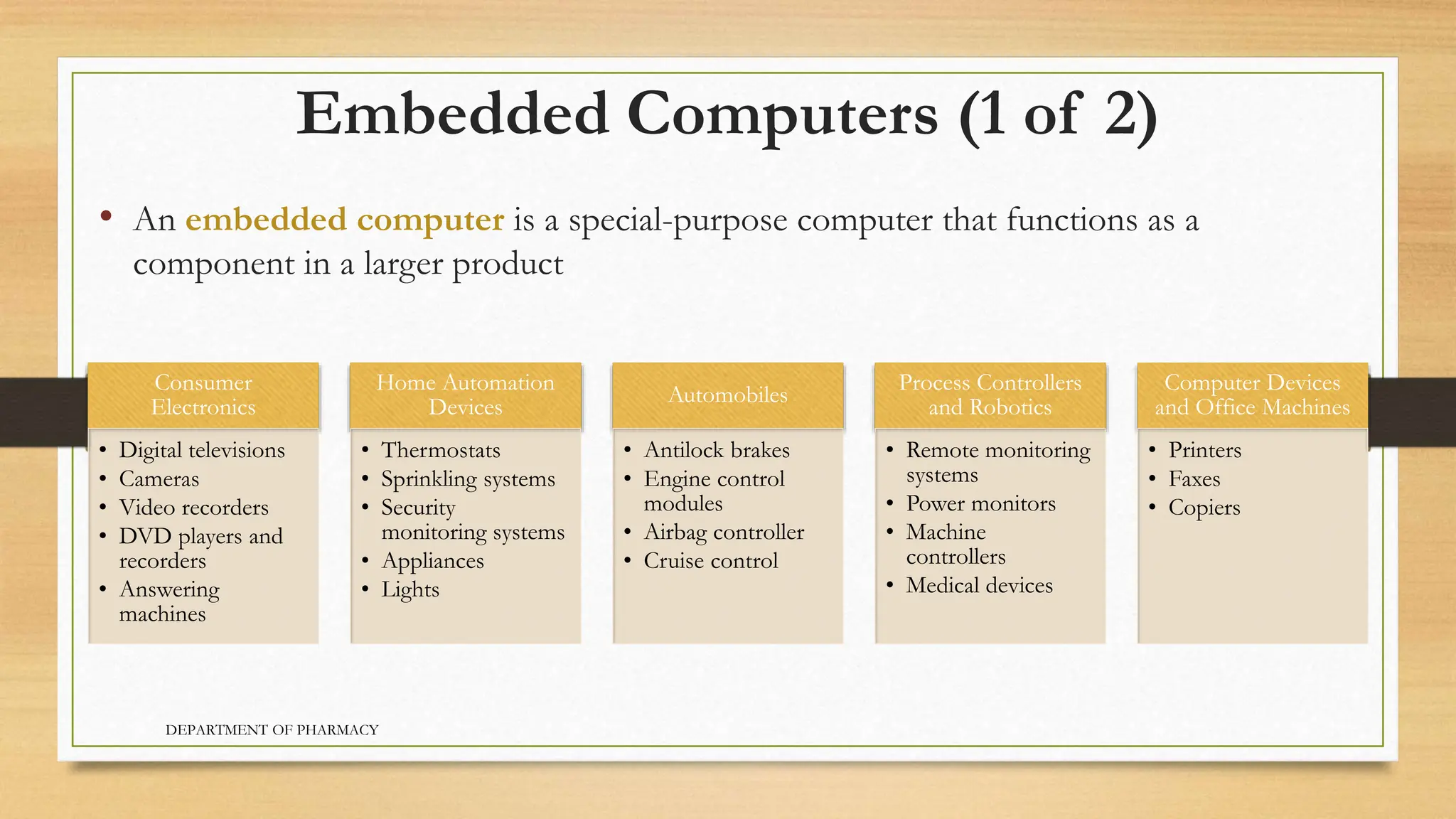
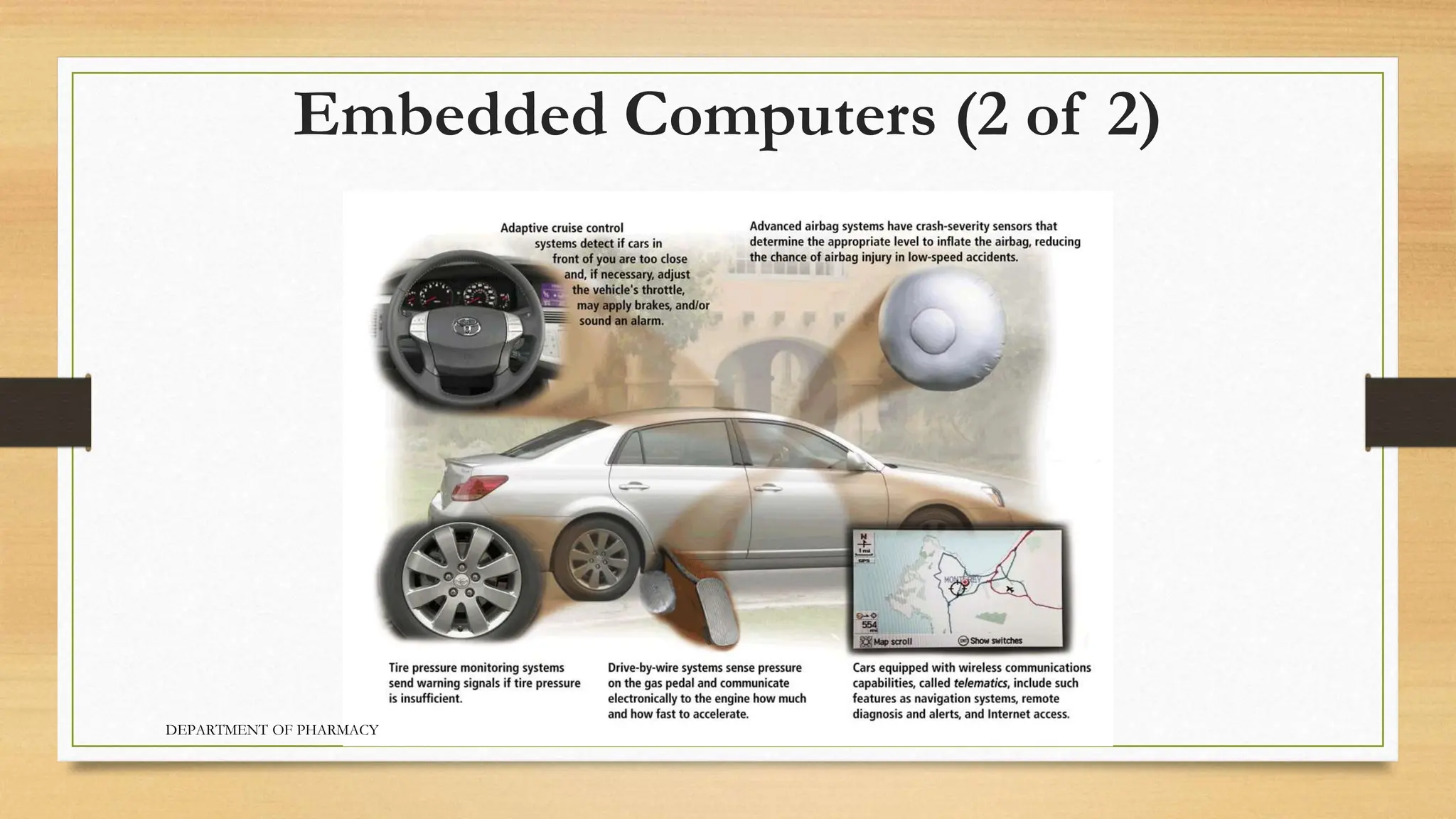
- There are several categories of computers including personal computers, mobile devices, servers, mainframes, supercomputers, game consoles, and embedded computers.
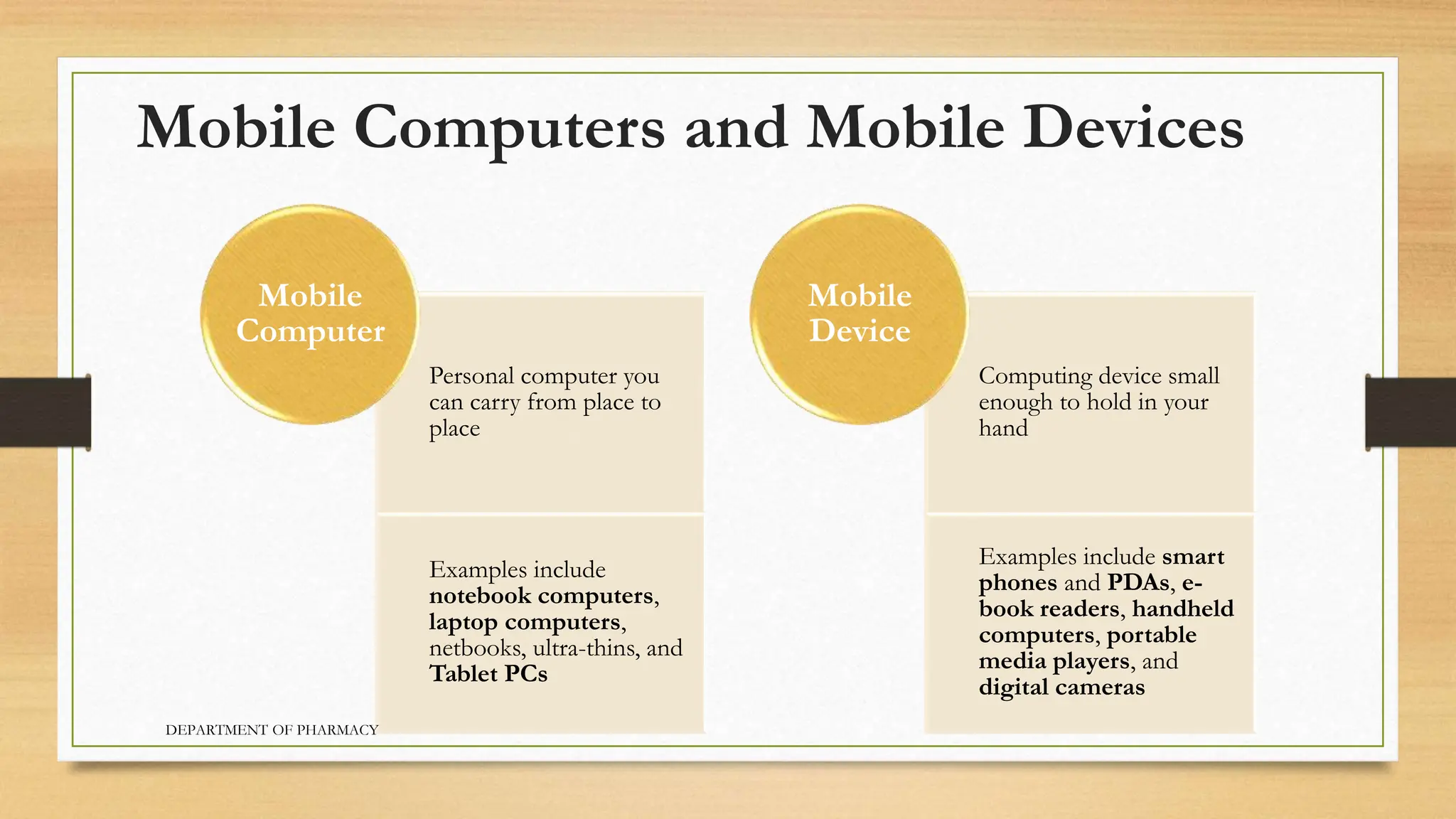
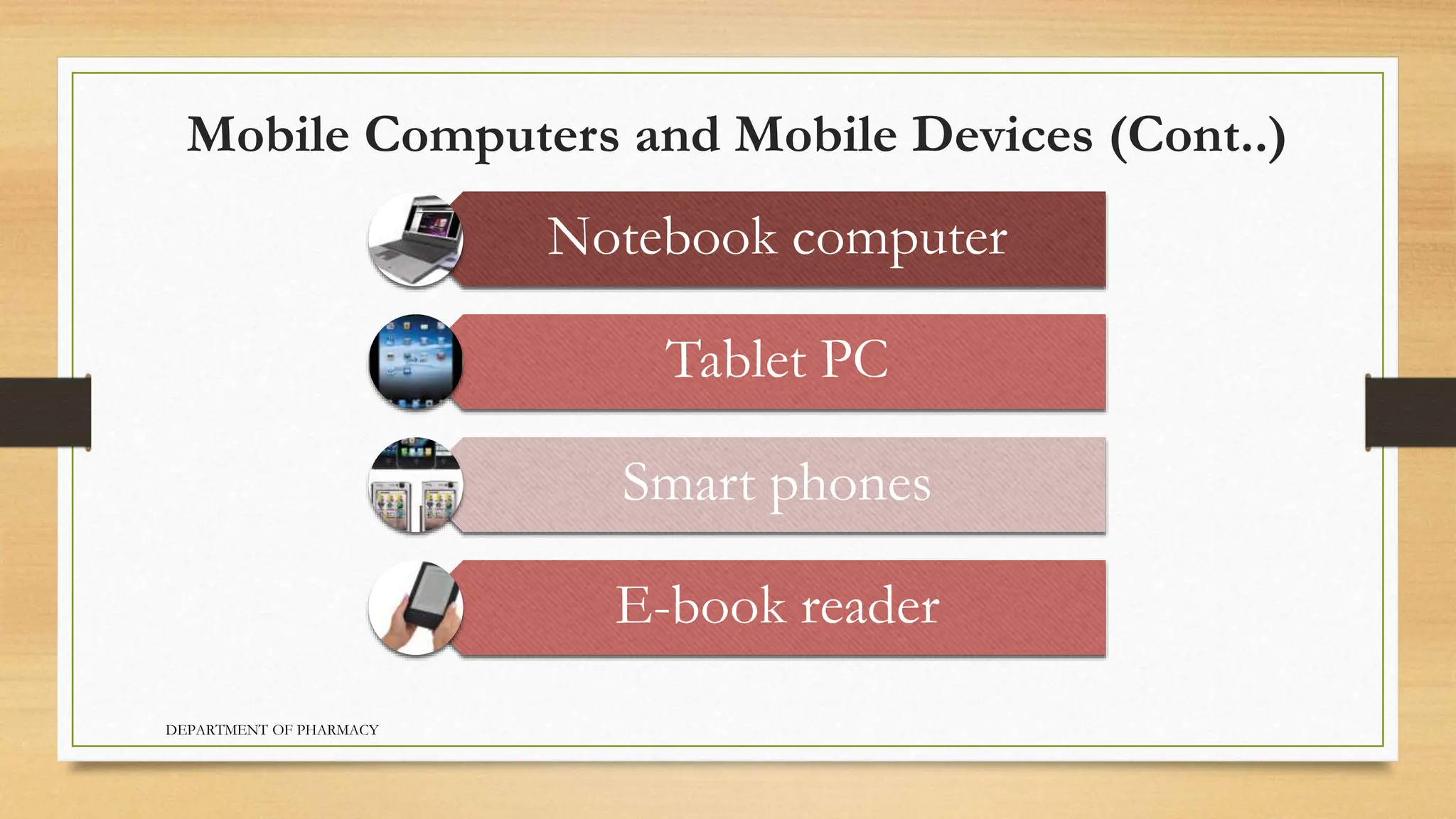
- Personal computers are designed for individual use and include benefits like low cost and portability. Mobile devices include smartphones, e-readers, and tablets.
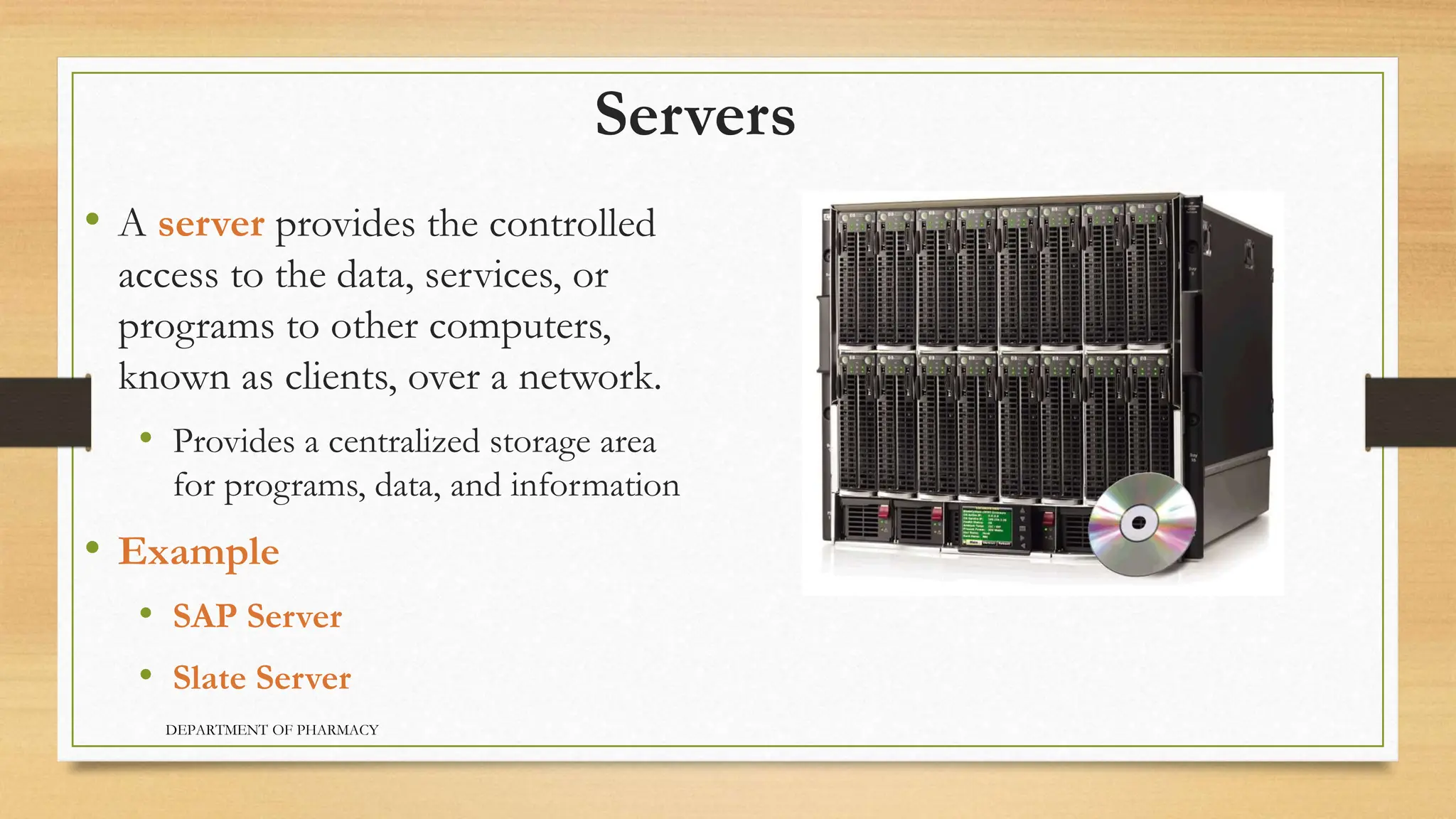
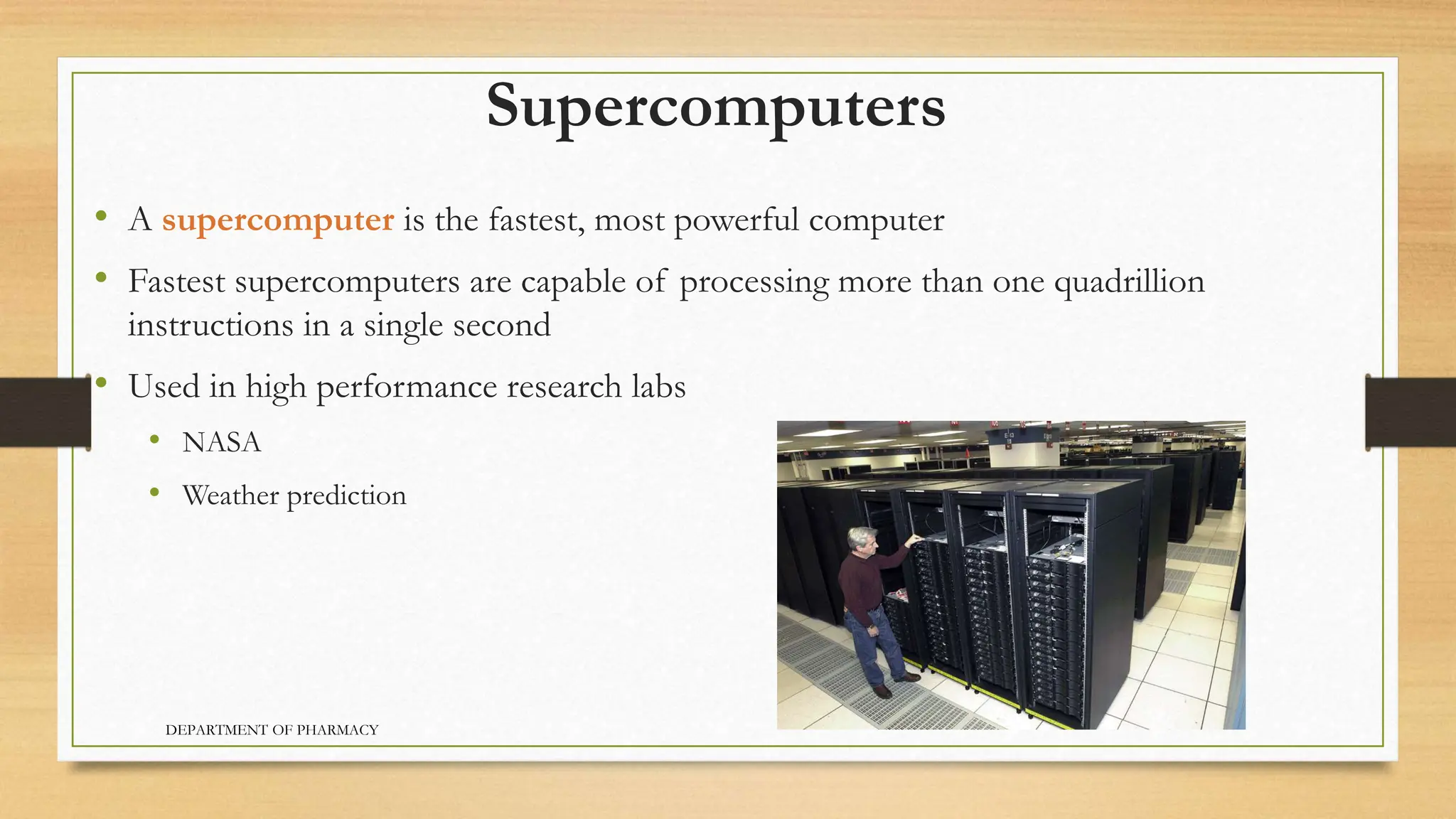
- Servers provide centralized access to data and programs over a network. Mainframes can handle hundreds of users simultaneously. Supercomputers are the fastest