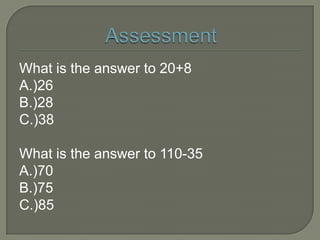
This document discusses adding and subtracting whole numbers. It defines whole numbers and the processes of addition and subtraction. It provides examples of measuring objects in a classroom and using the measurements to practice adding and subtracting whole numbers mentally, on paper, and using a calculator. It suggests other examples like ages and time that use whole numbers. An assessment with sample addition and subtraction problems is included at the end.