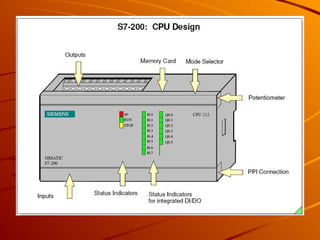
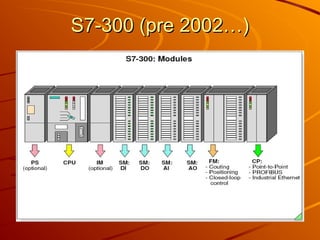
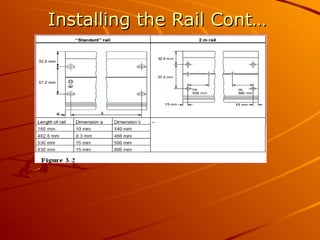
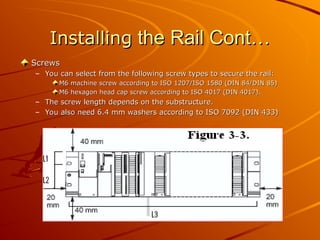
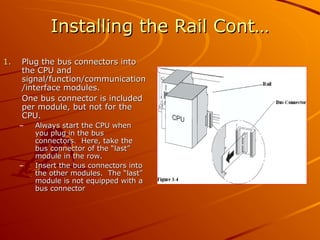
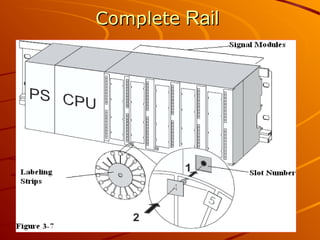
The document provides an overview of programmable logic controllers (PLCs) and their significance in modern automation tasks, highlighting their benefits over older hard-wired systems. It outlines various modules and components used in configuring S7-300 systems, including types of input/output modules, communication processors, and programming devices. Additionally, it discusses the integration of hardware and software for seamless operation within manufacturing environments.