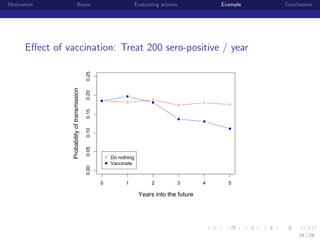
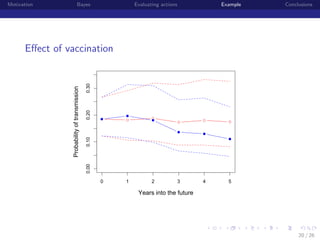
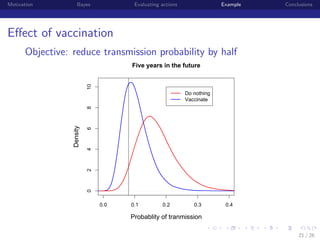
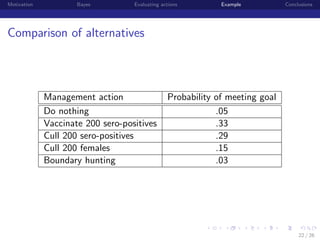
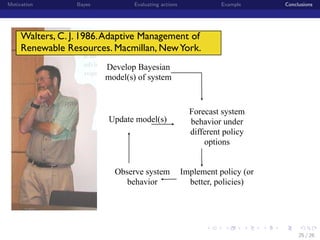
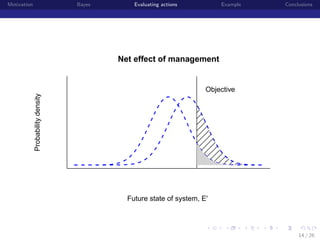
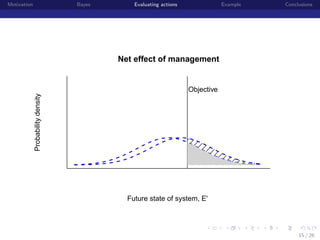
This document discusses using Bayesian modeling and uncertainty analysis to evaluate management actions for ecological systems. It presents the motivation for including uncertainty in forecasts to support policy. The document outlines a general Bayesian modeling approach and shows an example of using it to evaluate actions to reduce brucellosis transmission in Yellowstone bison. Vaccinating seropositive females each year was found to have the highest probability of meeting the goal of reducing transmission probability by half within five years, compared to other actions like culling or hunting. The document concludes by discussing limitations and benefits of the approach for informing management conversations.



![Motivation
Bayes
Evaluating actions
Example
Conclusions
A broadly applicable approach to ecological modeling in
support of management
[E, θprocess, θdata |data] ∝
[data|θdata , Et ] [Et |θprocess , Et−1 ] [θprocess , θdata , E0 ]
data
Et
Et
Process
✓process ✓data
Parameters
1
institution-logo
6 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-ahobbsesa2013-131202122225-phpapp02/85/Hobbs-Better-ignorant-than-misled-Including-uncertainty-in-forecasts-supporting-management-and-policy-6-320.jpg)
![Motivation
Bayes
Evaluating actions
Example
Conclusions
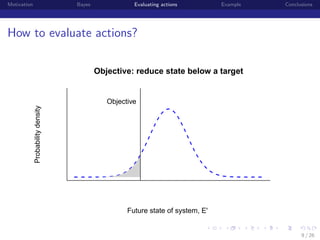
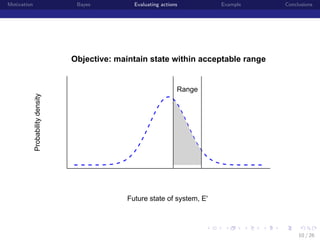
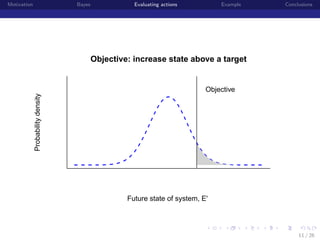
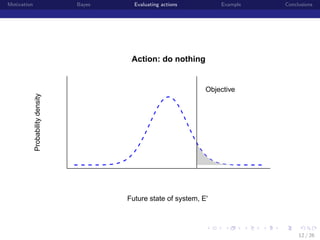
Posterior predictive distributions
State of Population (E or E’)
State of Ecological System (E or E')
[E |data] =
θ E [E |E , θdata , θprocess ] [E , θdata , θprocess |data] dE dθdata θprocess
Time
institution-logo
7 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-ahobbsesa2013-131202122225-phpapp02/85/Hobbs-Better-ignorant-than-misled-Including-uncertainty-in-forecasts-supporting-management-and-policy-7-320.jpg)



![Motivation
Bayes
Evaluating actions
Example
Conclusions
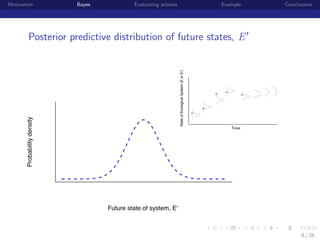
Bayesian matrix model with multiple sources of data
Mark recapture
yϕ[t]
Serology
Ysero[t]
Ground
Aerial
classifications
classifications
yp.µ[t]
yratio.calf[t]
yp.σ[t]
yσ[t]
n[t]
p
A[t] n[t
Census
yn.obs[t]
yn.sd[t]
psight
asd , bsd
1]
r[t]
Removals
yr[t]
Removal
Removal
age, sex
serology
yr.age[t]
yr.sero[t]
rcomp[t]
rsero[t]
rinfect[t]
, fc , fn , fp , , s, v
institution-logo
18 / 26](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/3-ahobbsesa2013-131202122225-phpapp02/85/Hobbs-Better-ignorant-than-misled-Including-uncertainty-in-forecasts-supporting-management-and-policy-18-320.jpg)