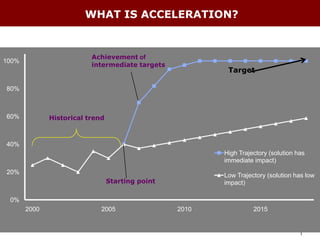
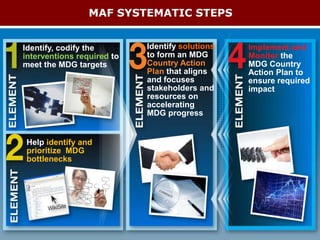
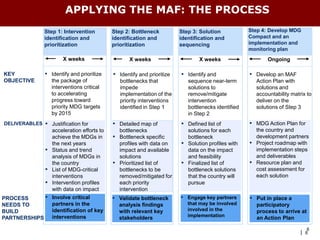
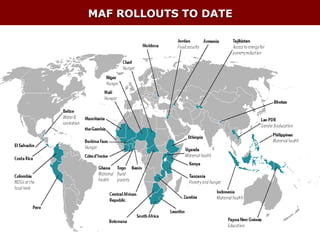
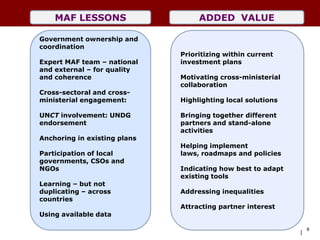
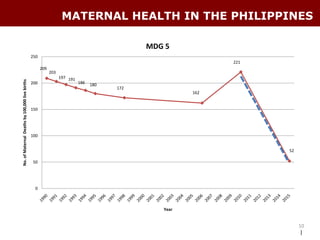
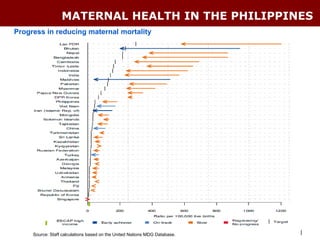
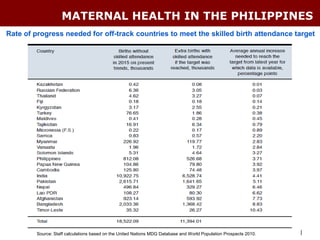
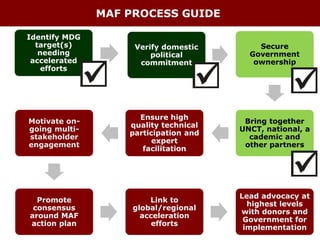
The document discusses using the MDG Acceleration Framework (MAF) to reduce maternal mortality in the Philippines. The MAF identifies bottlenecks preventing progress, then finds solutions to address those bottlenecks. In the Philippines, maternal mortality increased from 2010 to 221 deaths per 100,000 live births, far from the 2015 target of 52. The MAF could help prioritize existing solutions, address inequalities, and facilitate cross-sectoral collaboration needed to operationalize health policies and accelerate progress on maternal health. The process involves securing government commitment, bringing together stakeholders, and leading advocacy to support implementing an MAF action plan.