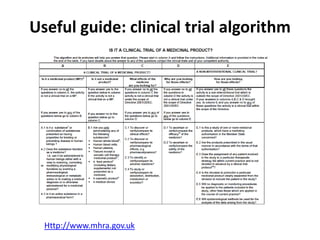
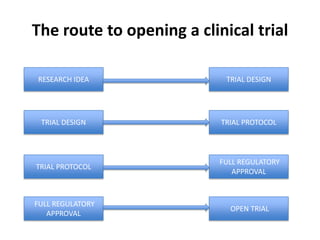
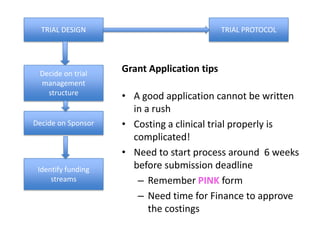
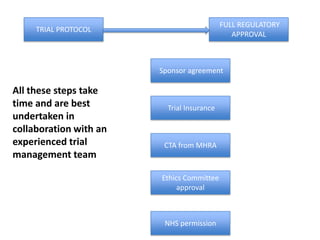
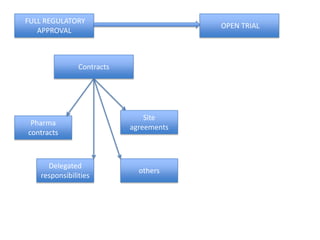
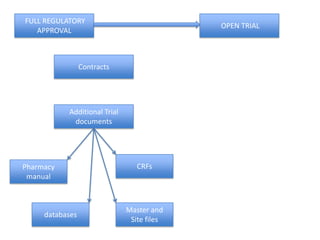
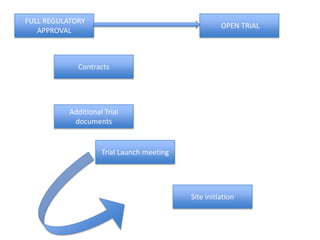
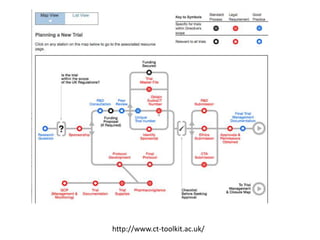
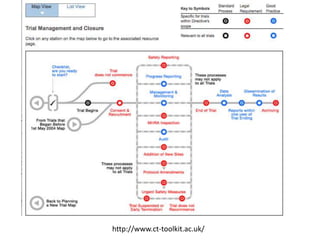
This document outlines the steps required to conduct a clinical trial of an investigational medicinal product (CTIMP) in the UK. It discusses determining if a trial is a CTIMP, designing the trial protocol, obtaining full regulatory approval, and opening the trial. Key steps include deciding on trial management structures, identifying funding, applying for grants and ethics approval, gaining sponsor and regulatory approval, and setting up contracts and documents. Advice is given to work closely with experienced trial teams to navigate this complex process which can take significant time.