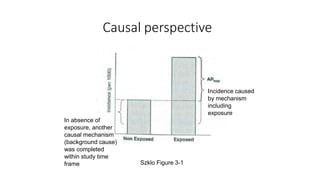
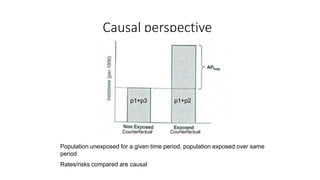
This document discusses measures of association used in observational epidemiology to compare disease rates between exposed and unexposed groups. It introduces both relative measures like risk ratios and odds ratios, as well as absolute measures like attributable risk and population attributable risk. While relative measures are more commonly used, absolute measures may better identify disease etiology and public health impact by taking into account differences in baseline risk between groups. However, these measures provide a lower bound on the true impact of an exposure, as individuals who develop disease due to other causes in the unexposed group are not distinguished.







![Absolute measures
• Alternative formulation:
• PAR = (AR)(Pe)
• Where does this come from?
• PAR = Rt – Ru
• PAR = [(Pe)Re + (1-Pe)Ru] - Ru
• PAR = (Pe)Re + Ru - (Pe)Ru - Ru
• PAR = (Pe)Re - (Pe)Ru
• PAR = (Re - Ru)(Pe)
• PAR = (AR)(Pe)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2-160808061437/85/2-5-summary-9-320.jpg)