This document presents a physical model for nitride-trapping non-volatile memories with a tri-gate structure. The model simulates Fowler-Nordheim tunneling during write/erase operations using a 1D approach that accounts for planar and corner regions. Experimental data from fabricated tri-gate SONOS and THiONOS devices matches the model's predictions for programming window, width dependence, and temperature effects. The model indicates corners will have a greater impact on charge trapping at smaller dimensions, and scaling to high-density cell sizes could enable faster write dynamics.



![Literature Few recent models on the subject Si nanocrystal Tri-Gate [Perniola L., IEDM 07] BE-SONOS Tri-Gate [Hsu T.-H.,IEDM 07] Si nanocrystal Tri-Gate [Nowak E., NVSMW 08] E.Nowak et al. IEDM 2008](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/227Nowak4-123136904575-phpapp02/85/Nowak-IEDM-08-5-320.jpg)




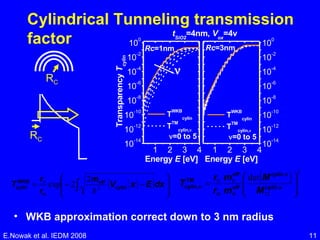
![1D Model 1D potential & capacitance calculation for planar and corner regions Total programming window is weighted sum of each regions E.Nowak et al. IEDM 2008 planar geometry cylindrical geometry [Nowak E., NVSMW 08] V G V D V S R C](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/227Nowak4-123136904575-phpapp02/85/Nowak-IEDM-08-10-320.jpg)









![Scaling perspectives: HC-FET Reducing cell size smaller Δ V T at saturation faster dynamics E.Nowak et al. IEDM 2008 [D. Kwak et al, VLSI 07] // // // // //](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/227Nowak4-123136904575-phpapp02/85/Nowak-IEDM-08-22-320.jpg)

