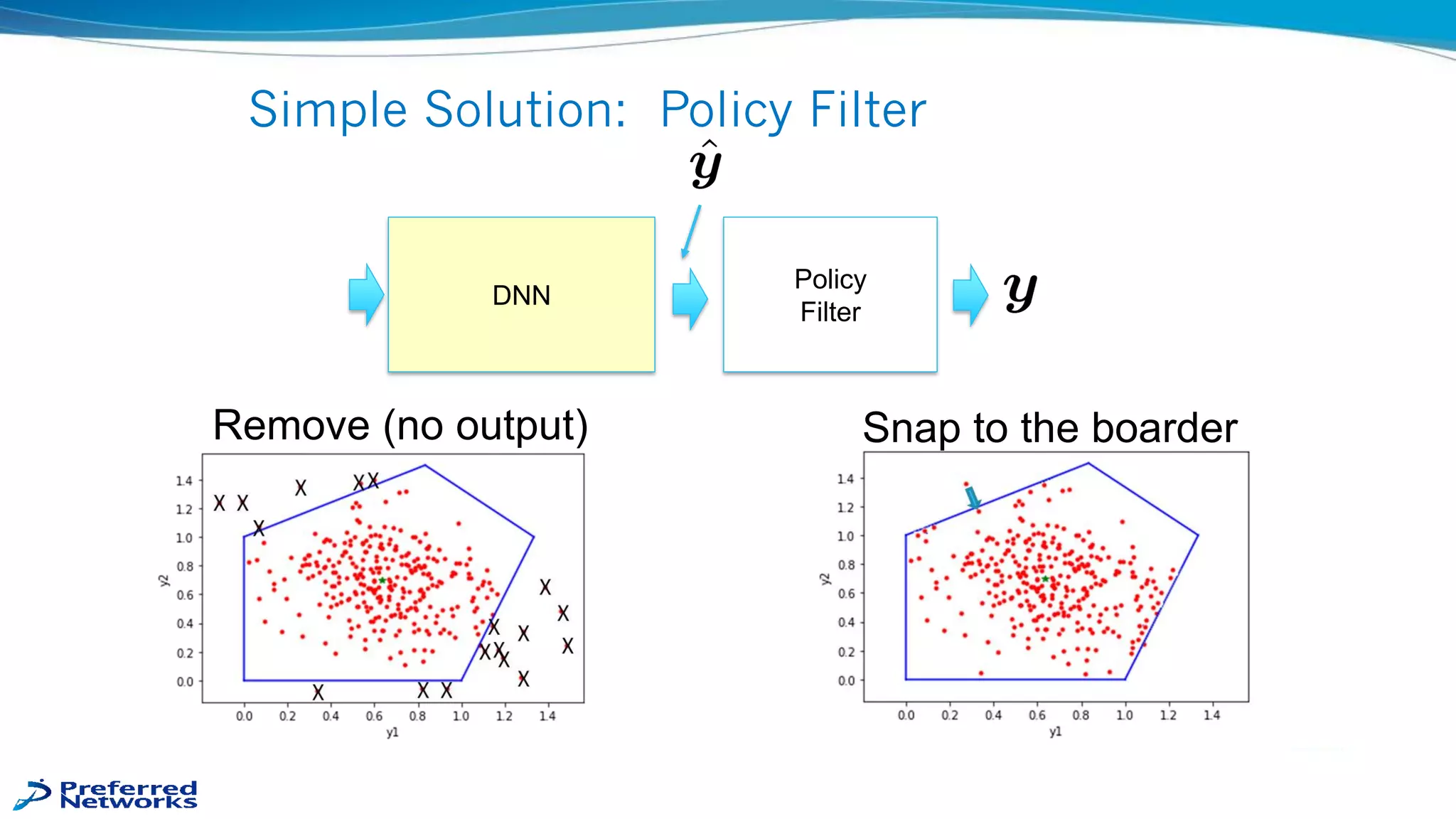
1) Deep neural networks can output any point in space but this is problematic when outputs must remain within a defined feasible region.
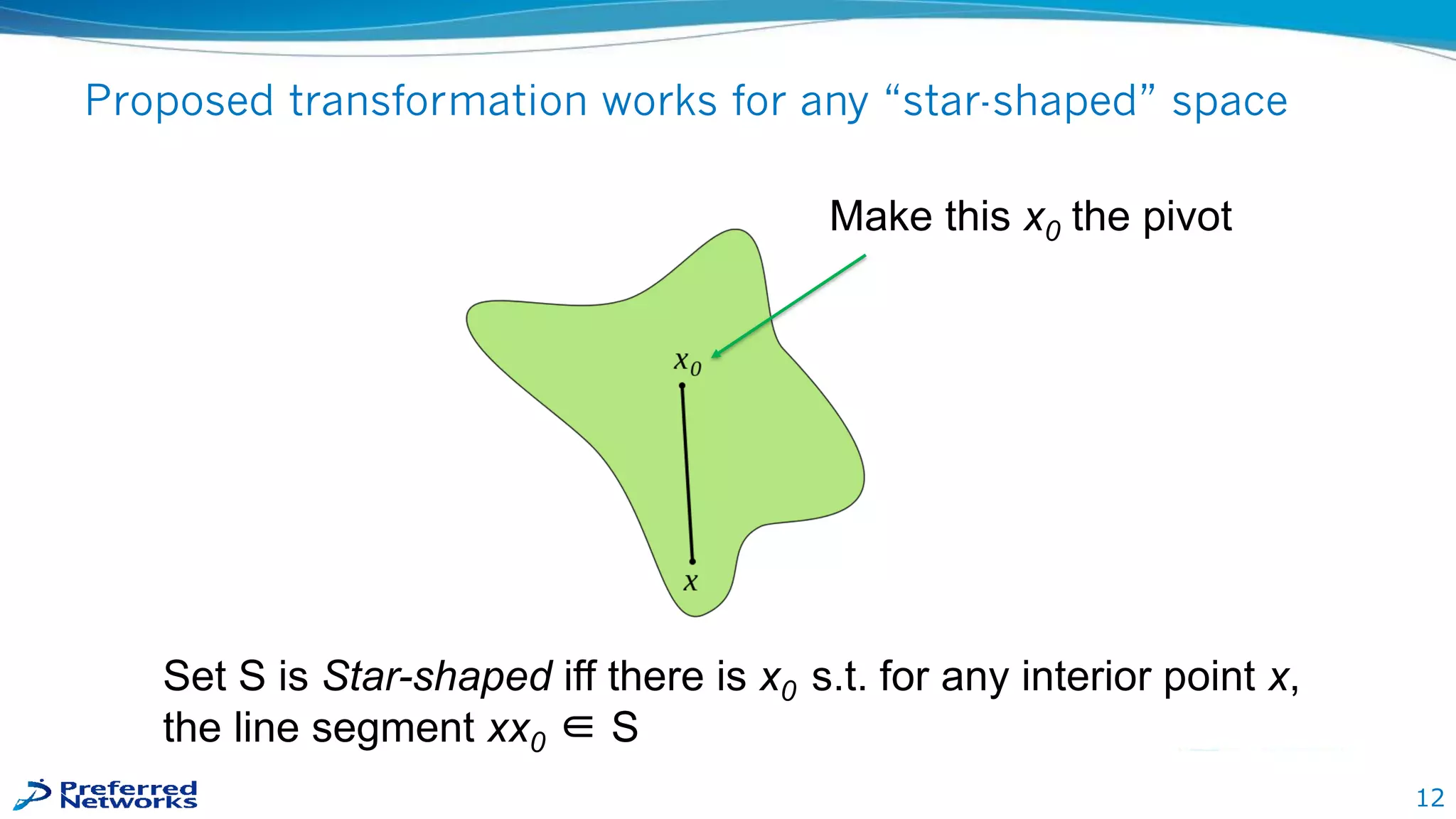
2) The presentation proposes transforming the output space to guarantee outputs fall within the feasible region. This is done by bounding the space to a hypercube around a pivot point, then shrinking/extending points toward the origin while keeping the pivot interior.
3) With this transformation, the output is guaranteed to remain feasible for any model parameters or inputs, allowing training to continue while enforcing constraints.