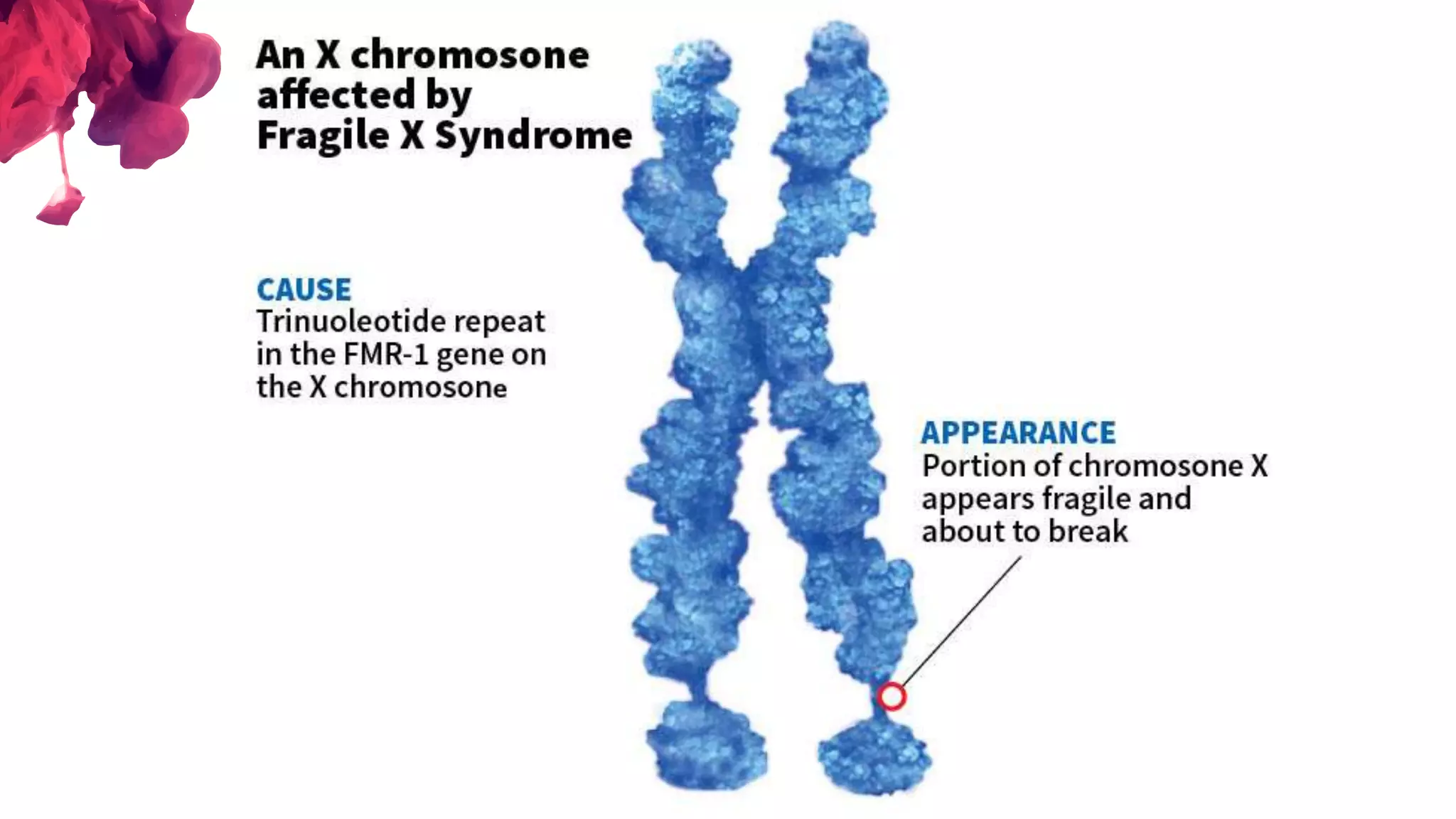
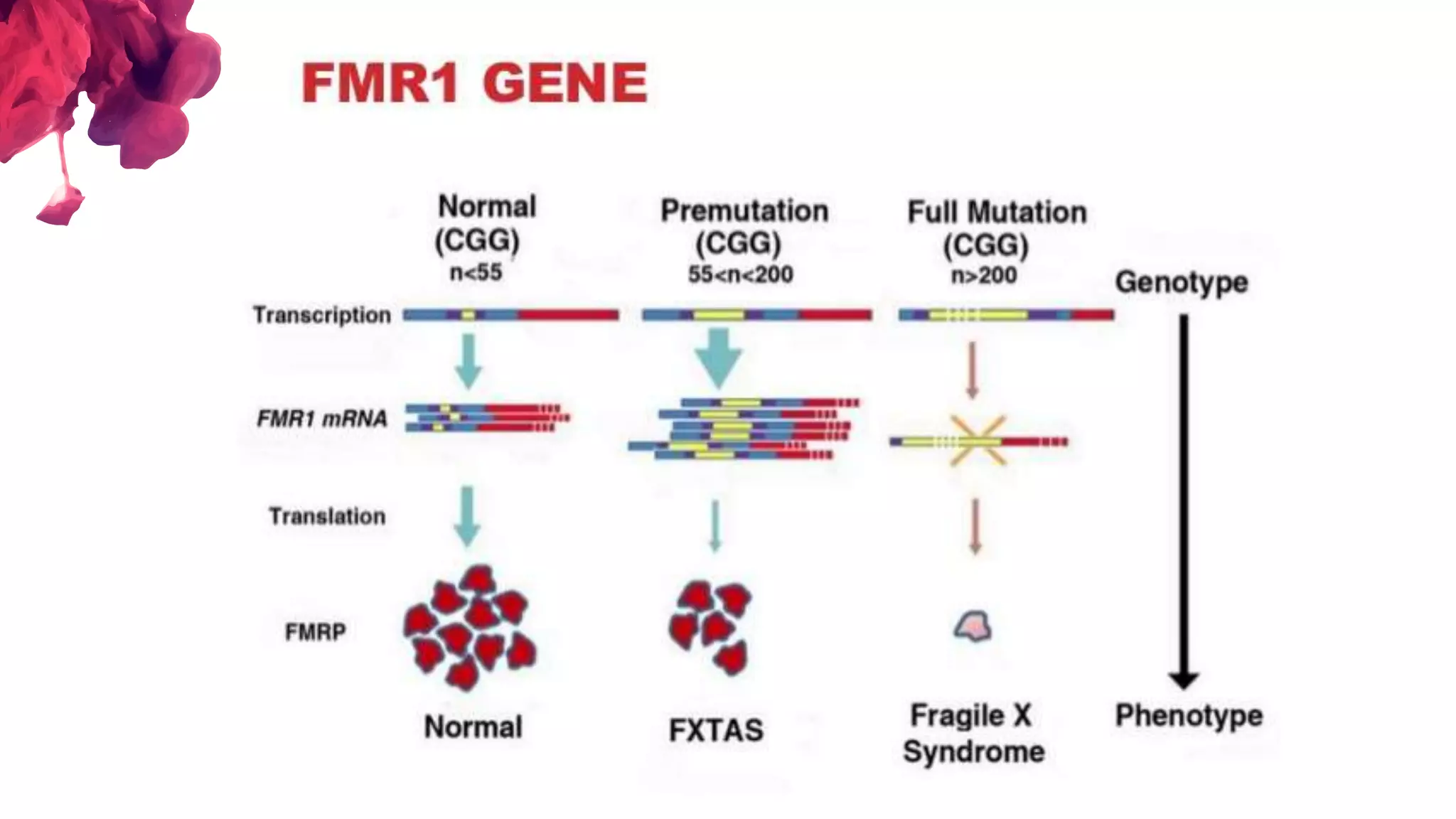
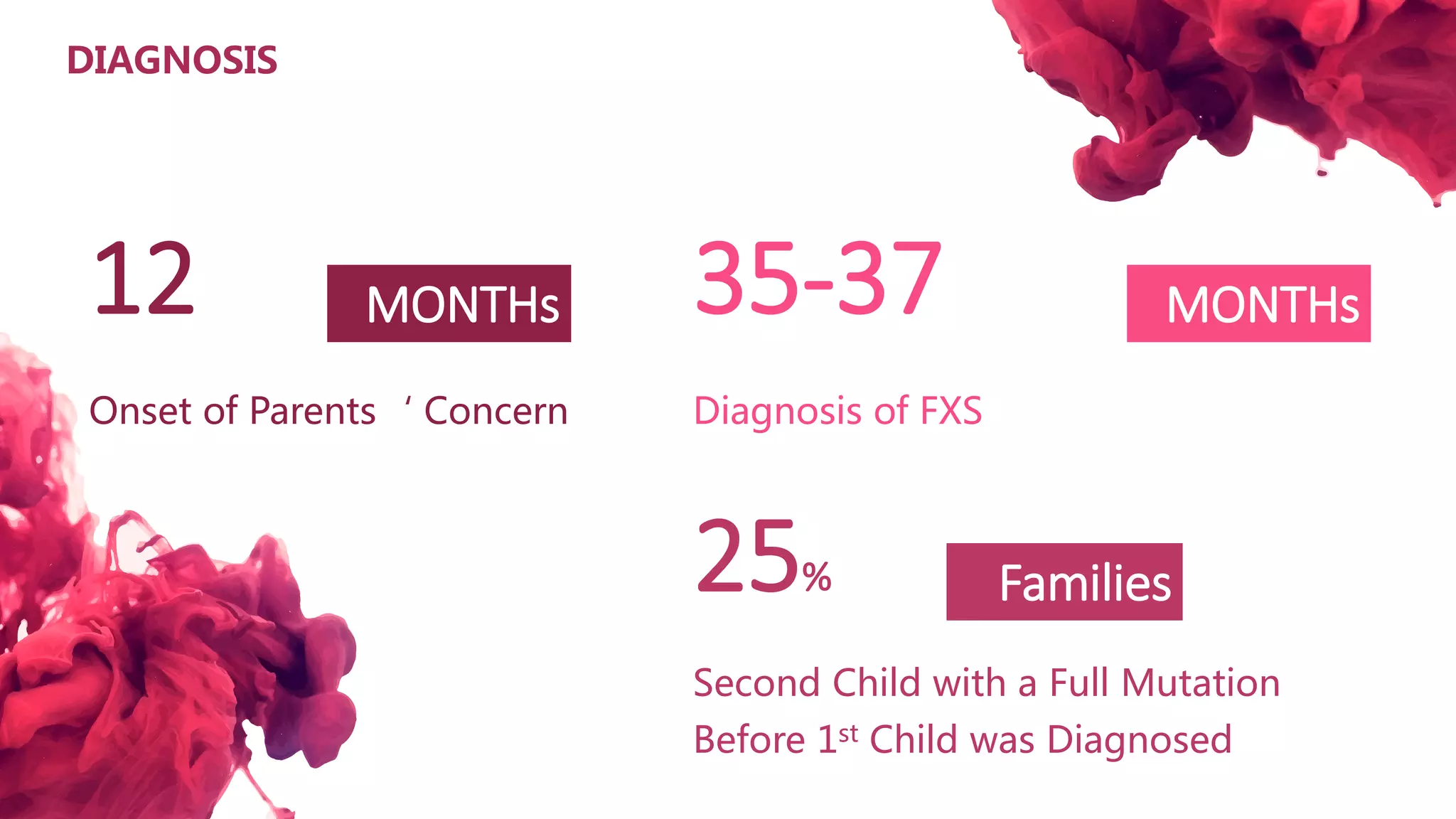
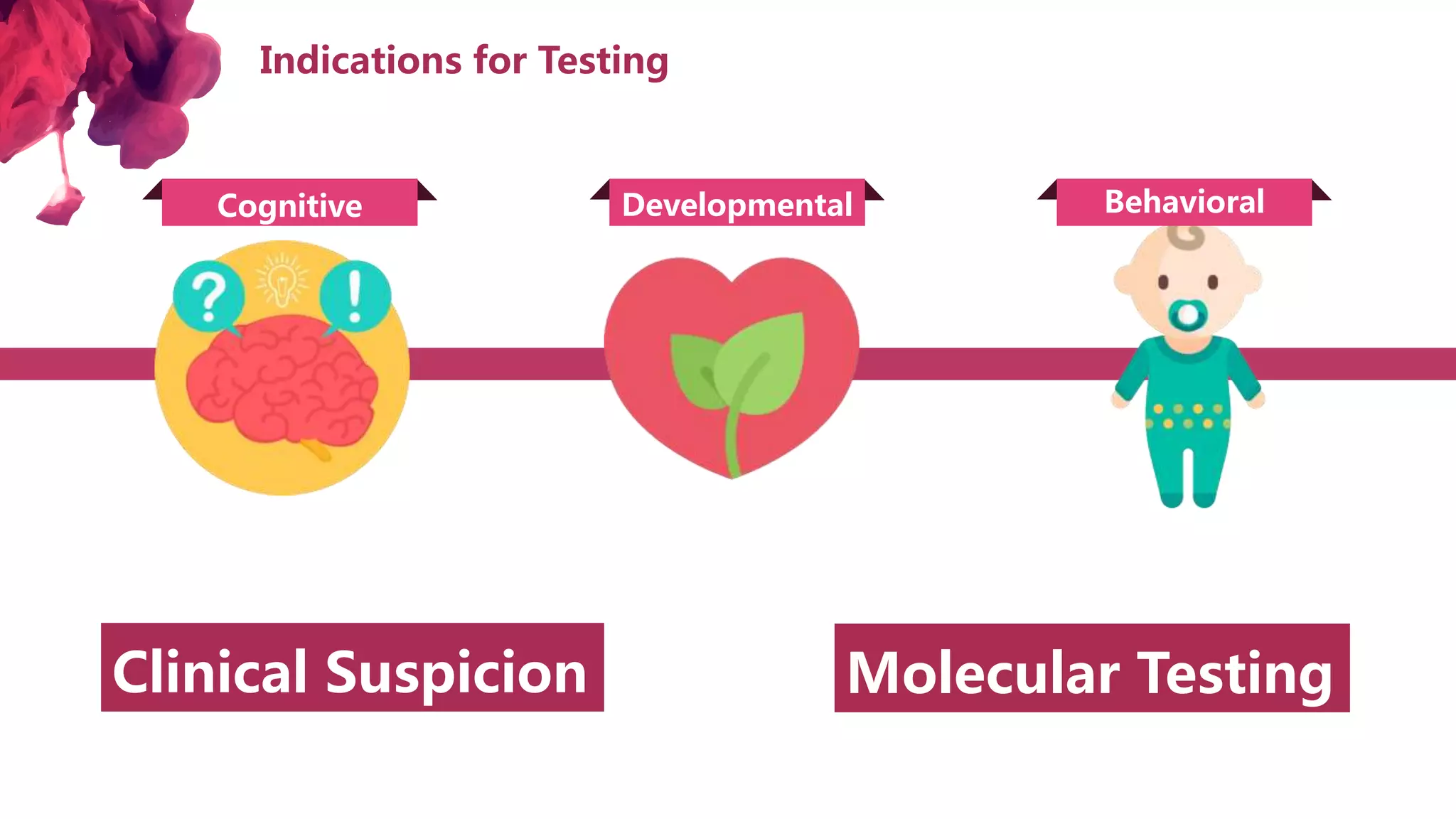
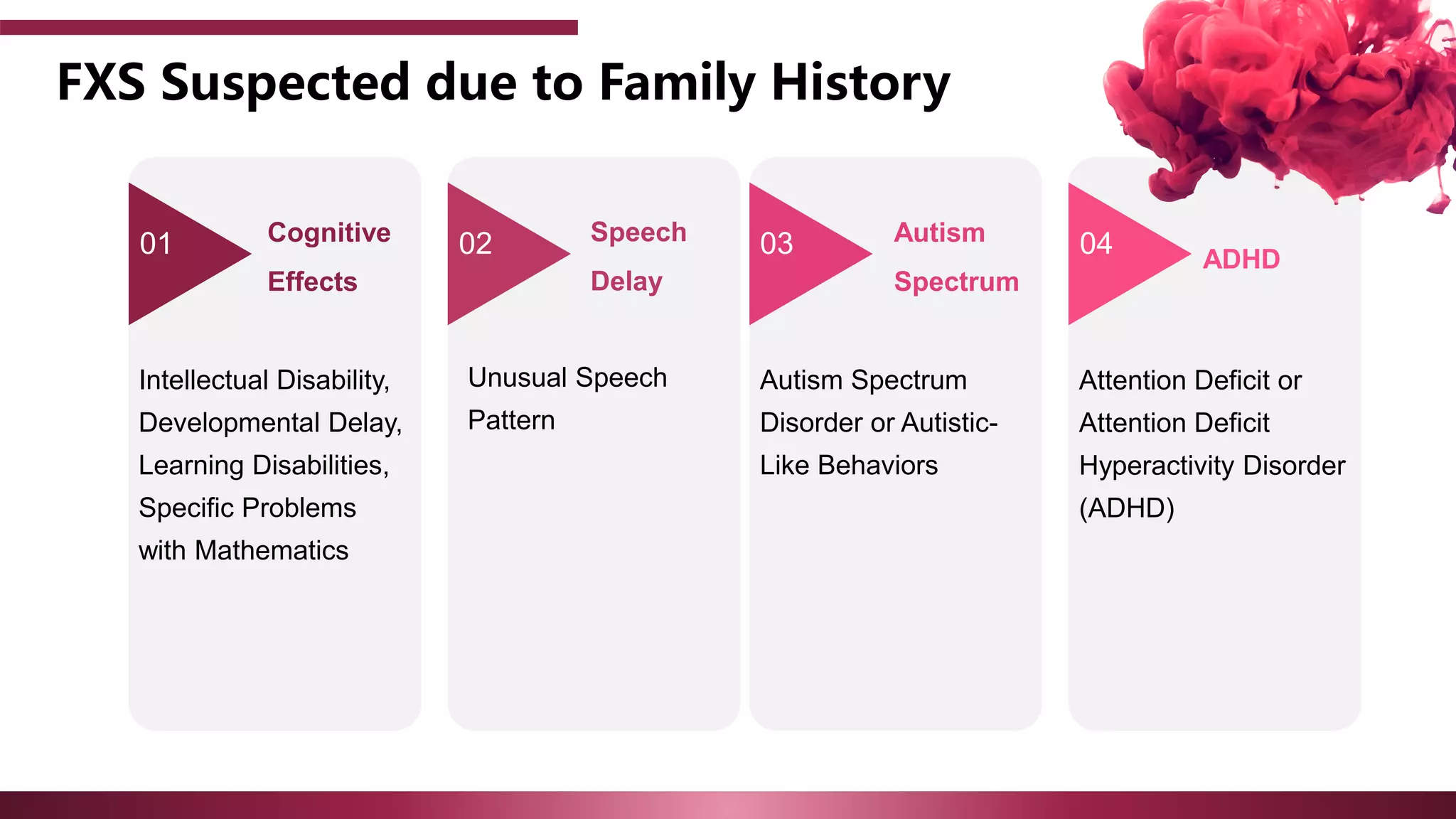
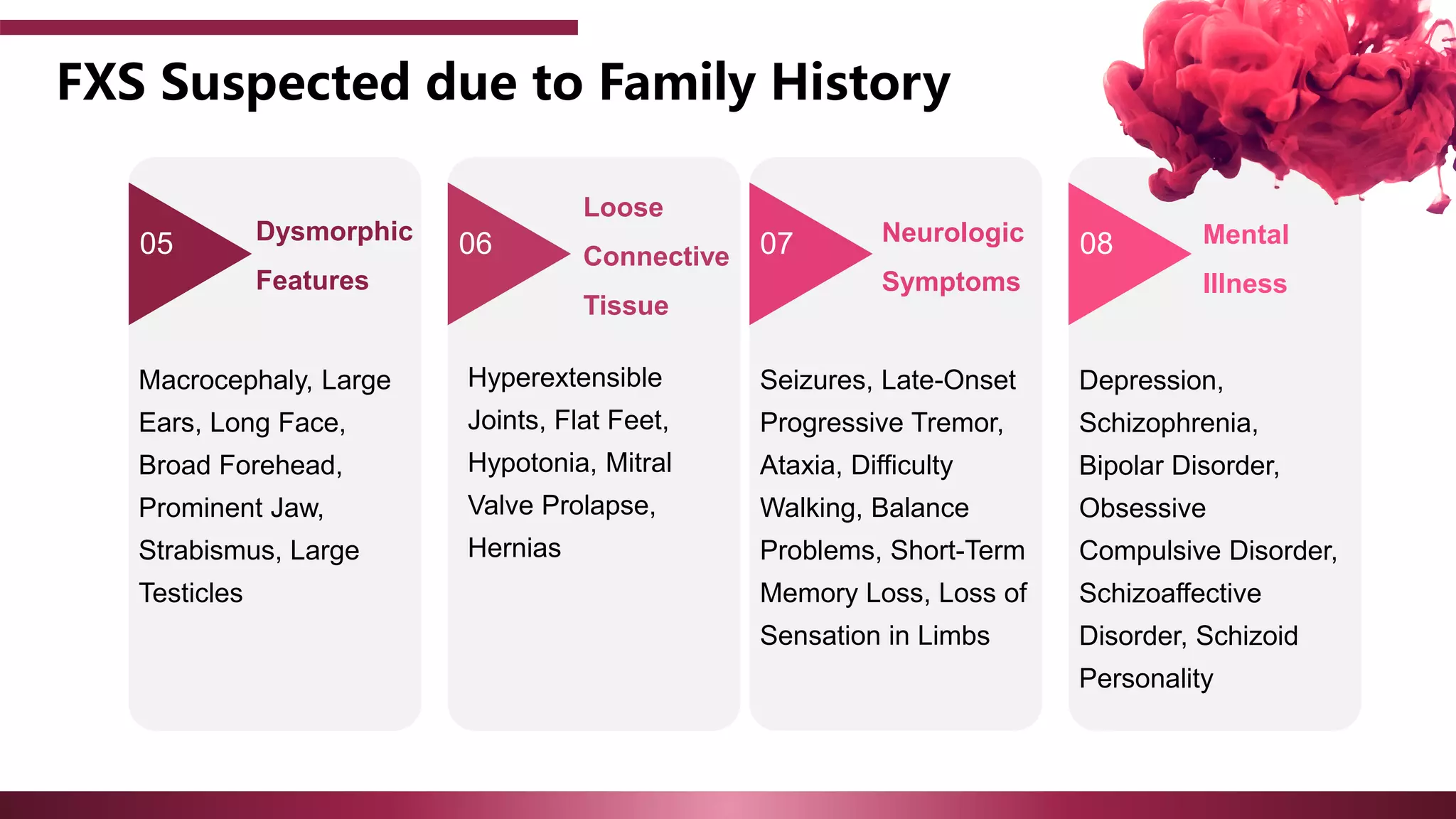
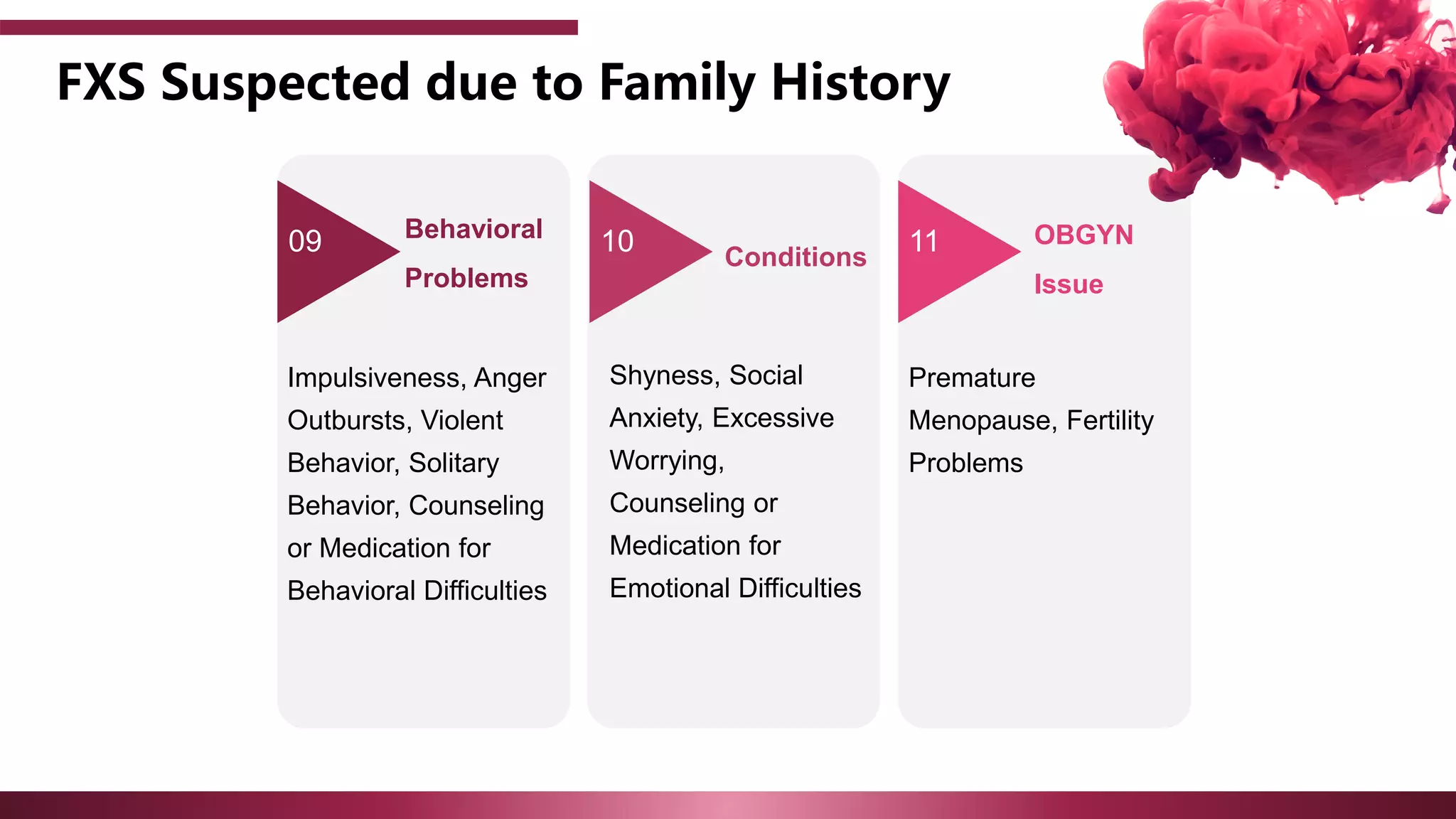
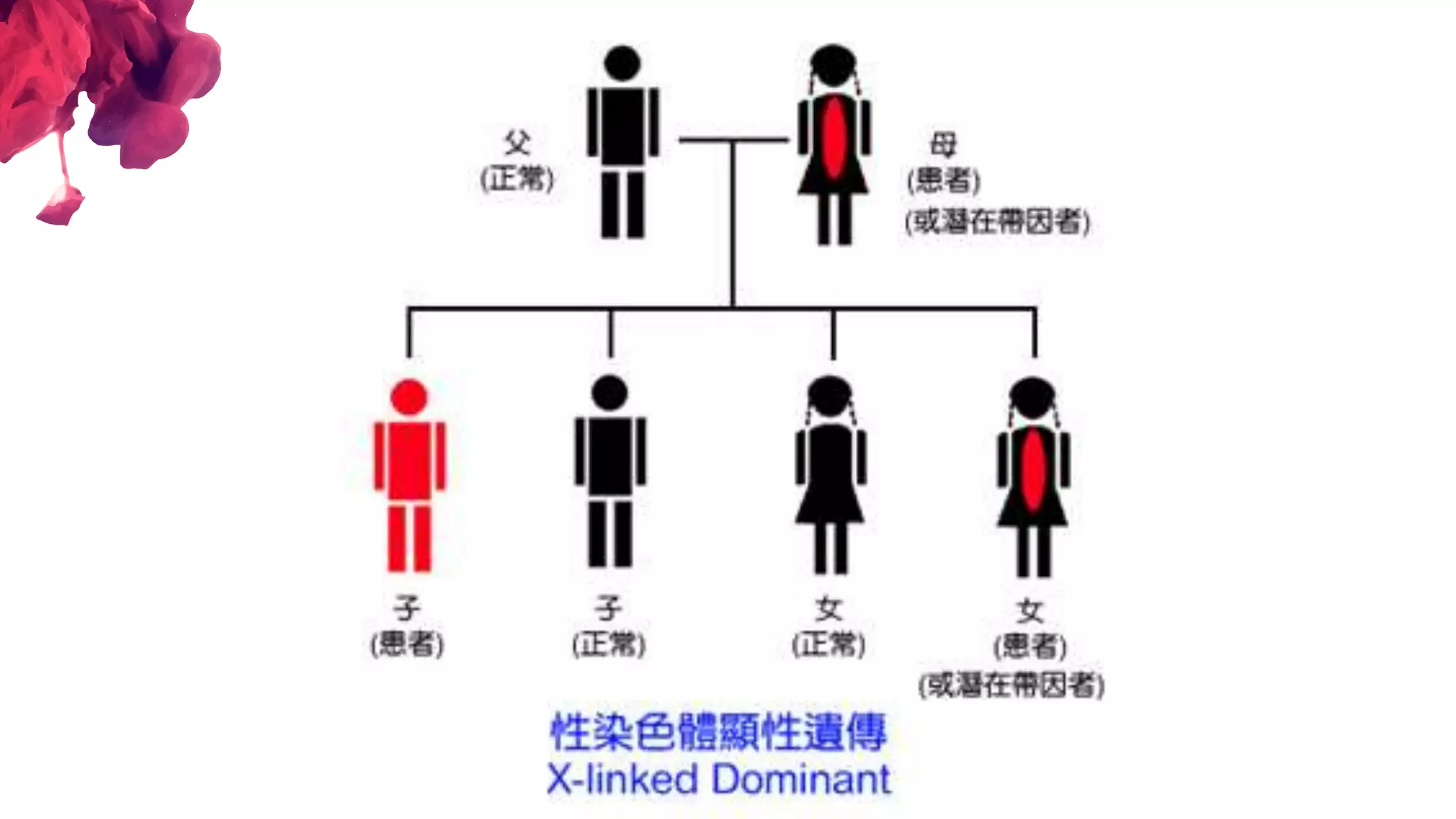
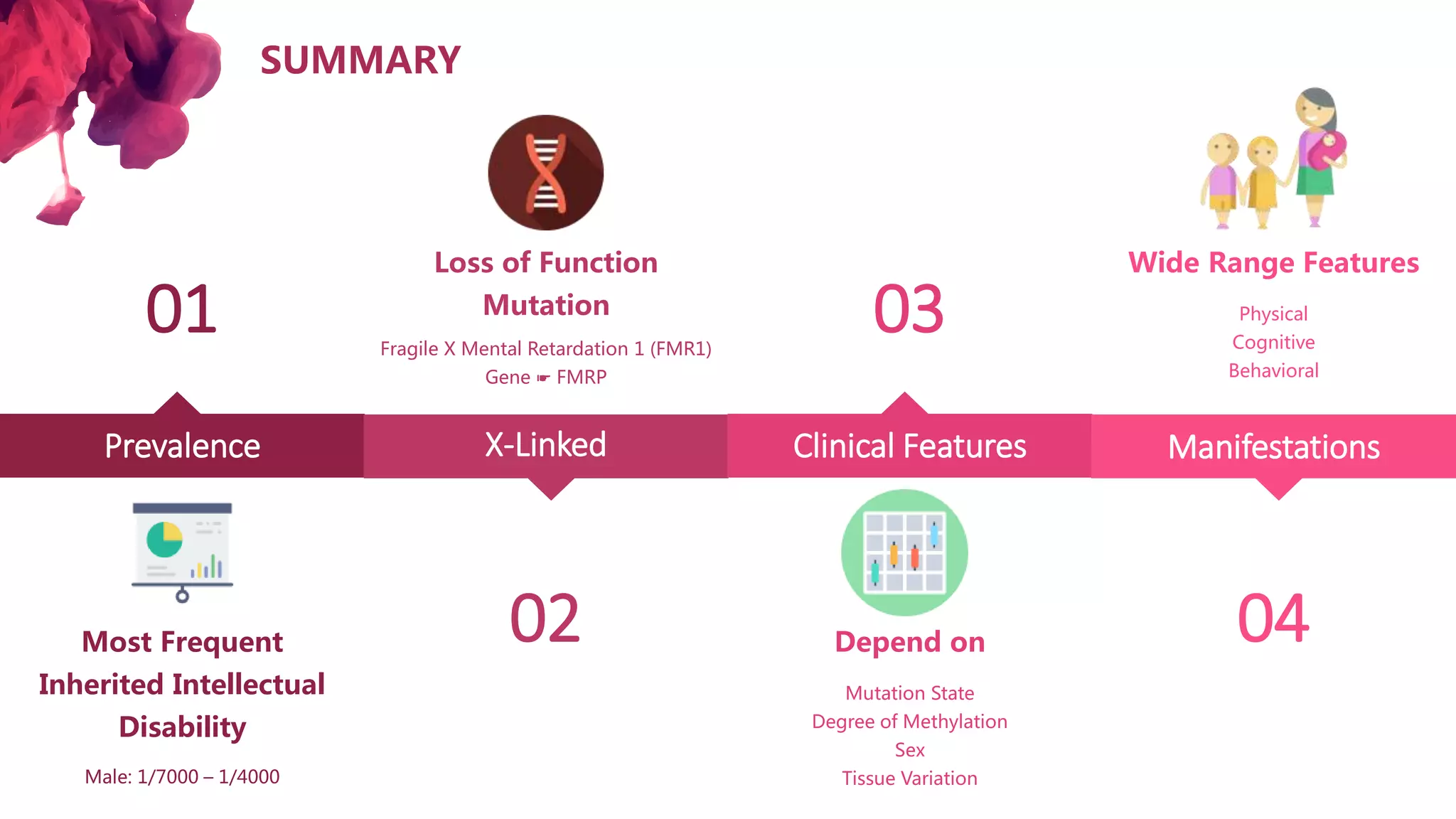
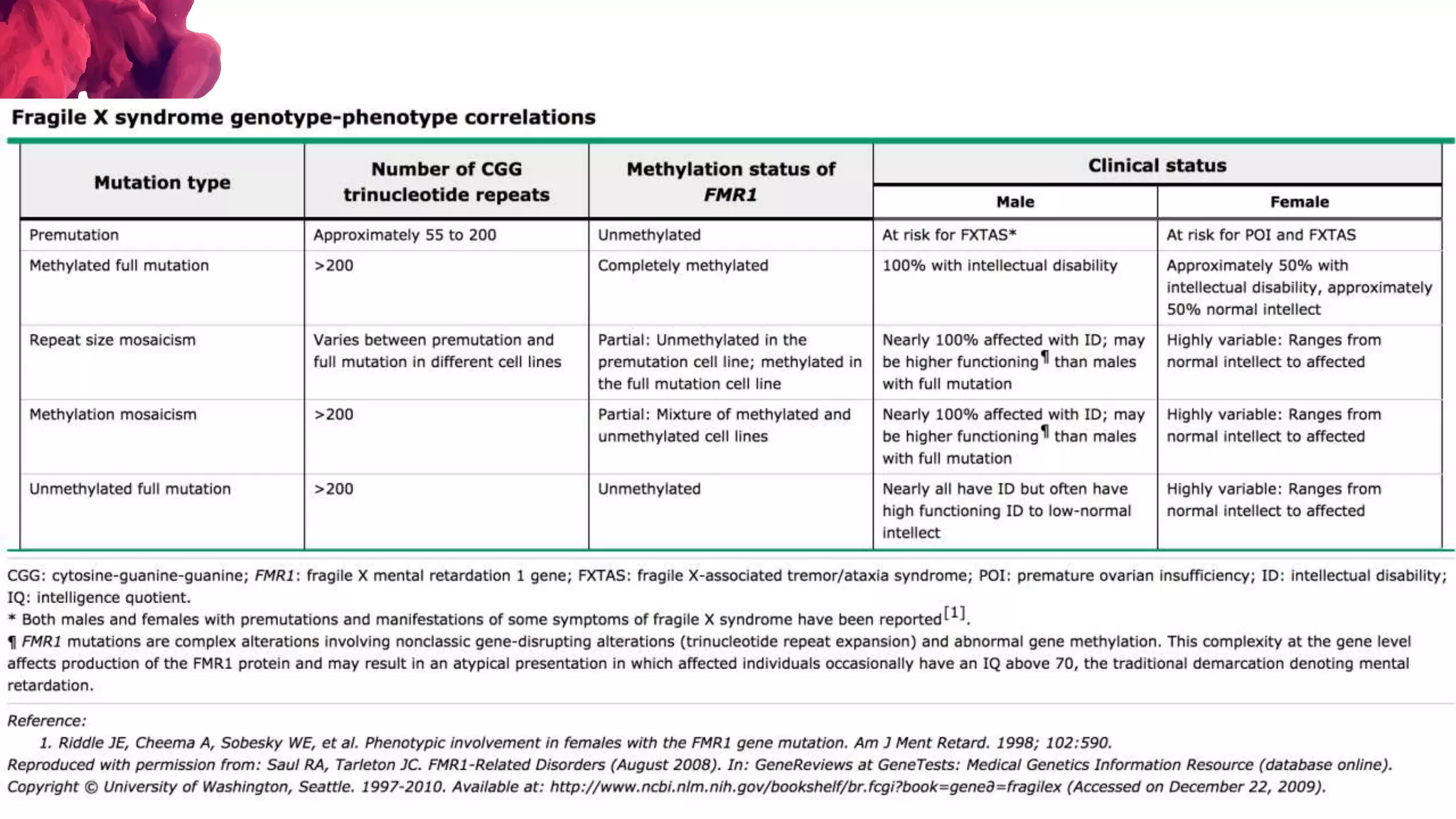
The document discusses the diagnostic criteria and differential diagnoses for Fragile X syndrome (FXS), emphasizing the importance of genetic testing in suspected cases. It outlines various cognitive, behavioral, and physical indicators associated with FXS and identifies potential differential diagnoses such as autism and attention deficit hyperactivity disorder. The prevalence of FXS is highlighted along with its association with the FMR1 gene mutation, making it the most common inherited intellectual disability.