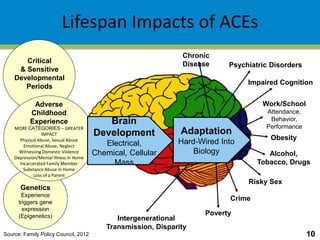
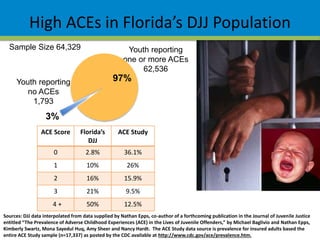
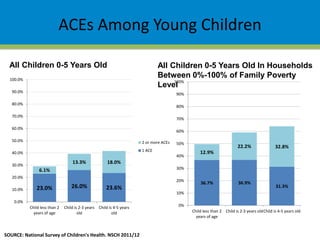
This document summarizes research from the Adverse Childhood Experiences (ACE) Study, which found strong associations between adverse experiences in childhood (such as abuse, neglect, household dysfunction) and negative health and social outcomes later in life. The ACE Study showed that two-thirds of participants reported at least one ACE, with higher ACE scores correlated with increased risk for health problems (like heart disease and cancer), mental health issues, risky behaviors, and early death. Further research cited found high rates of ACEs among at-risk groups like juvenile delinquents and Head Start children, as well as links between ACEs and problems with learning, behavior, and health among young children and students.