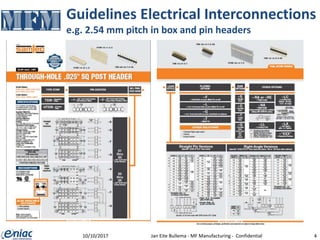
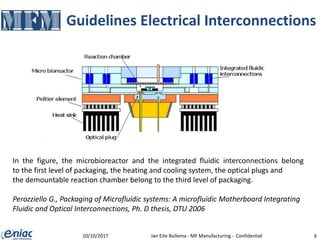
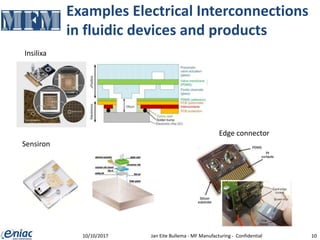
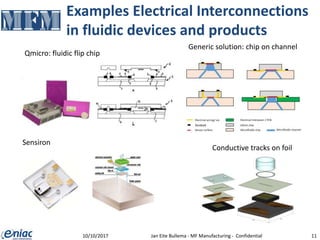
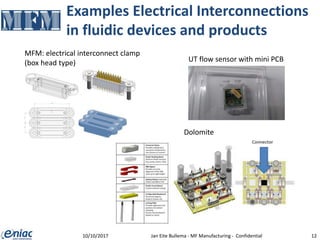
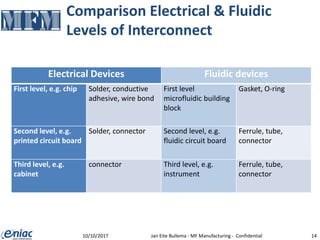
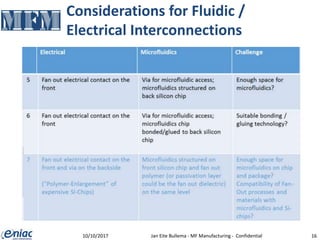
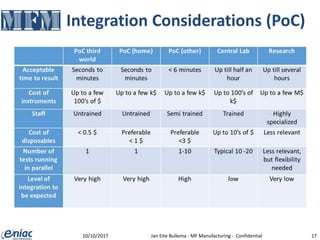
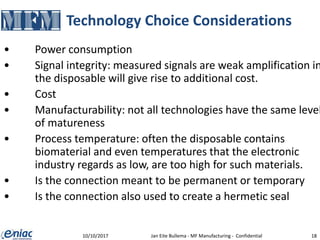
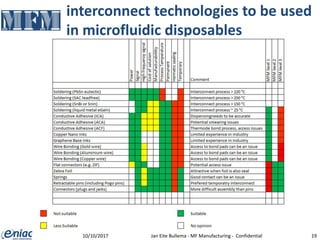
The document outlines guidelines for electrical interconnections in microfluidics, aiming to address standardization challenges and integration considerations. It discusses the importance of avoiding electrical interconnections in fluidic devices, recommending external solutions if necessary, and suggests using connectors or springs when interconnections must be integrated. The text highlights the need for careful consideration of technology choices to ensure manufacturability and maintain the integrity of biomaterials.