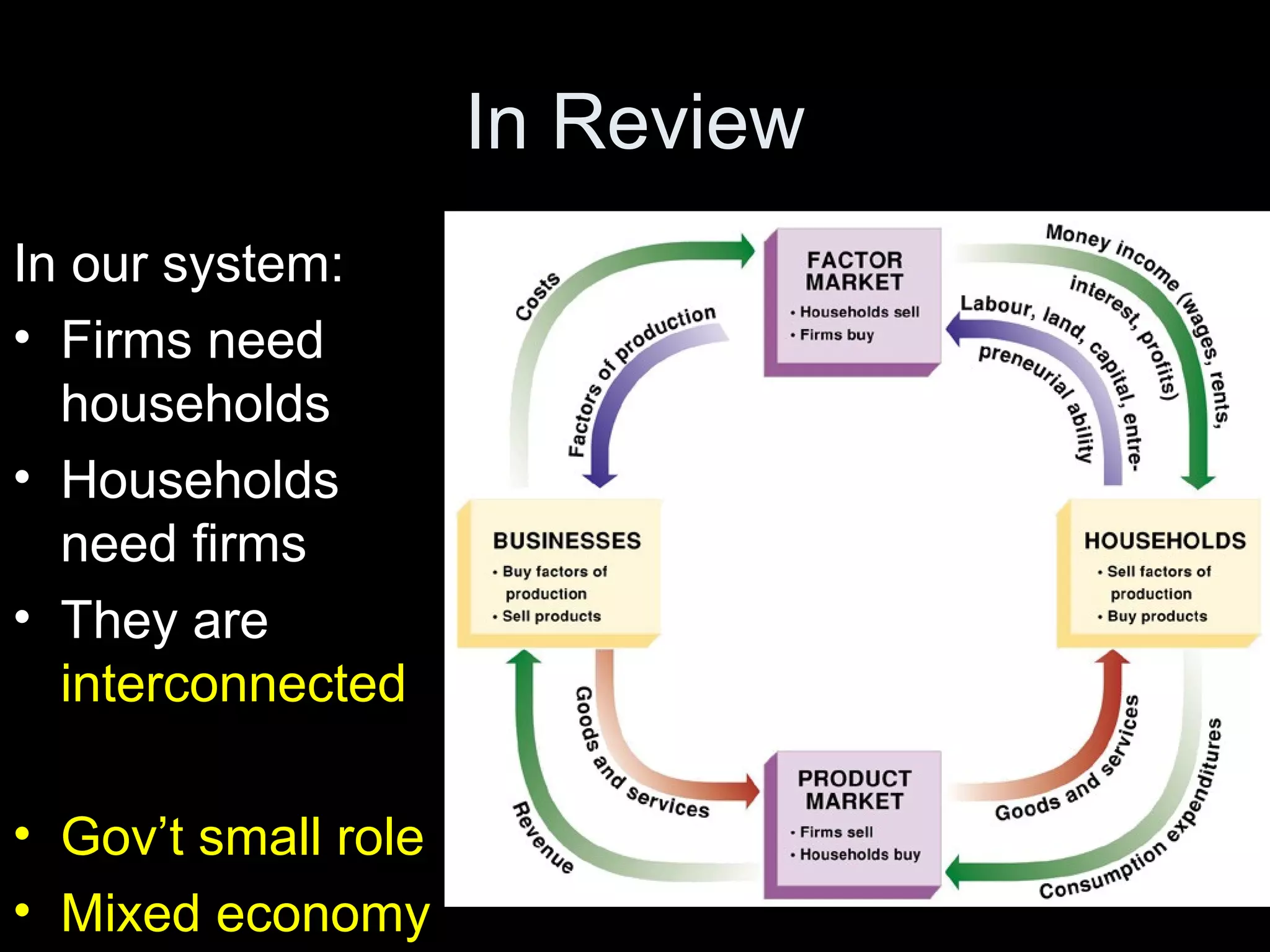
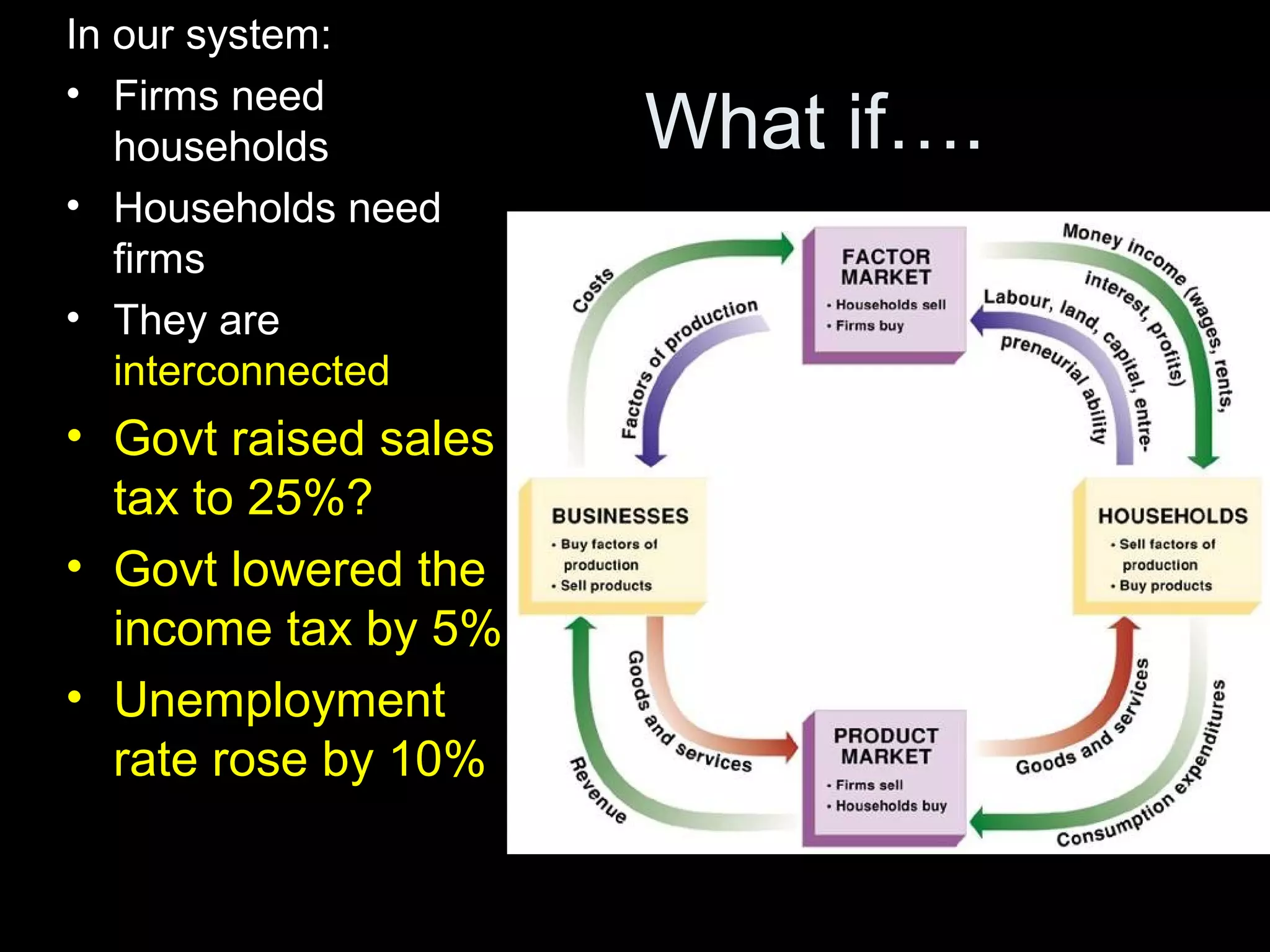
The document contains a quiz covering various economic concepts including defining a firm, opportunity cost, and why entrepreneurs are important to society. It also includes sample activities on trade, business organizations, and investing. Students are asked questions about starting a business, different business structures like corporations and non-profits, and key economic models such as the circular flow and mixed economies.