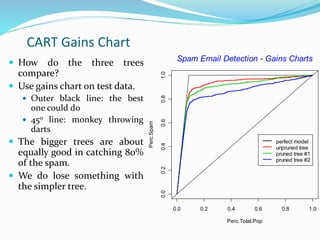
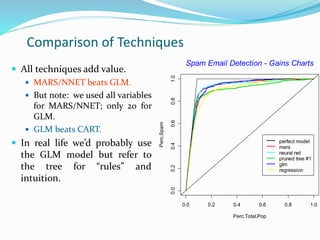
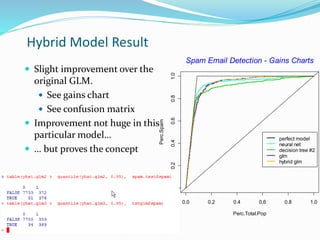
The document compares different models for spam email detection, including decision trees, MARS, neural networks, logistic regression, and multiple regression. It finds that logistic regression performs better than a decision tree model but not as well as MARS or a neural network when using all variables. However, logistic regression beats these methods when only using the top 20 predictive variables. Finally, the document shows that a hybrid model combining logistic regression with interaction terms identified by the decision tree provides a slight improvement over the basic logistic regression model.