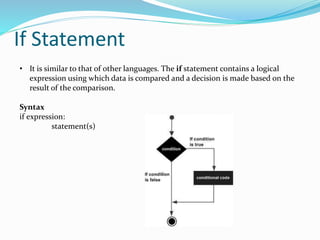
This document discusses decision making structures in Python, including if, if-else, and if-elif-else statements. It provides the syntax and examples of using each type of statement to evaluate conditions and execute code blocks based on whether the conditions evaluate to True or False. The if statement executes code if the expression is true, if-else adds an else block for when the expression is false, and if-elif-else allows checking multiple expressions and executing the block for the first one that is true.