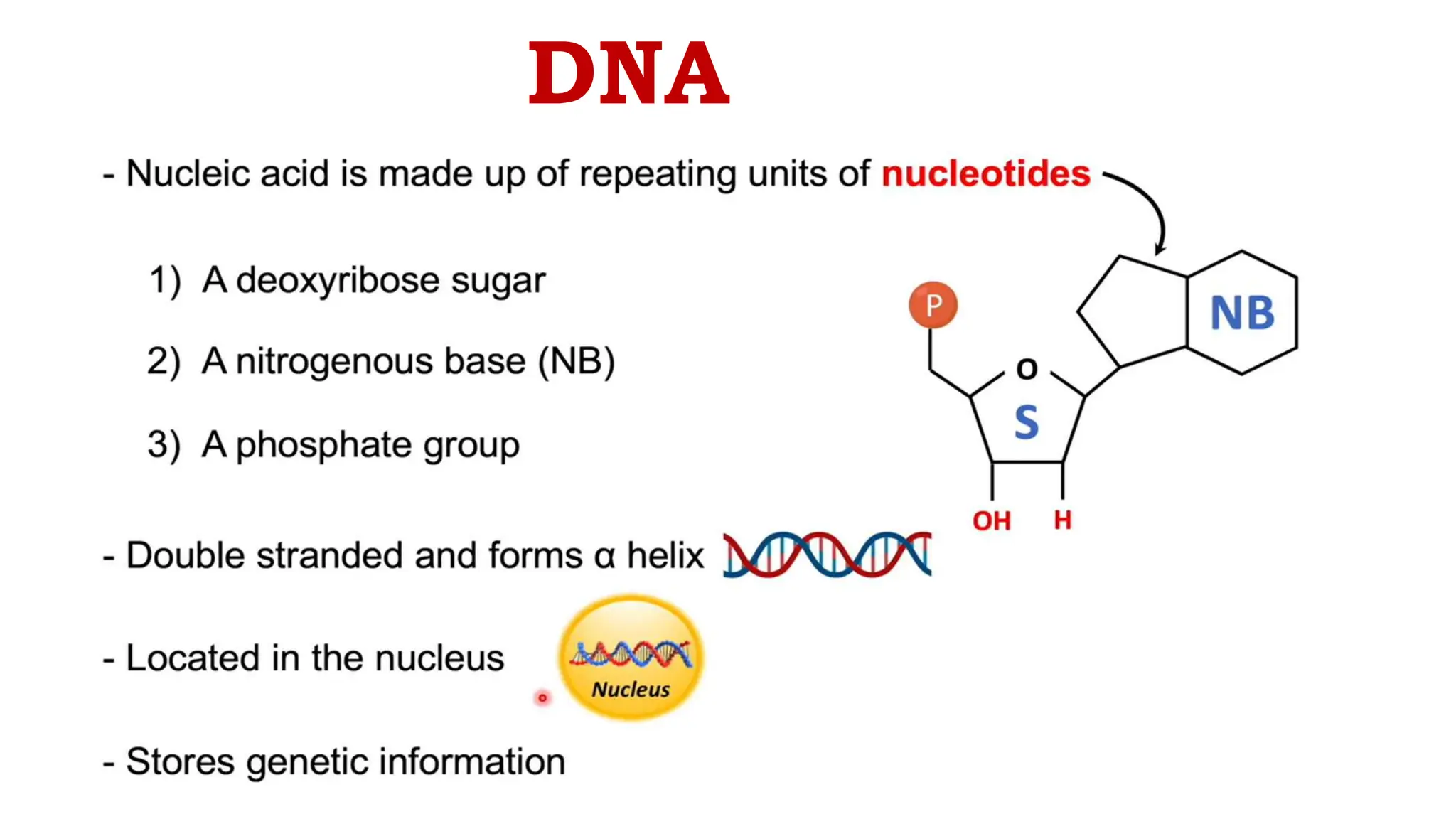
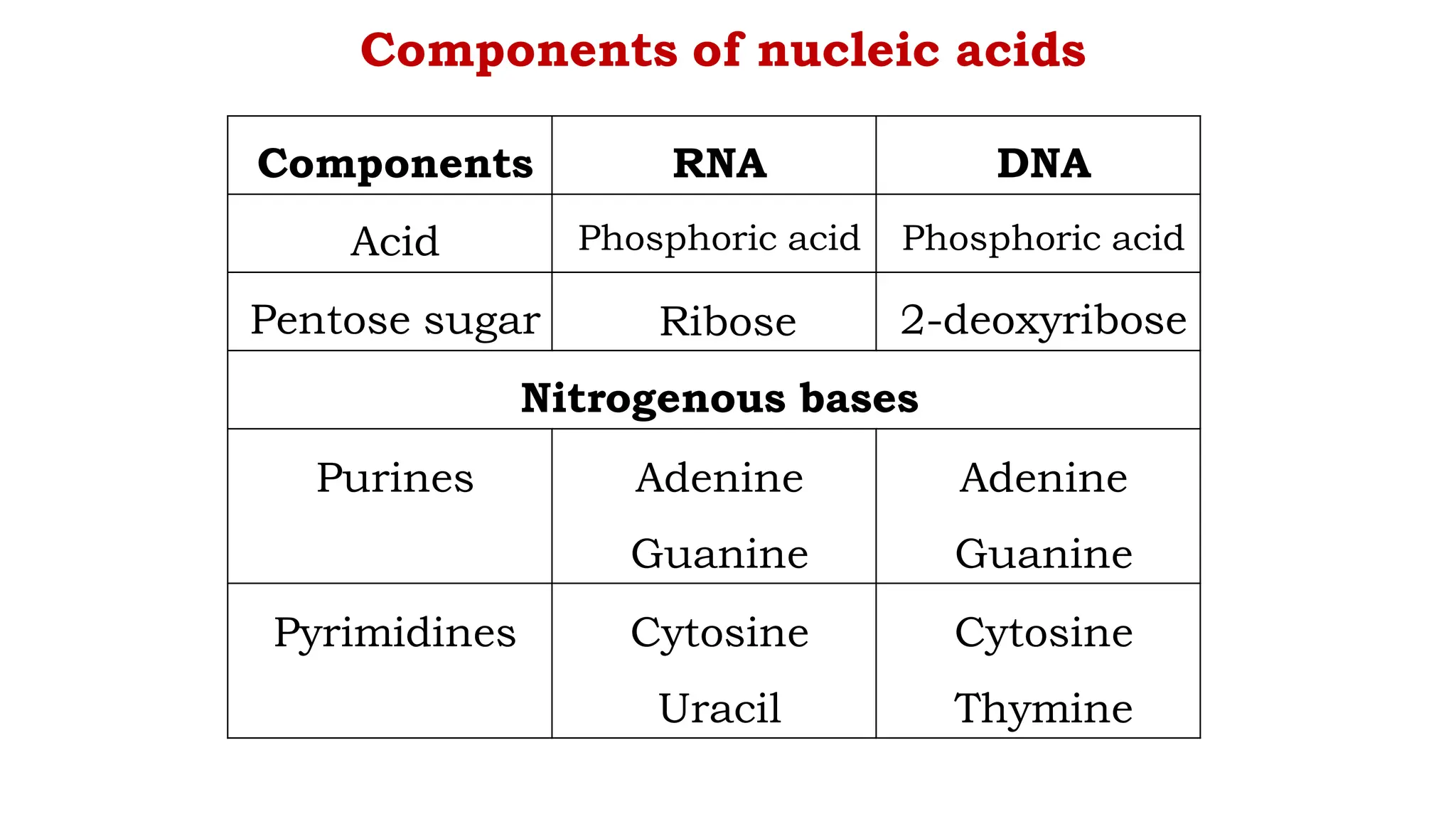
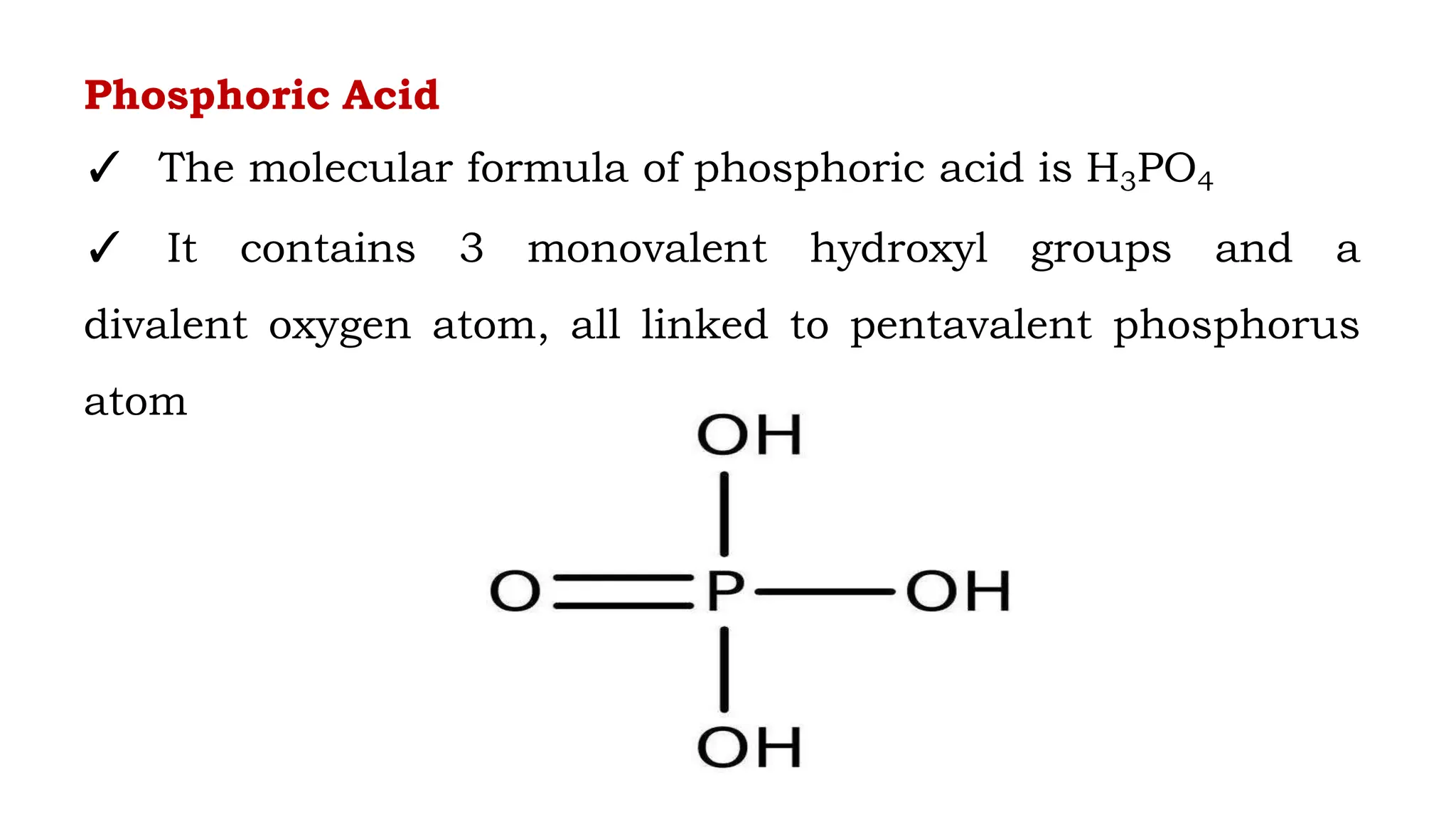
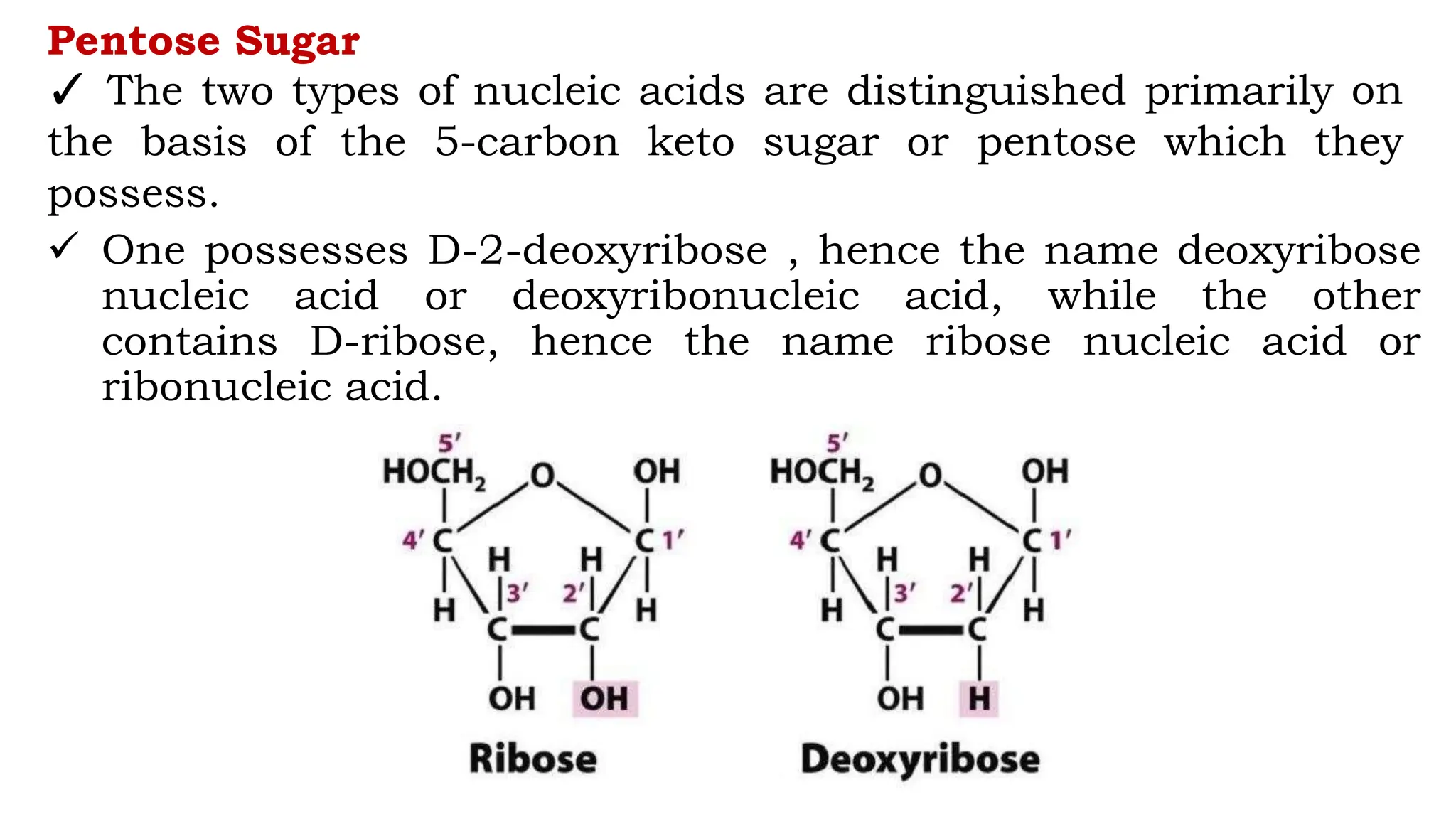
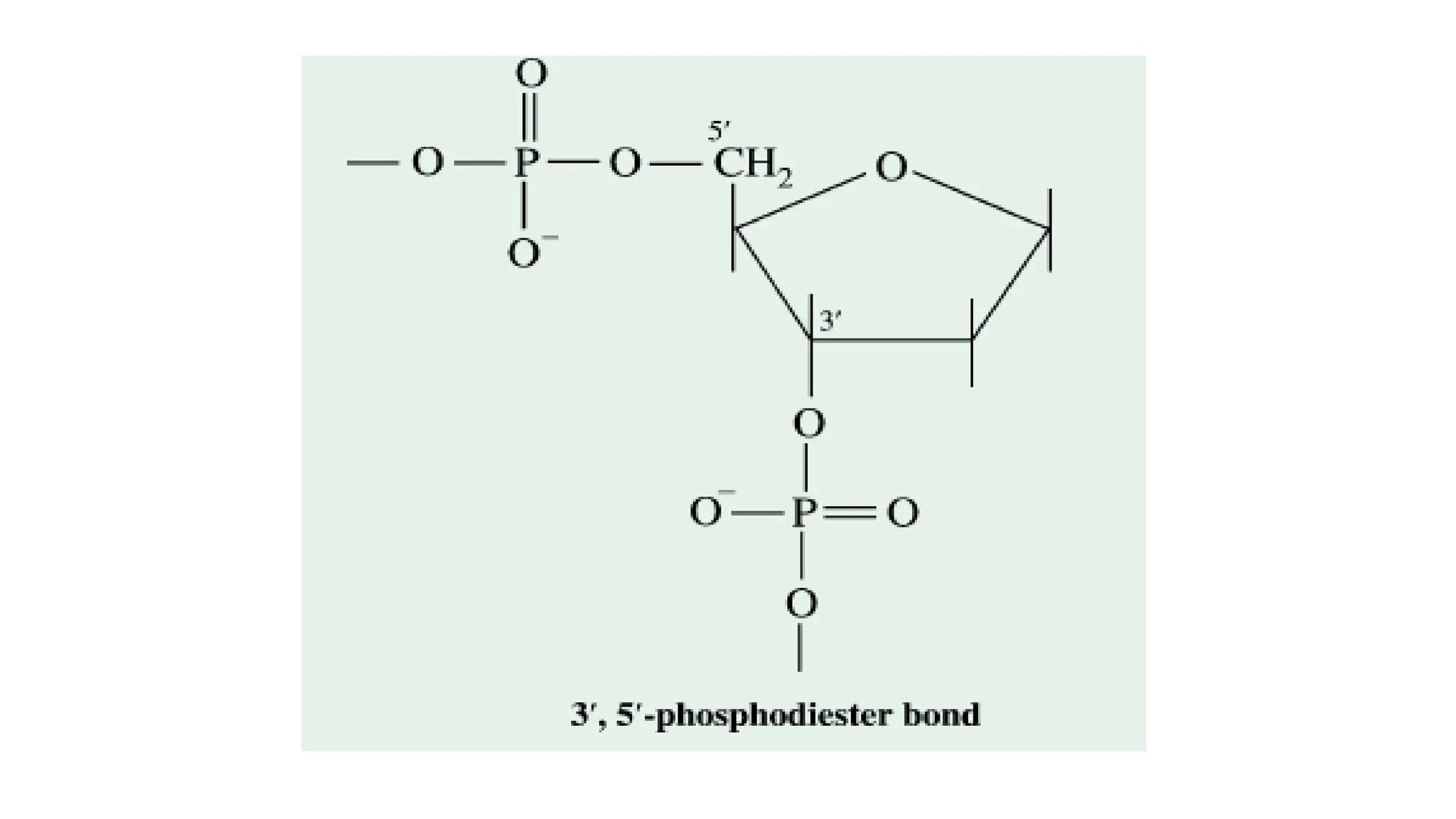
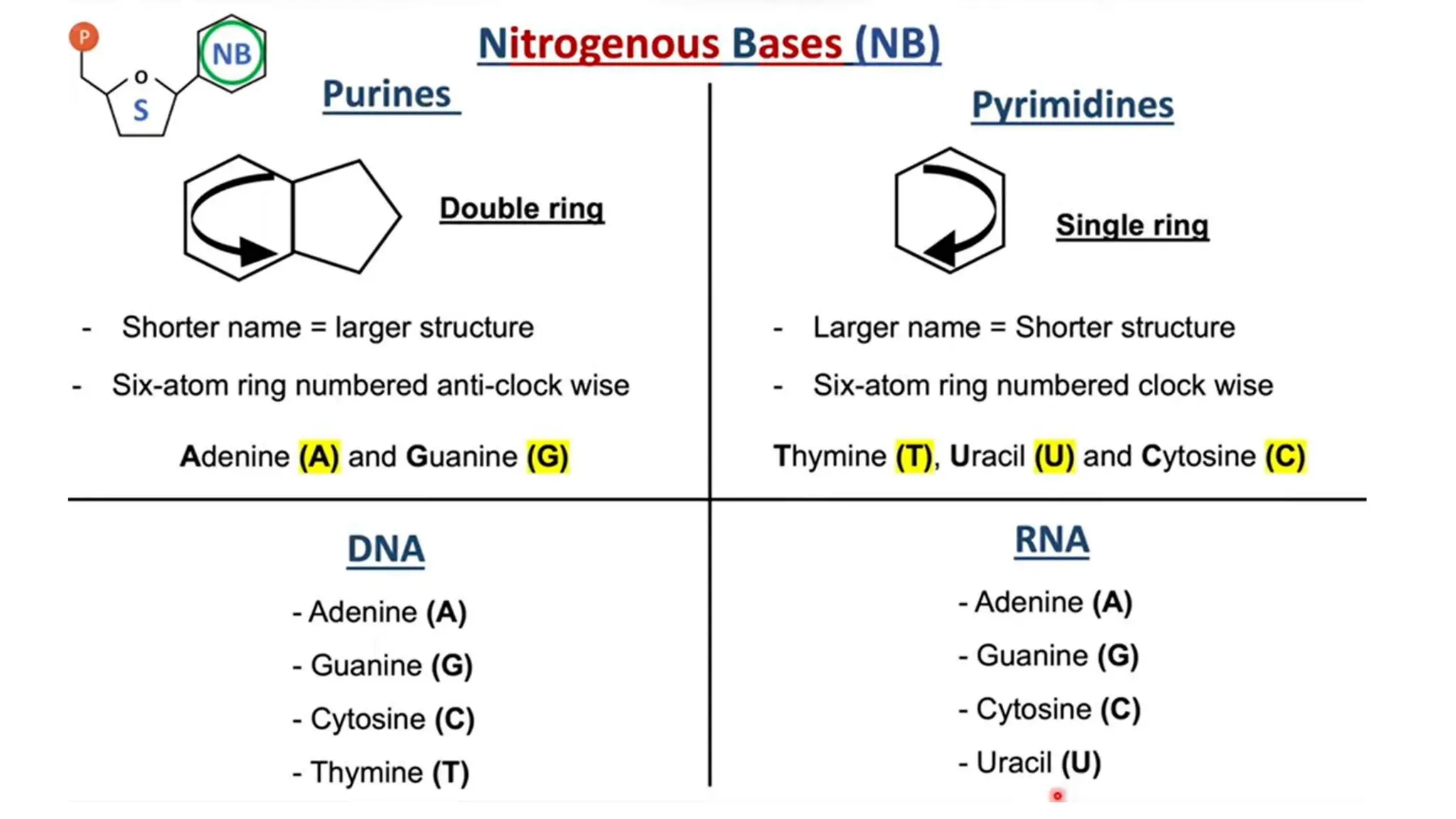
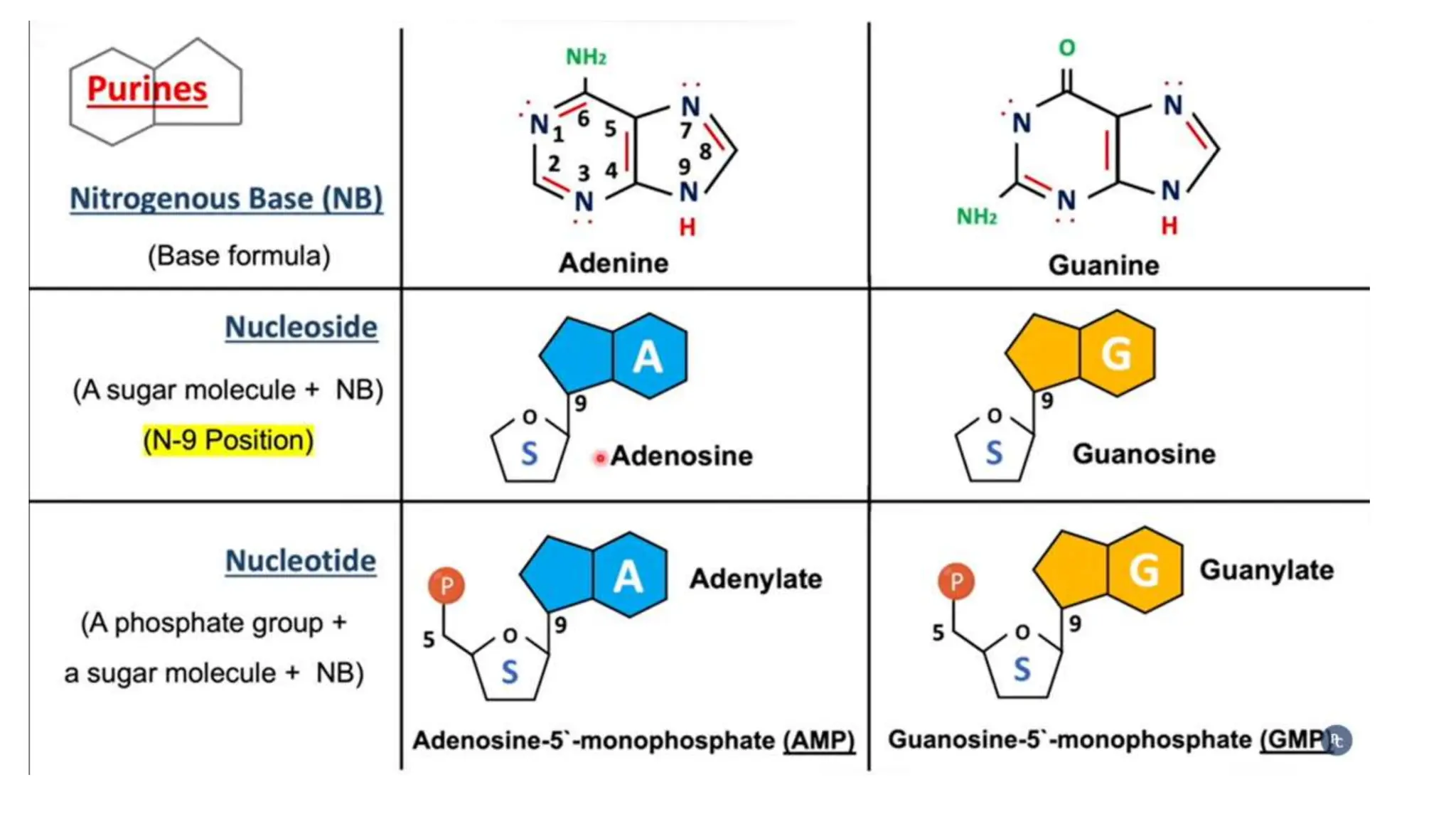
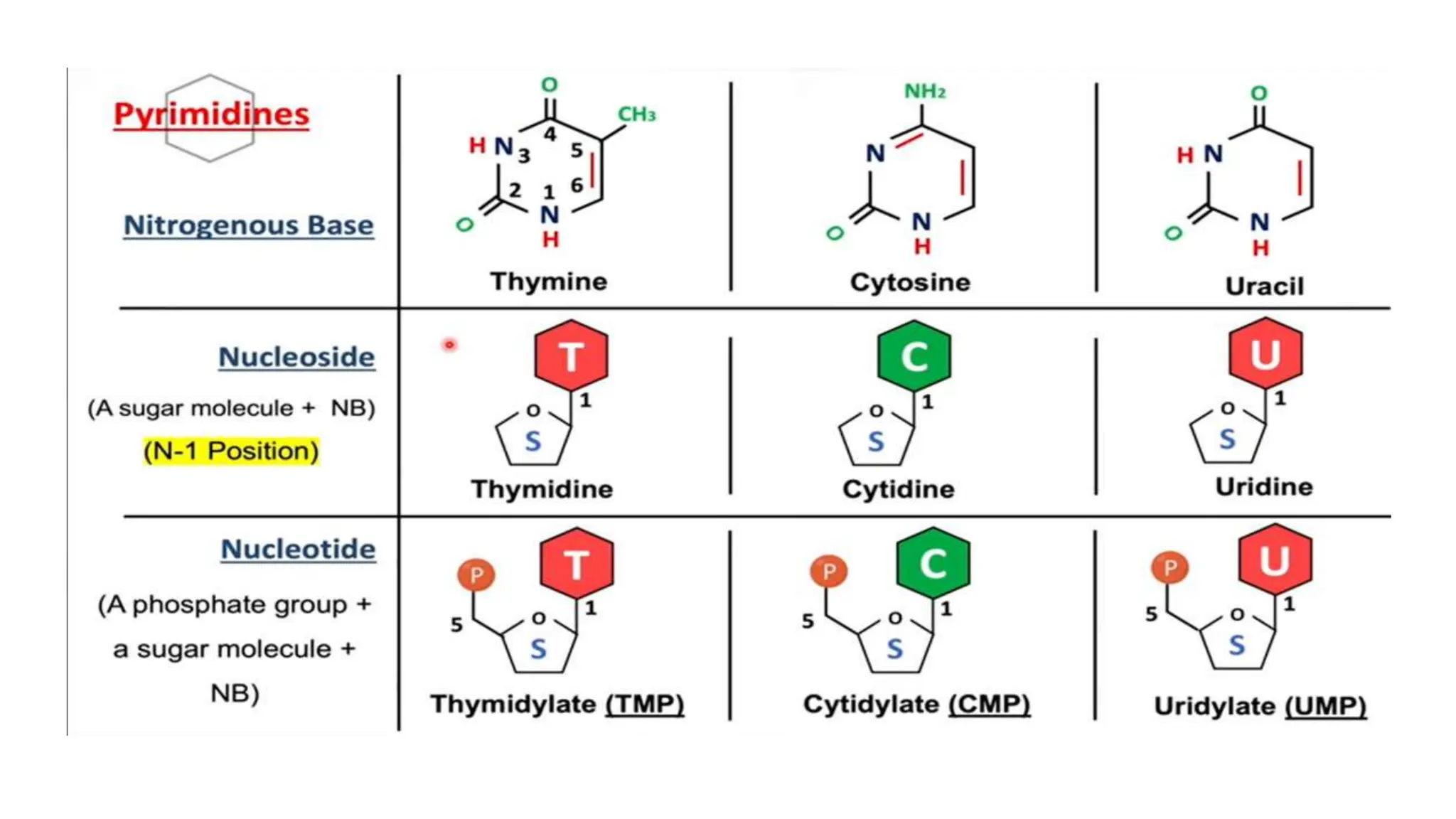
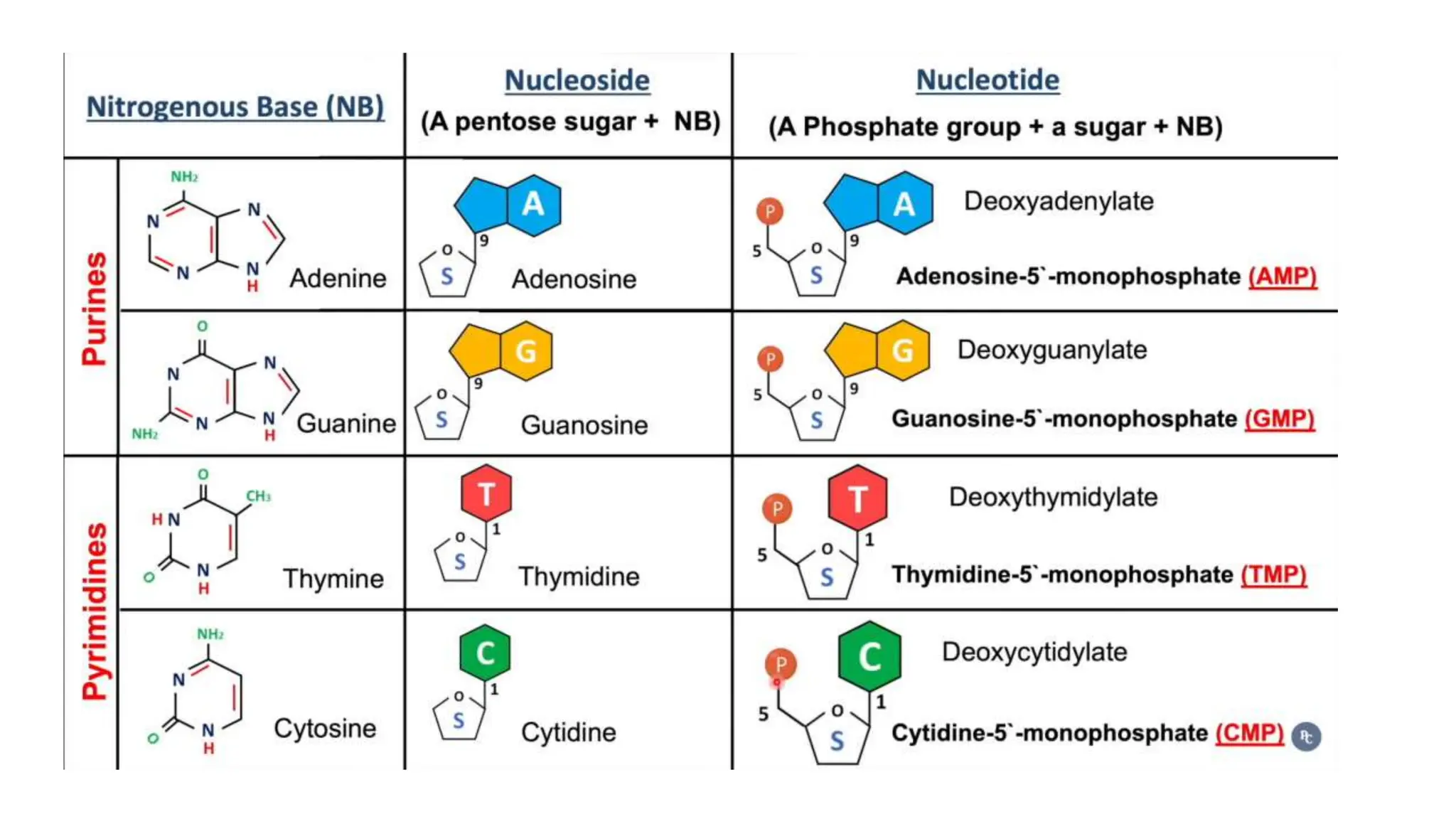
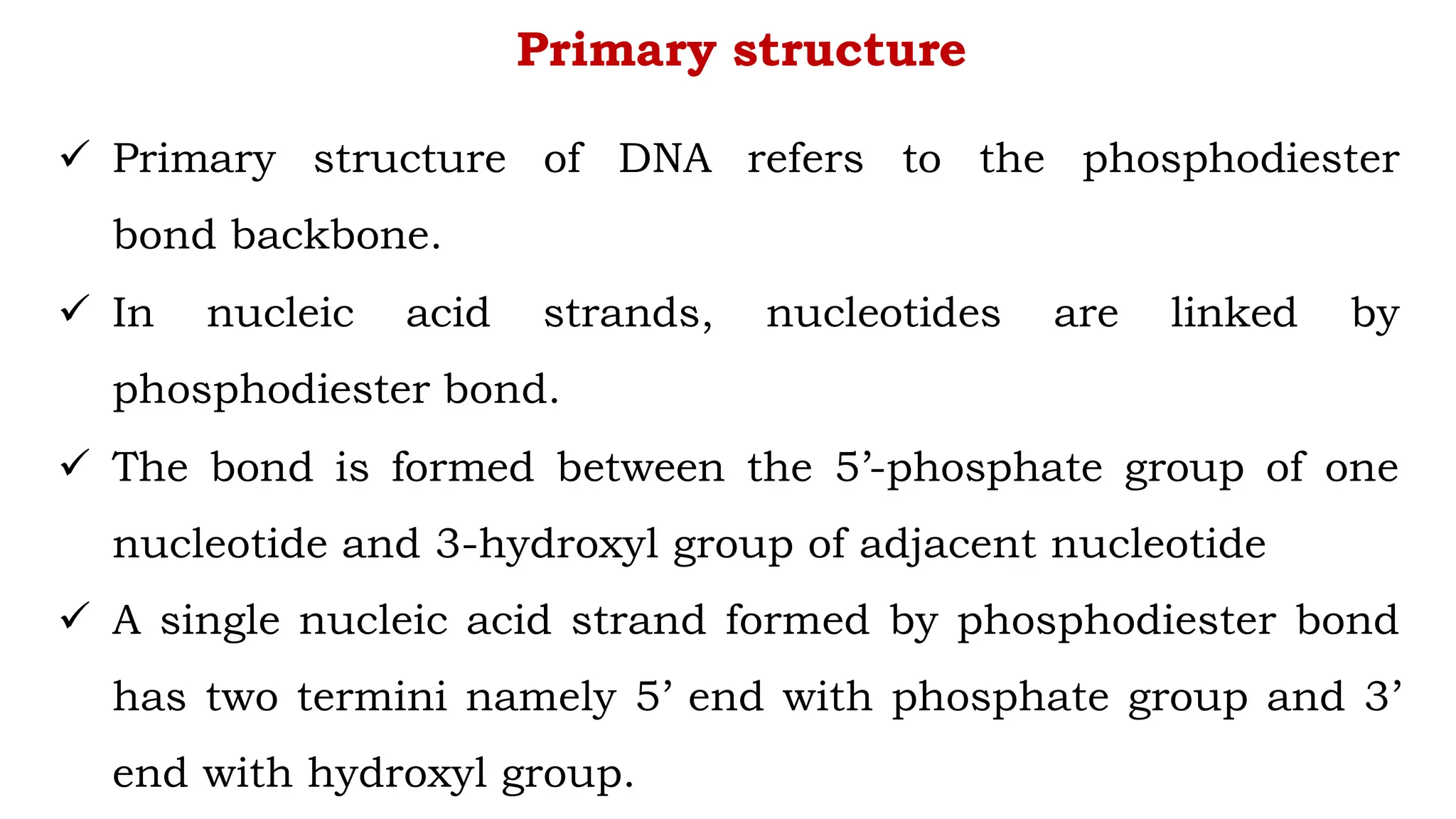
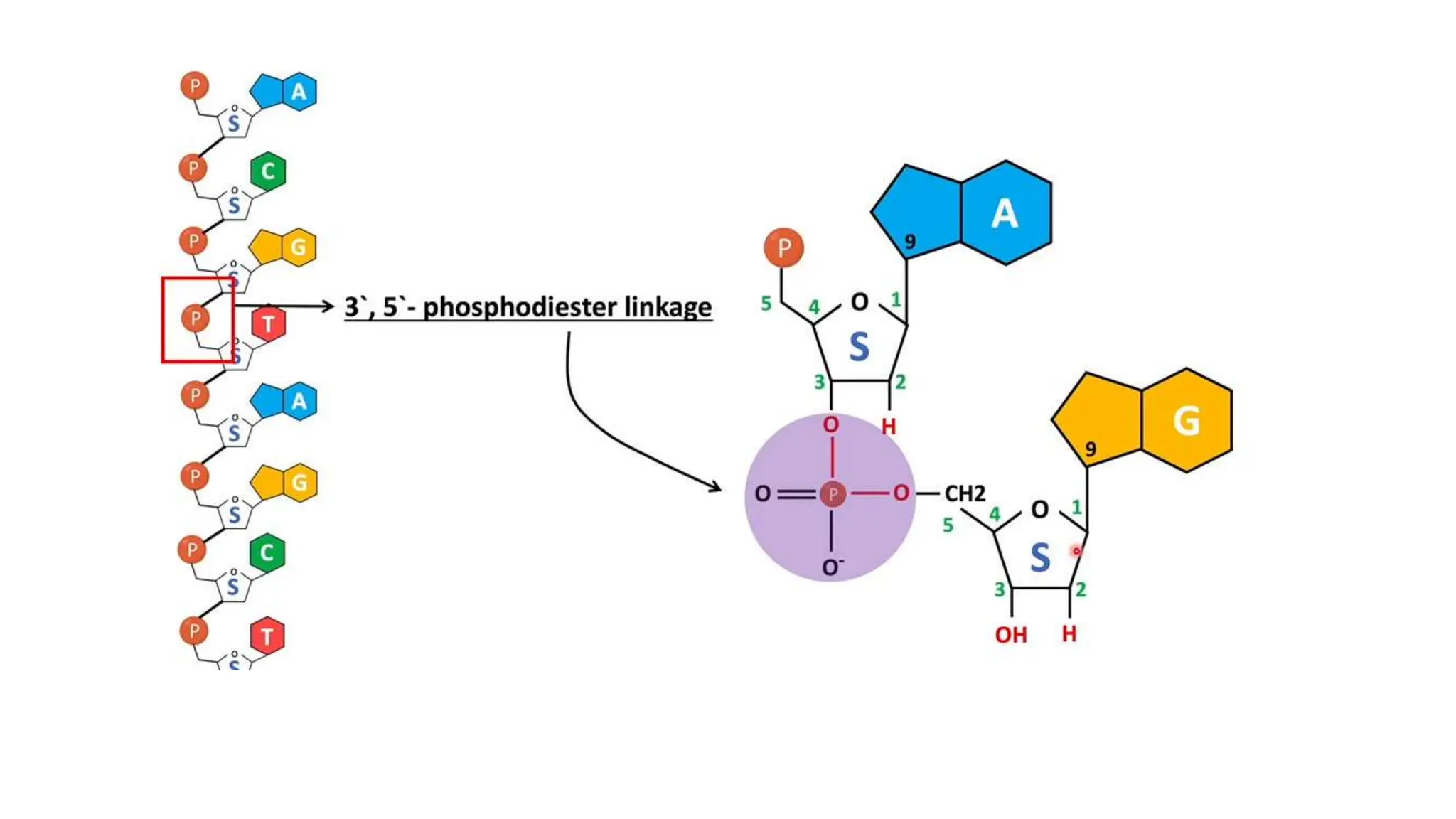
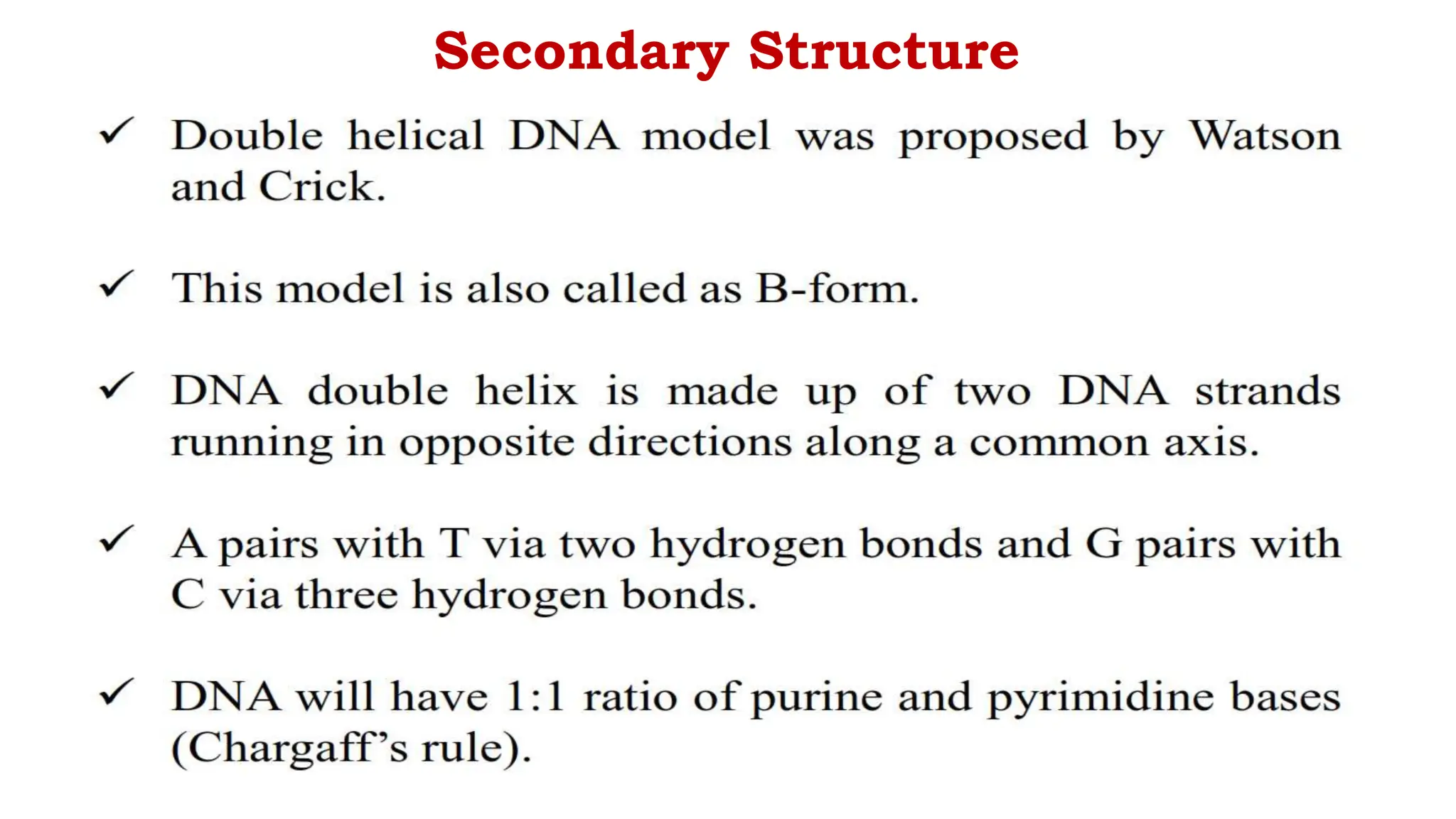
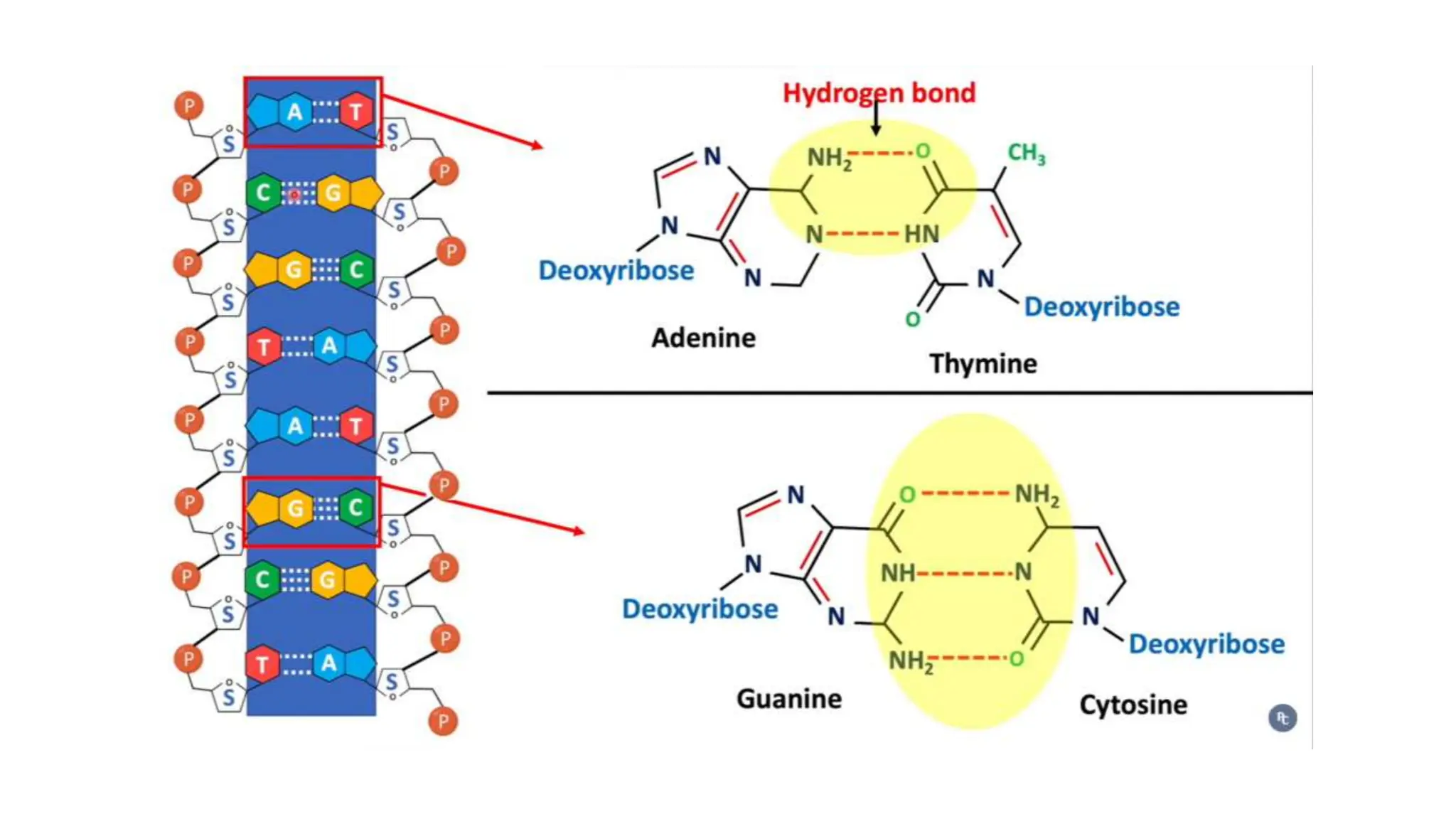
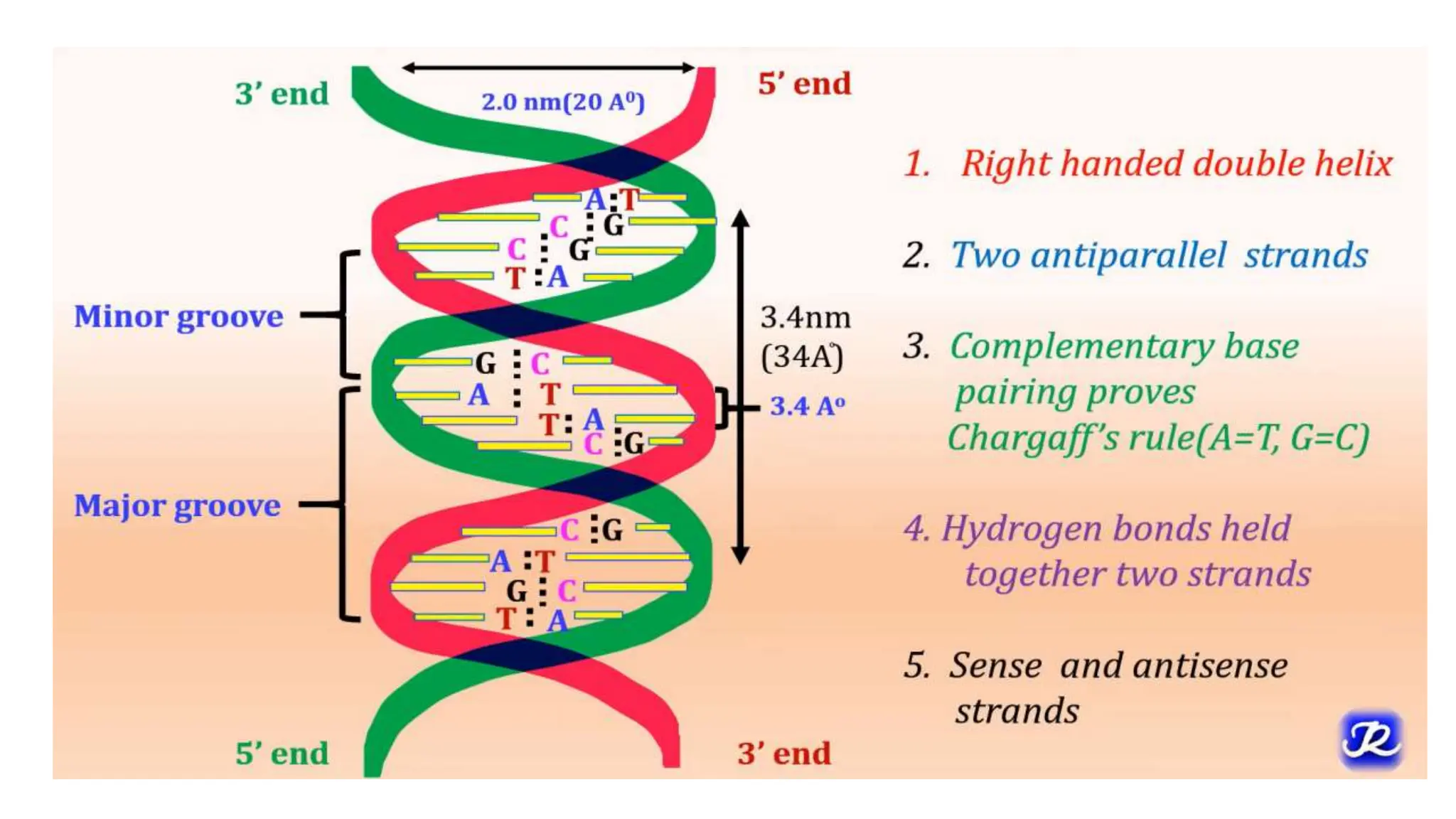
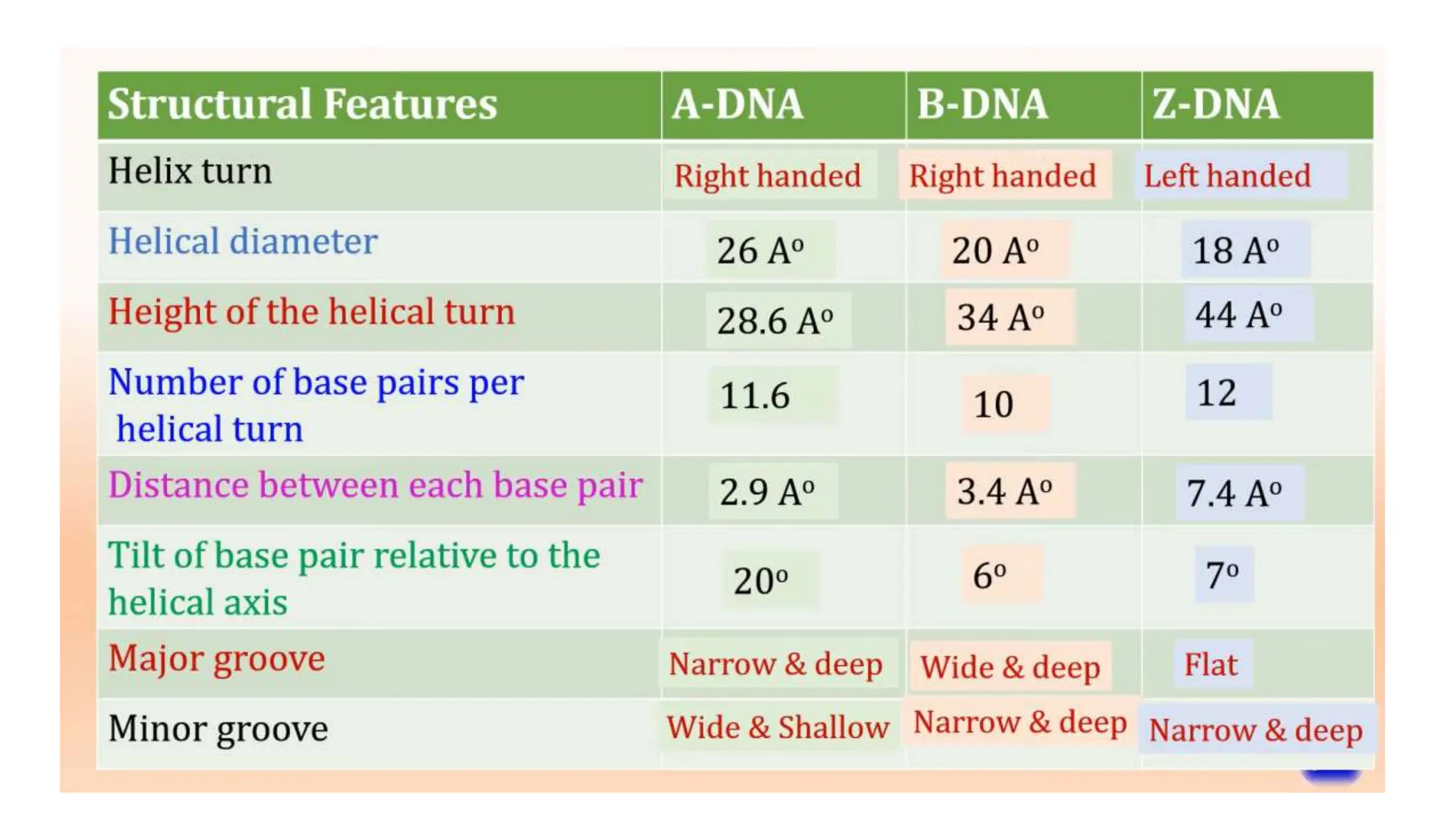
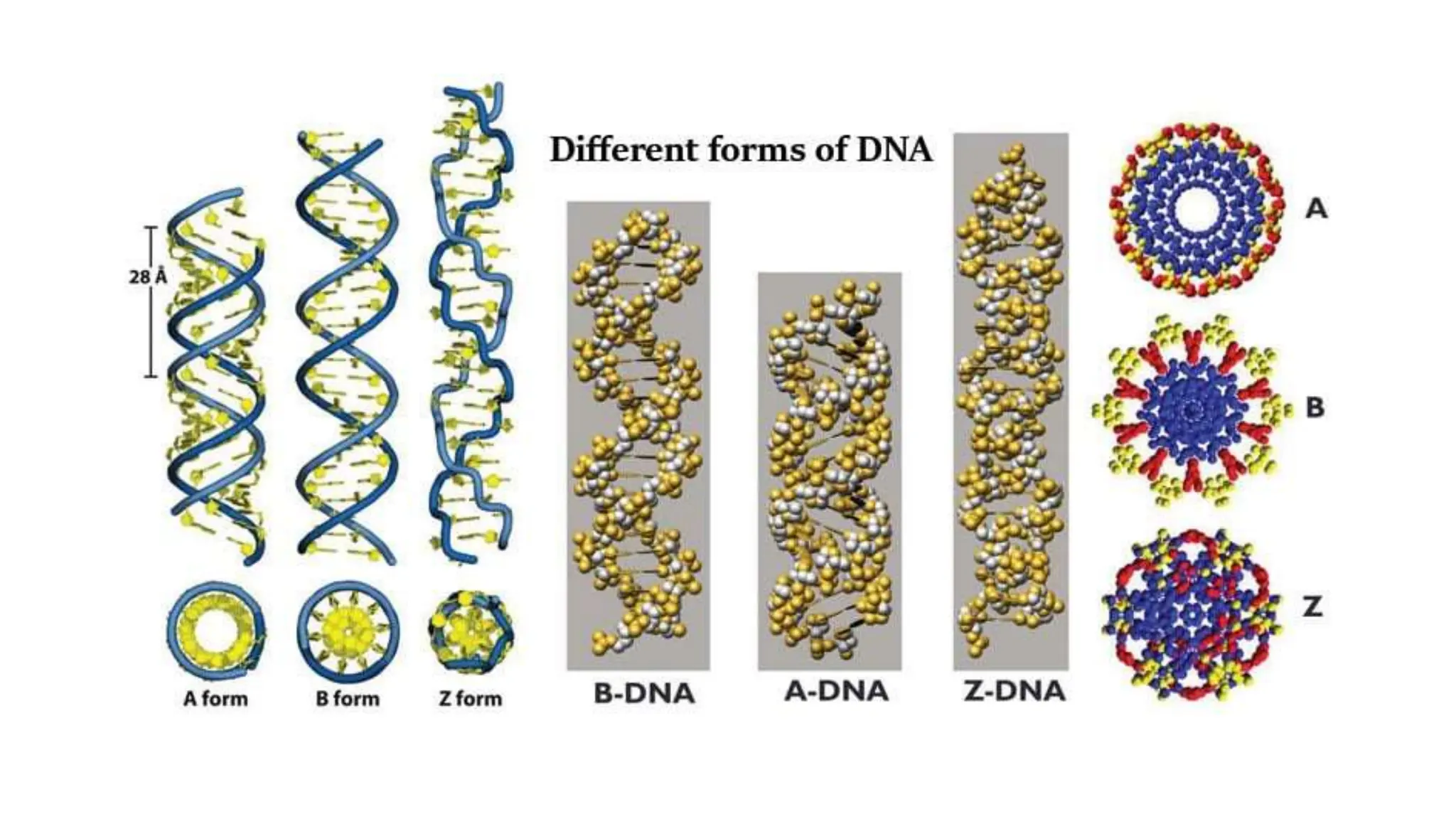
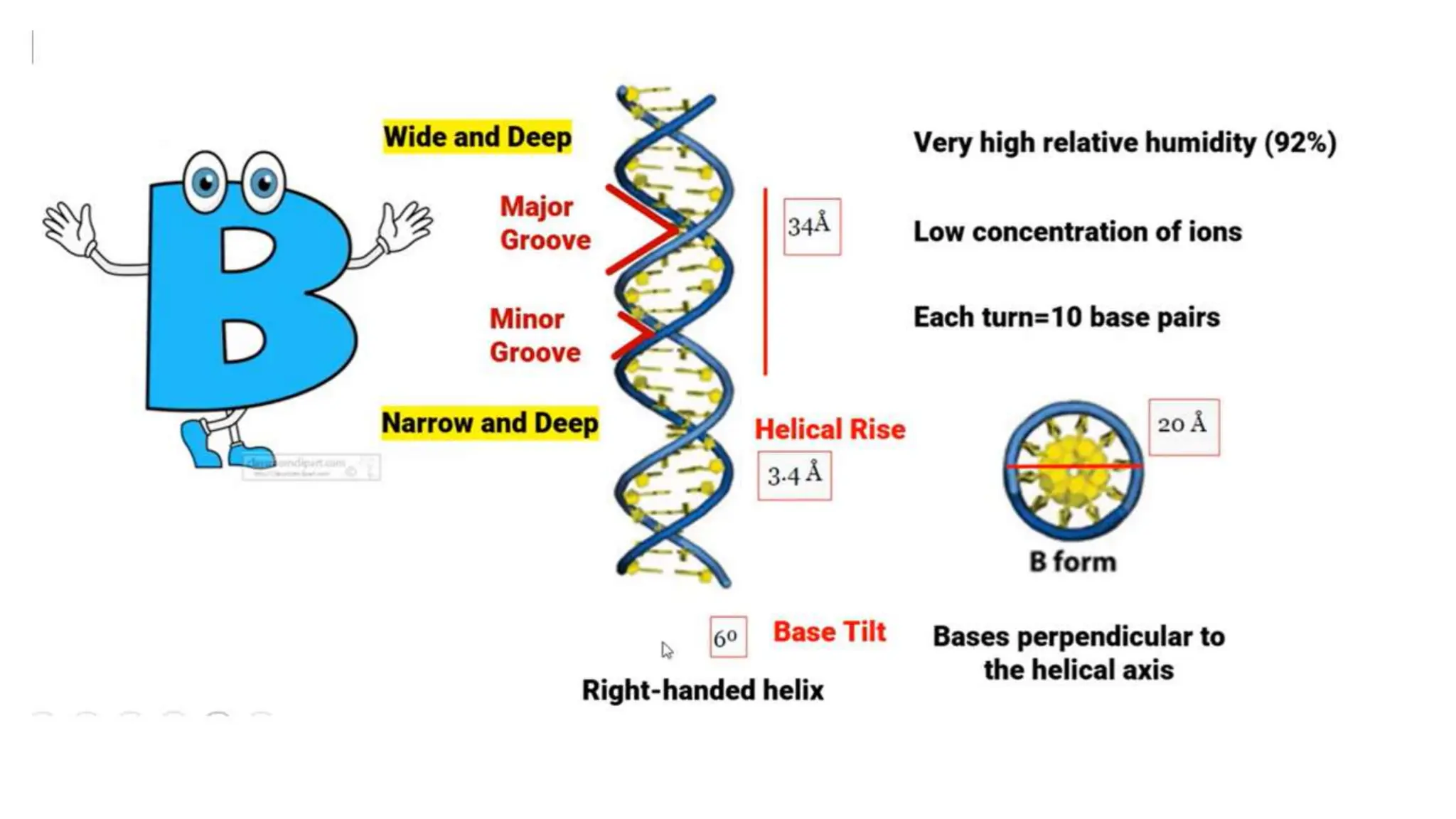
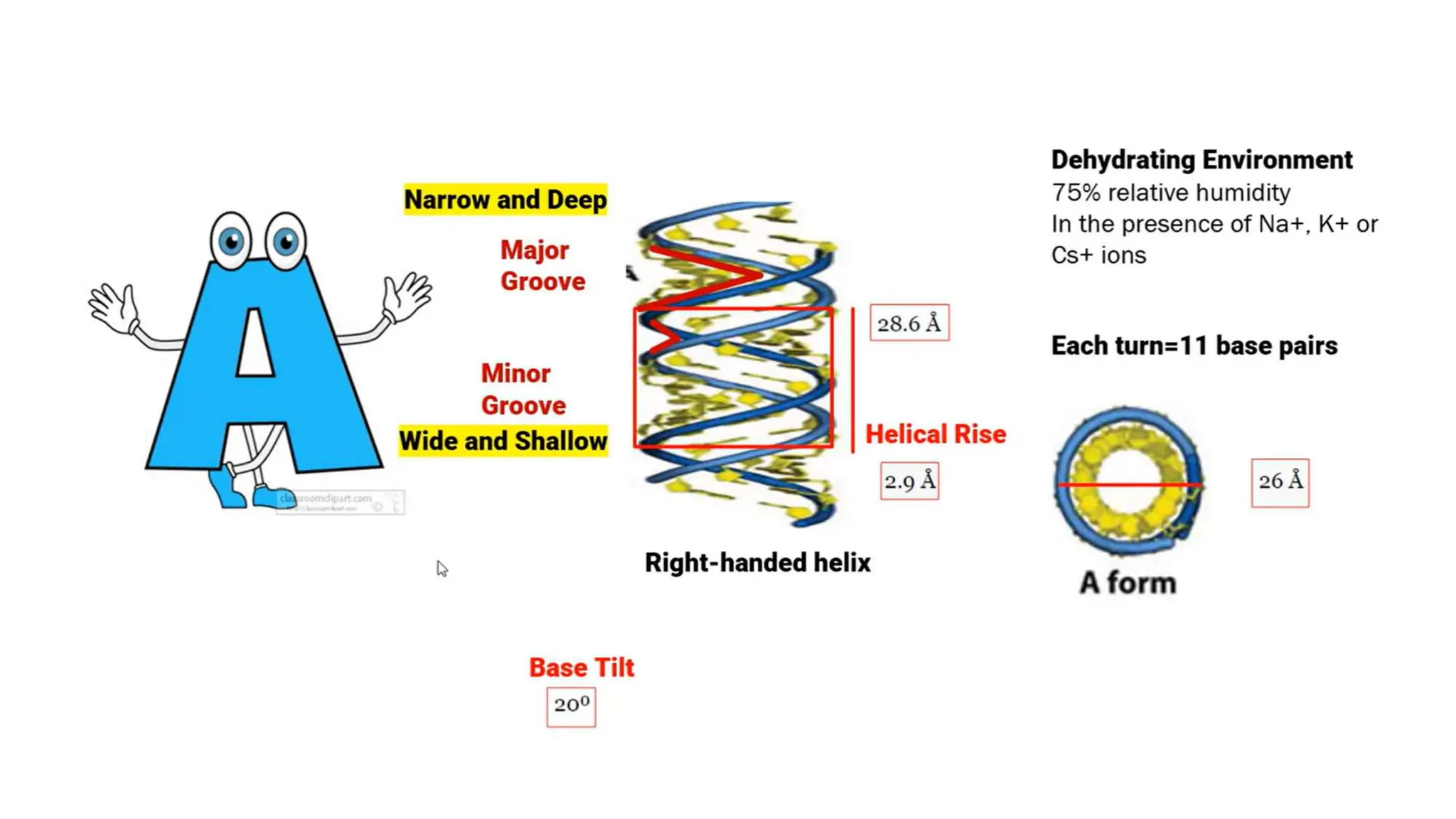
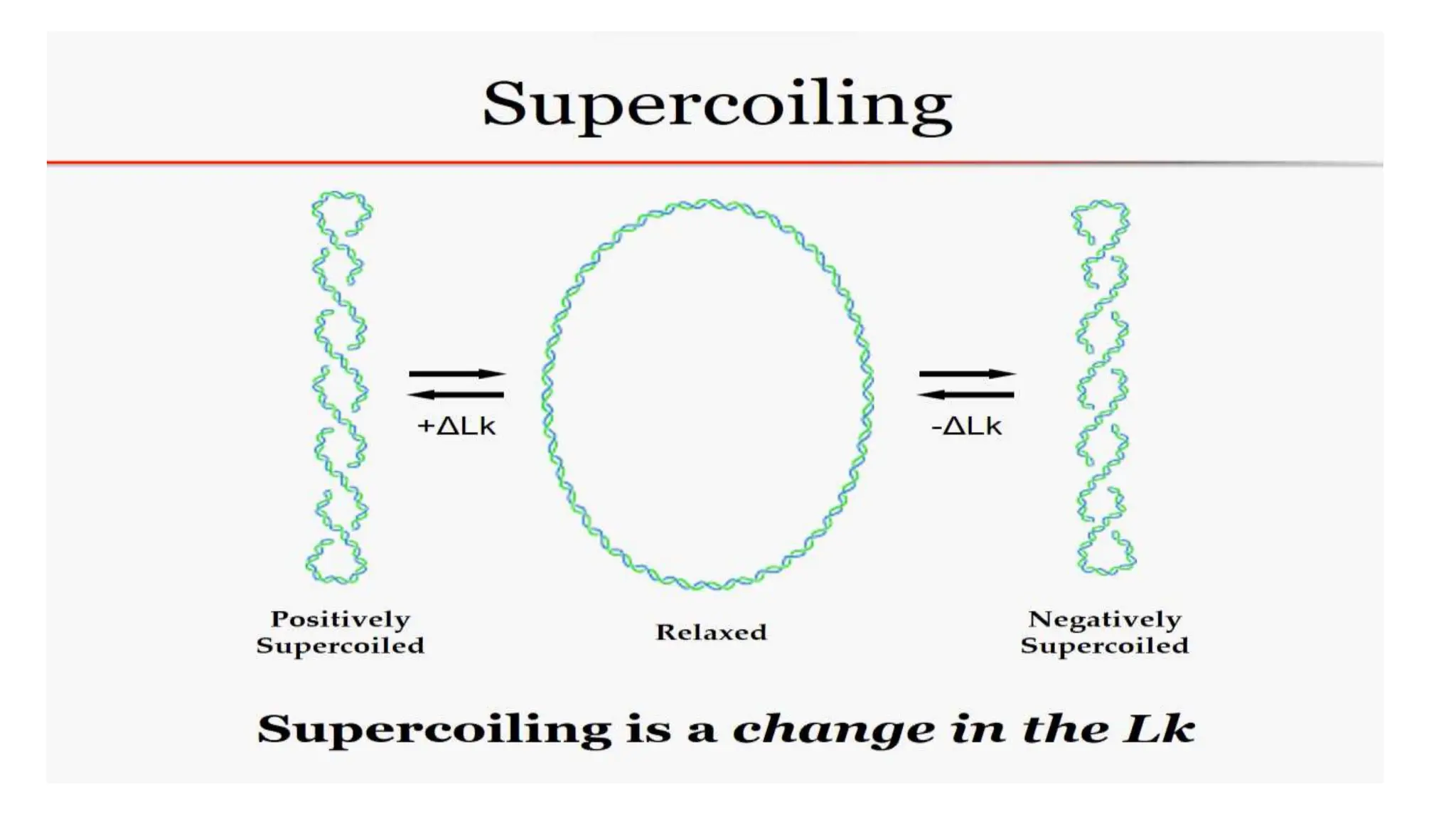
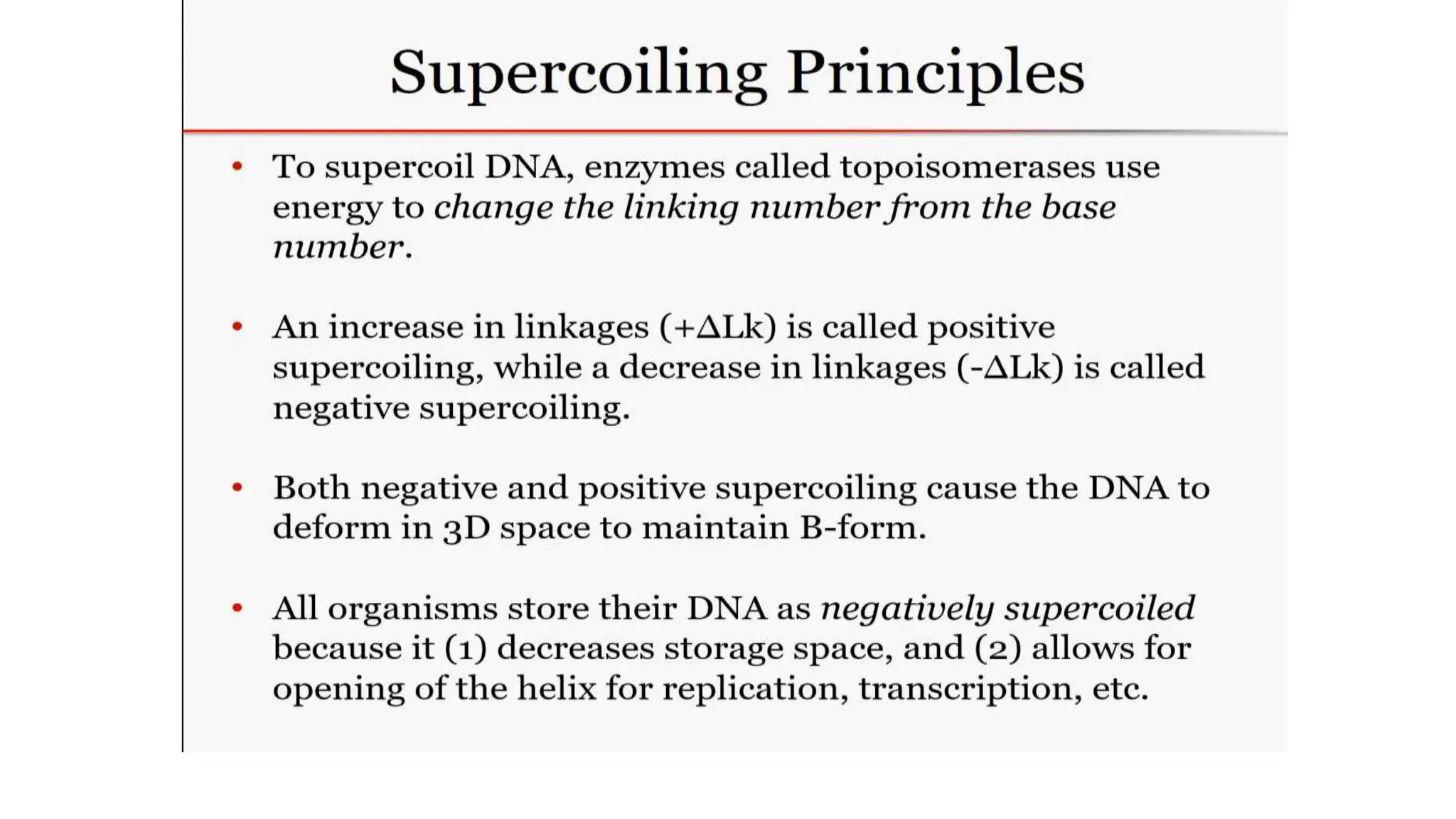
DNA is composed of nucleotides containing phosphoric acid, a pentose sugar (deoxyribose), and one of four nitrogenous bases. The nucleotides are linked by phosphodiester bonds between the 5' phosphate of one nucleotide and the 3' hydroxyl of the next, forming the primary structure of DNA. The primary structure twists into the familiar double helix tertiary structure, with the bases pairing between the strands and the sugar-phosphate backbones coiling around the outside. This regular double helix contains a major and minor groove that help proteins recognize and bind to DNA.