This document discusses the structure and history of discovery of DNA. It provides details on:
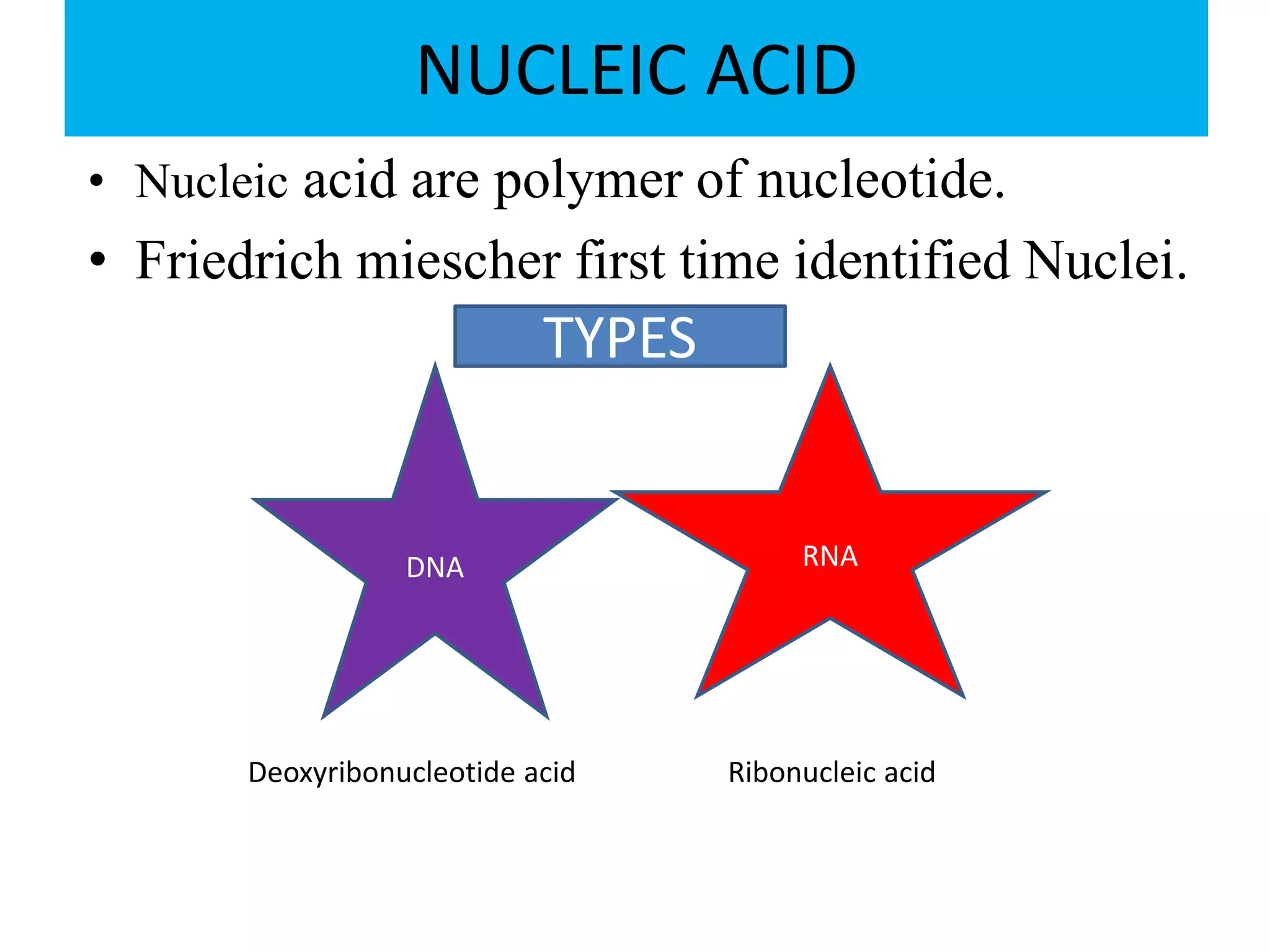
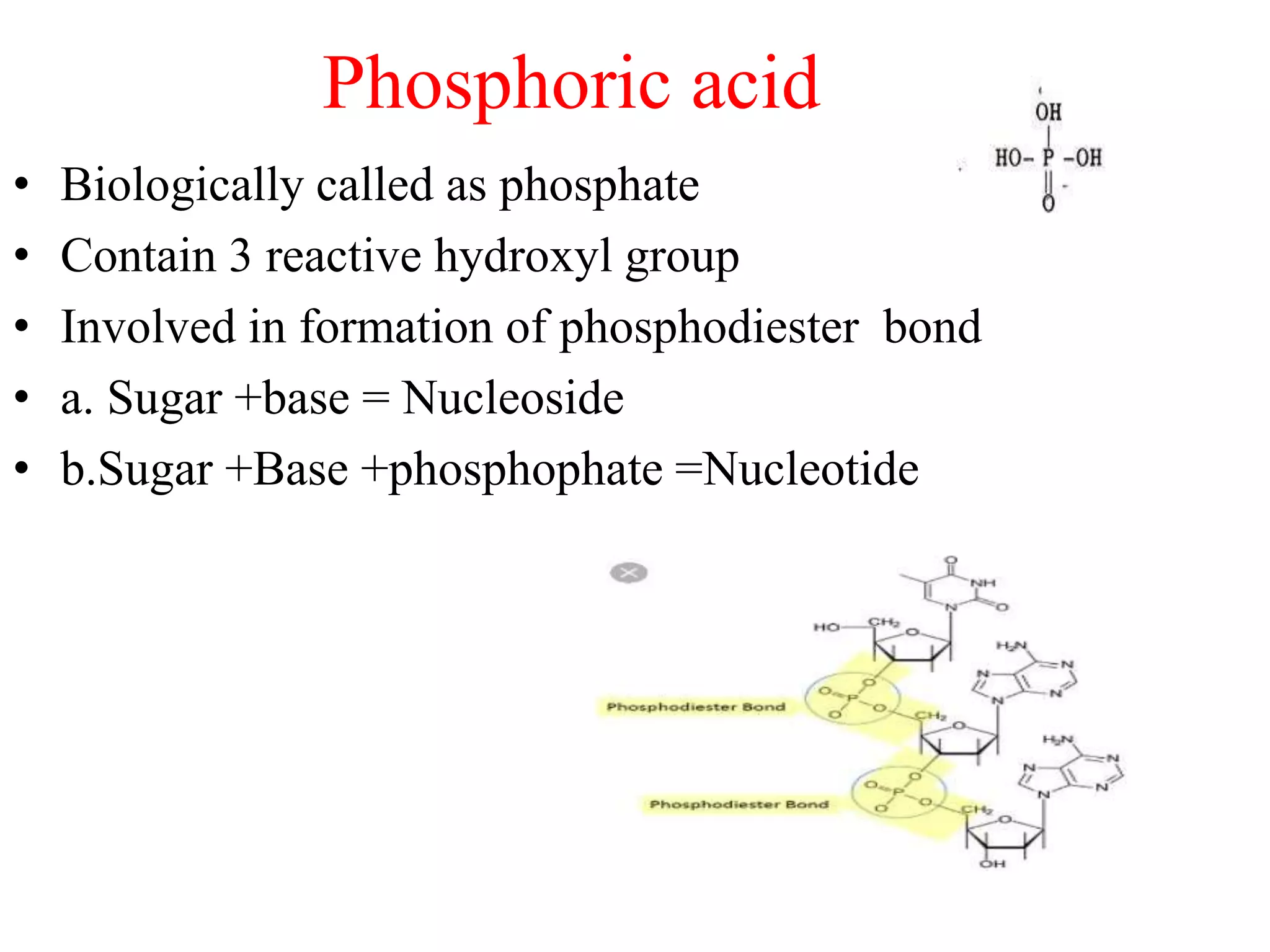
1) Nucleic acids being polymers of nucleotides composed of nitrogenous bases, sugars, and phosphates. Friedrich Miescher first identified nuclei.
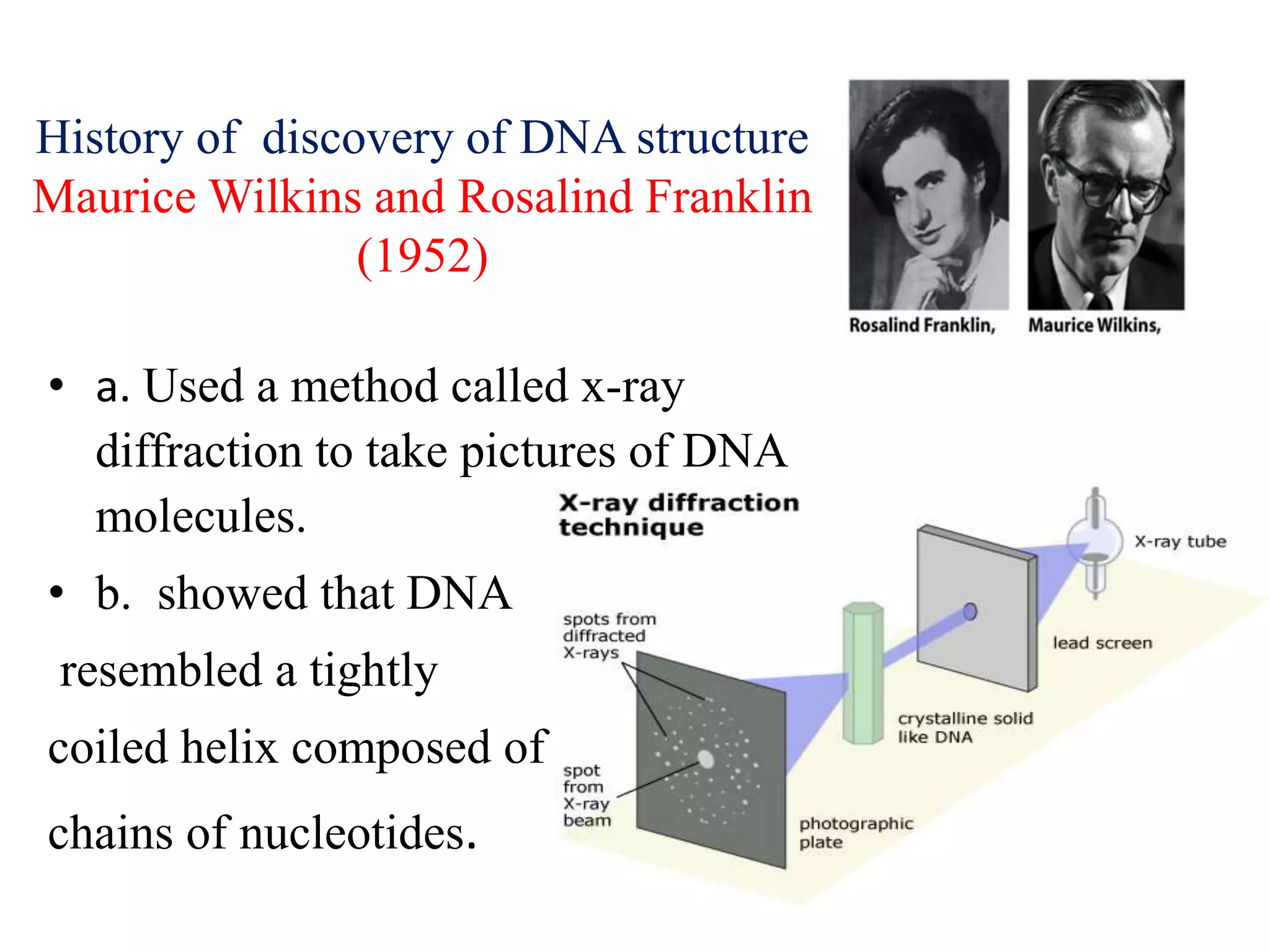
2) Watson and Crick proposing the double helix structure of DNA in 1953 based on prior work by Chargaff, Wilkins, Franklin showing DNA resembles a coiled helix.
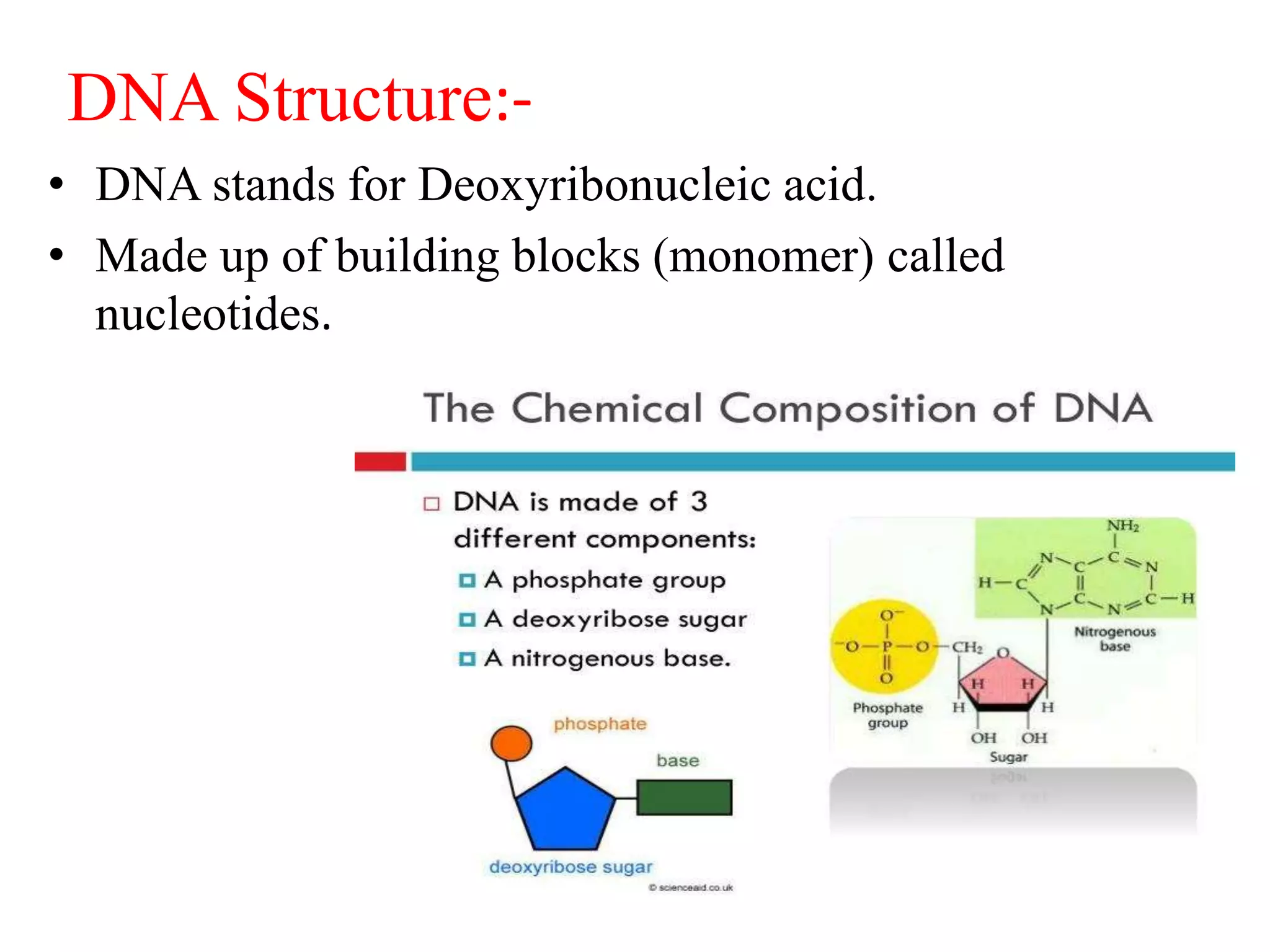
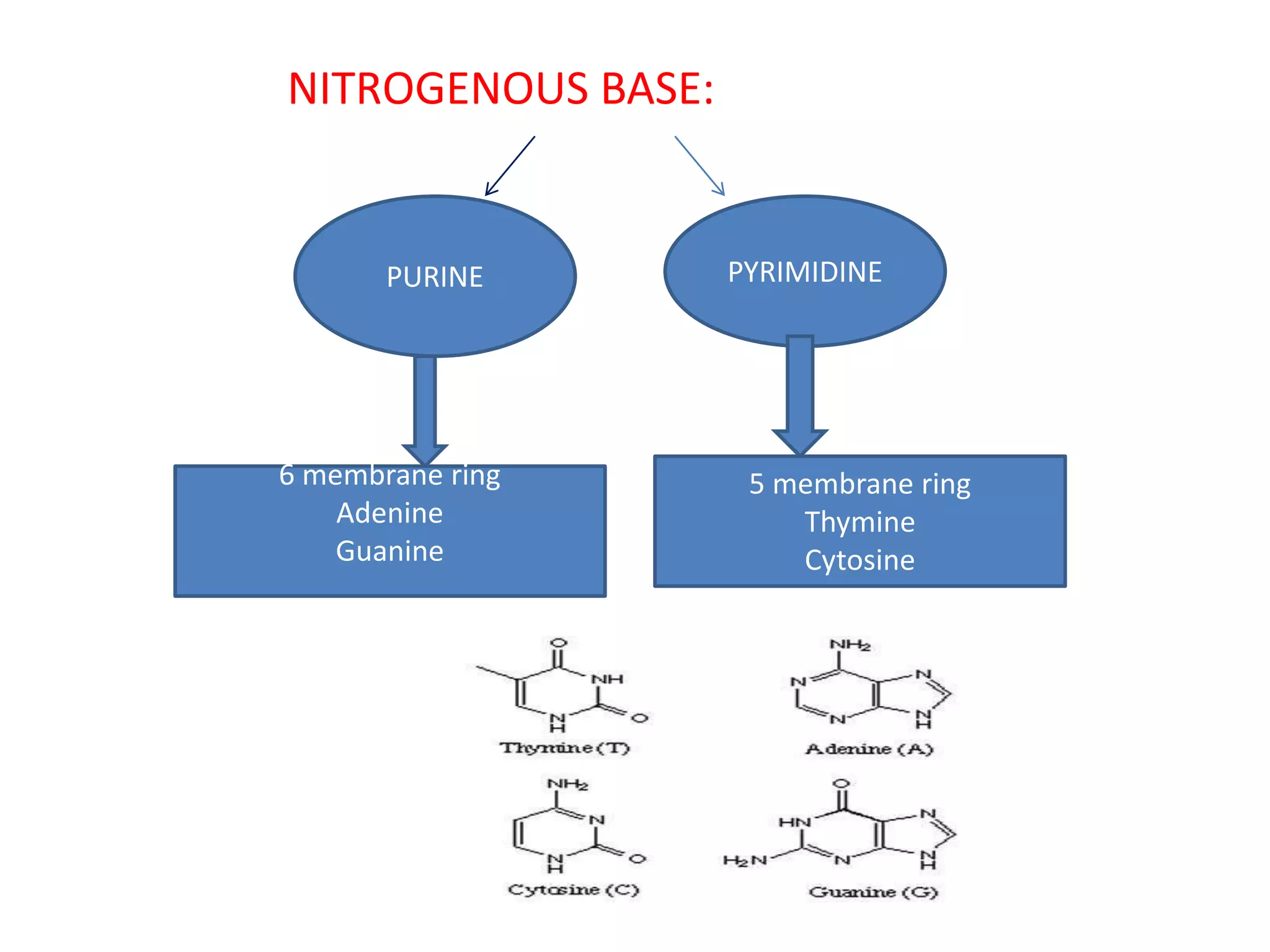
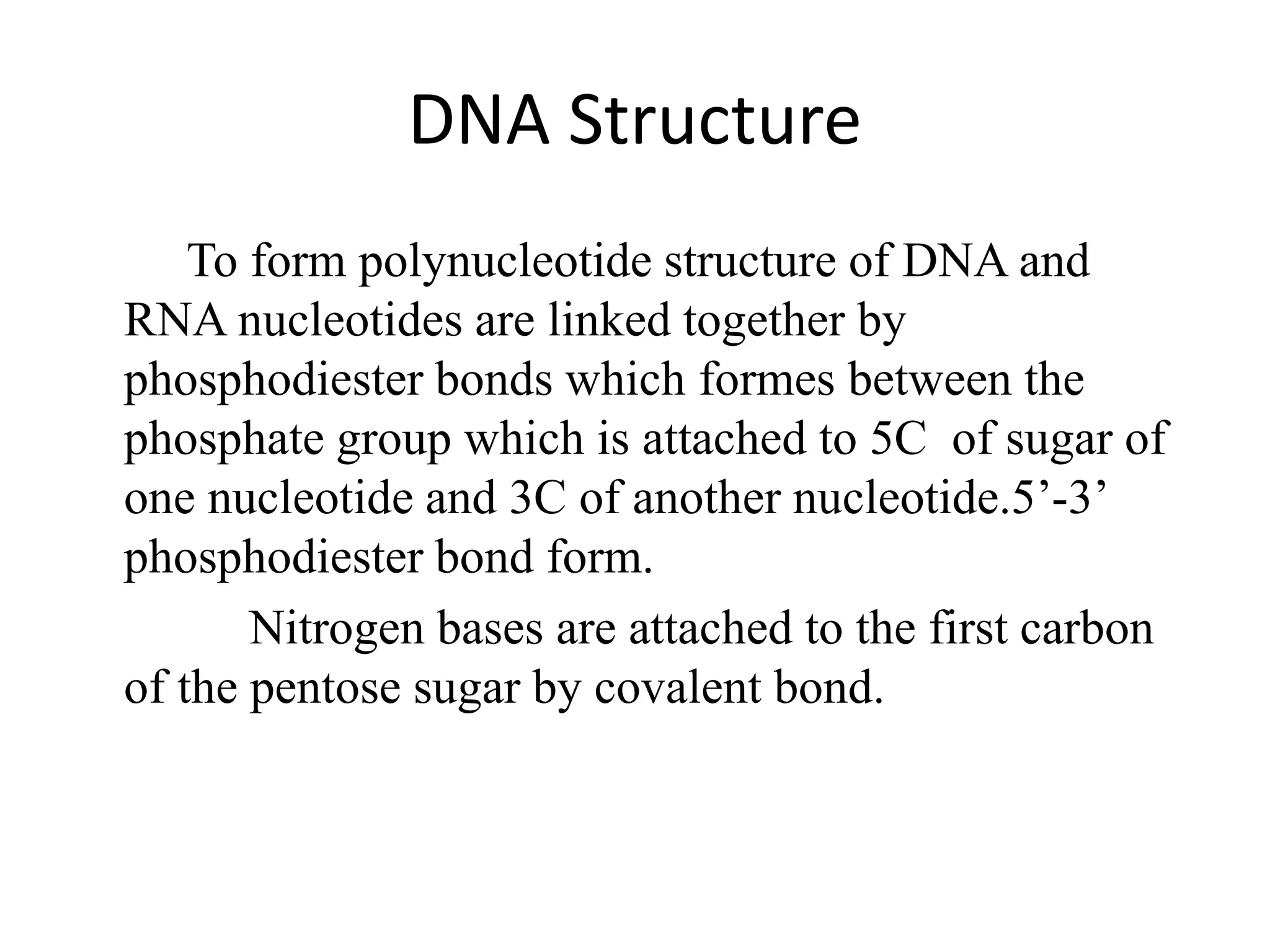
3) DNA being composed of nucleotides containing a sugar (deoxyribose), phosphate group, and nitrogenous base that form the double helix structure through base pairing between adenine-thymine and guanine-cytosine.






![Diameter of helix 20⁰A
• One strand oriented in 5’ to3’D and another
strand is oriented in 3’ to 5’D.
• 10 base pair present in per turn.
• The interaction between base and sugar form
grooves . Major groove [large angle between
base and sugar] and Minor groove [naarow
angle between base and sugar]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnastructure-200229163704/75/Dna-structure-13-2048.jpg)
![Different types of DNA
Parameter A-DNA B-DNA Z-DNA
Helix sense
right-
handed
right-
handed
left-
handed
Residues per turn 11 10.5 12
Helix pitch(°) 28 34 45
Base pair tilt(°) 20 6 7
Rotation per residue (°) 33 36 30
Diameter of helix [Å] 23 20 18
Glycosidic Bond configration
anti anti
syn](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dnastructure-200229163704/75/Dna-structure-14-2048.jpg)
