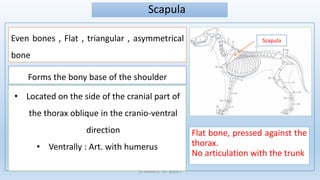
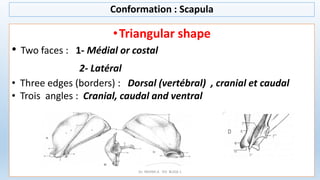
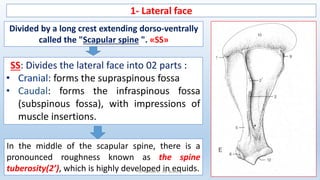
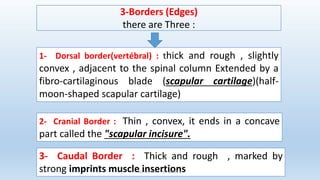
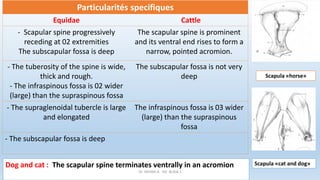
The document outlines the anatomy and conformation of the thoracic limb skeleton, particularly focusing on the scapula. It describes the scapula's structure, its various parts and angles, and how they contribute to adaptations in locomotion. Specific differences in scapula features among equids and cattle are also highlighted.