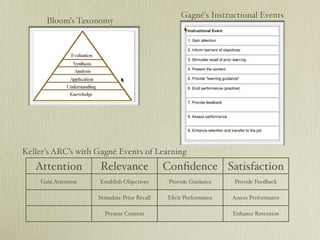
The document discusses learning through games and game genres. It covers key concepts in instructional design like cognitivist and constructivist views, Gagne's instructional events, and Keller's ARCS model. The document also discusses different game genres like action, fighting, driving/flying games. It provides criteria for designing engaging learning experiences through games, like thematic coherence, clear goals, balanced challenges, and direct manipulation. The document recommends sample games for learning in subjects like algebra, vocabulary, biology and more.