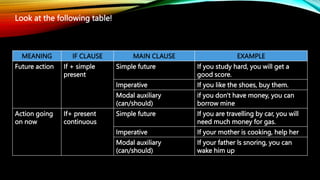
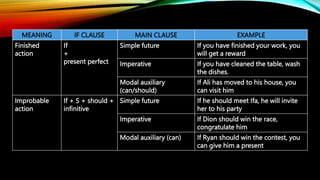
This document discusses the use of if-clauses with imperative verbs, can, and should. It explains that while first conditional clauses typically use the simple present or future tense, imperative verbs or modal auxiliaries like can and should can also be used to give commands or suggestions. Specifically, can is used to suggest future ability or make a recommendation, and should is used to suggest or advise about an outcome. Examples are provided to illustrate using imperatives, can, and should in if-clauses to give commands or indicate likelihood.