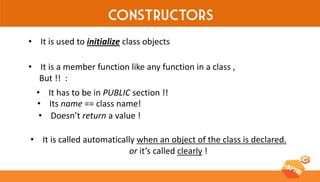
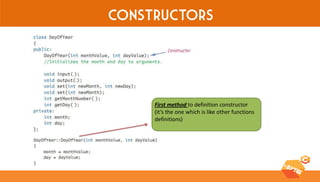
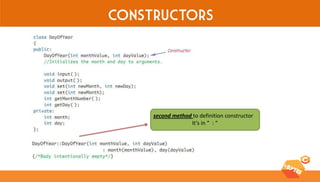
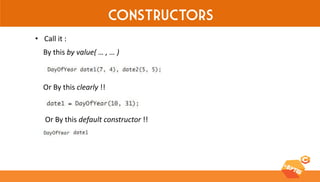
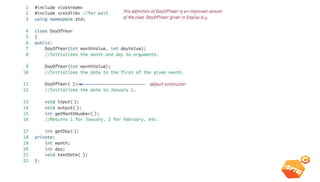
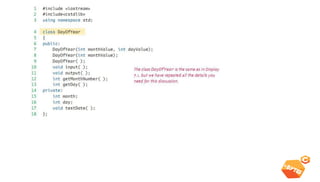
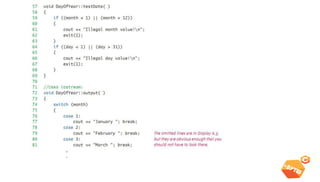
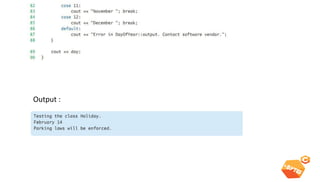
This document discusses various C++ concepts like constructors, static members, nested and local classes, and vectors. Constructors initialize class objects and have the same name as the class. Static members are initialized once outside the class. Nested classes can be public or private, while local classes are defined within a function. Vectors are like dynamic arrays that initialize elements using default constructors and add elements with push_back().



































![Vectors
•The member function push_back adds an element in the next available position.(back of vector)
•Changing value : v[i] = 42;
• size() to determine how many elements are in a vector.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2bytesccourse2014c6constructorsandothertools-141107073251-conversion-gate01/85/2-BytesC-course_2014_c6_-constructors-and-other-tools-48-320.jpg)



