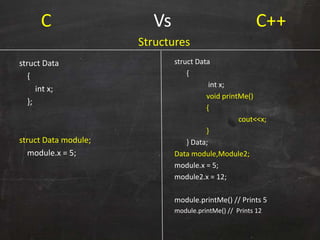
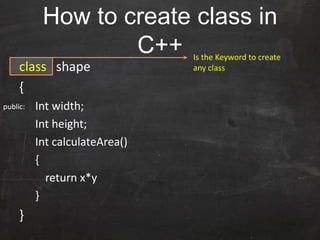
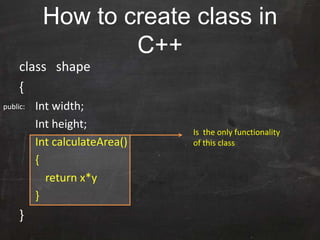
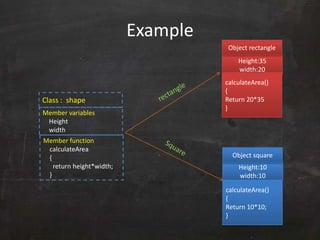
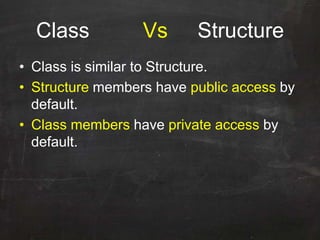
C++ was originally developed as an extension of C to add object-oriented capabilities. While C++ retains much of C's syntax and functionality, it introduces important new concepts like classes, objects, and inheritance. A class defines the common properties and behaviors (methods) that objects of that class will have. Objects are instances of classes that allocate memory at runtime. This allows C++ to support object-oriented programming by encapsulating data into objects that can receive messages.





![C Vs C++
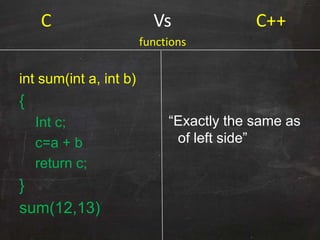
Int a[10];
Int b[] = {1000, 2, 3,
50}; “Exactly the same as
of left side”
Arrays](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoc-part-1-140329015202-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-c-part-1-9-320.jpg)

![C Vs C++
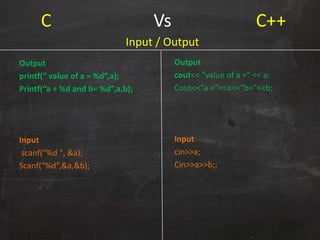
char str[10];
str = "Hello!"; //ERROR
char str1[11] = "Call
home!";
char str2[] = "Send
money!";
char str3[] = {'O', 'K',
'0'};
strcat(str1, str2);
string str;
str = "Hello";
string str1("Call
home!");
string str2 = "Send
money!";
string str3("OK");
str = str1 + str2;
str = otherString;
Strings](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/introductiontoc-part-1-140329015202-phpapp02/85/Introduction-to-c-part-1-12-320.jpg)