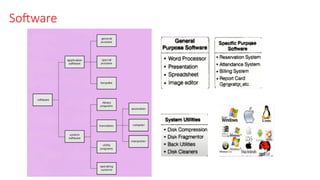
The document provides an overview of computer architecture, particularly focusing on bus structures, software types, and performance metrics. It discusses the significance of hardware and software in computers, including examples like operating systems and compilers, and emphasizes the importance of optimizing execution time to enhance performance. Additionally, it introduces concepts such as CPU execution time and benchmarking performance between different systems.