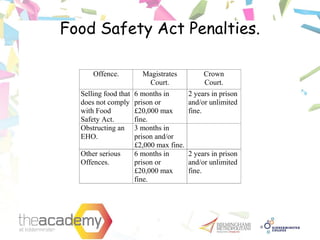
This document discusses the importance of maintaining personal health, hygiene, and cleanliness when working with food. It notes that good hygiene practices help reduce the risk of food contamination and food poisoning. The document then outlines regulations from the Food Safety Act of 1990 and the Food Safety (General Food Hygiene) Regulations of 1995 that require food handlers to engage in proper hygiene practices like regularly washing hands and wearing protective clothing. It also discusses the most common sources of food poisoning like bacteria found on skin and in the nose or mouth.