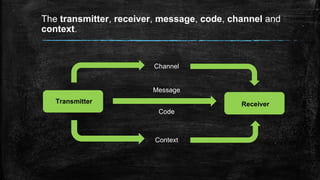
Visual communication involves the exchange of messages through images. The basic elements include a transmitter, receiver, message, code, channel, and context. Symbols, signs, and logos are considered images. Throughout history, images have been used for informative, aesthetic, communicative, and expressive purposes. The meaning of an image is made up of its expressive values, theme, and symbolism. Before photography, common techniques to create images included drawing, painting, and etching. Today, most visual messages come from the press, advertising, television, and the internet. Mass media information comes from these sources as well as radio. The main aim of images in advertising is to encourage consumption of products and services. The main difference between television