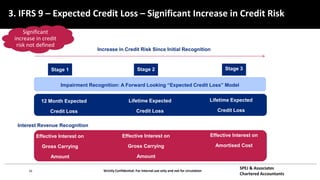
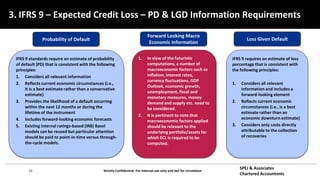
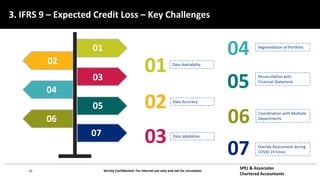
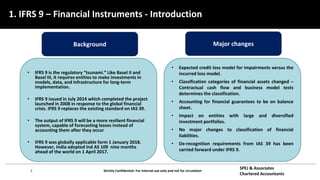
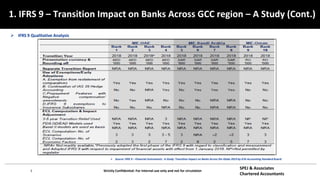
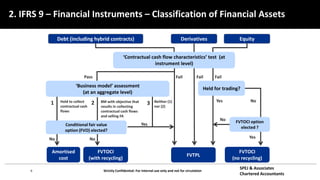
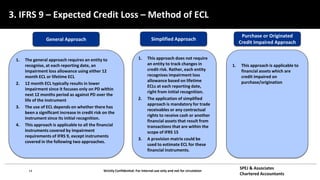
This document discusses IFRS 9 expected credit loss requirements. It provides an overview of topics to be covered, including introduction of IFRS 9 and its impact on UAE banks, classification of financial assets and liabilities, impairment of financial assets using the simplified, general and POCI approaches, examples, and Q&A. The document also analyzes IFRS 9 transition impact on GCC banks and provides guidance on significant credit risk increase, ECL calculation methodology, and information requirements for probability of default and loss given default estimates.










![15 Strictly Confidential: For internal use only and not for circulation
SPEJ & Associates
Chartered Accountants
Is asset being tested a trade receivable, lease
receivable (IFRS 16/IFRS 17) or contract asset
(IFRS 15)?
Policy choice
Calculate the credit loss provision using the 3 stage IFRS 9 model
Analyse credit risk deterioration or improvement since initial recognition
[Stage 1, 2 and 3]
Stage 1:
12 month expected credit loss
Stage 2 and 3:
Lifetime expected credit loss
No
Consider forward looking information
Does the asset have a significant financing
component?
Yes
No
Yes
Lifetime expected credit losses
3 stage IFRS 9 model
Provision matrix
approach
3. IFRS 9 – Impairment model – Decision Tree
Option 1
Option 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/1icaidubaiifrs9expectedcreditlossfinal-221107195749-9eaa224f/85/1_icai_dubai_ifrs_9_expected_credit_loss_final-pdf-15-320.jpg)