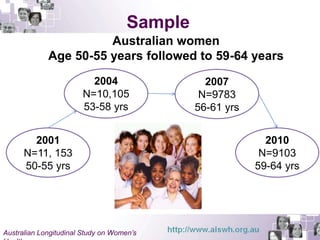
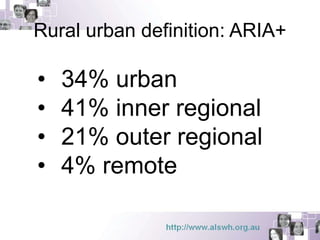
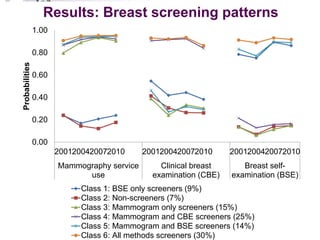
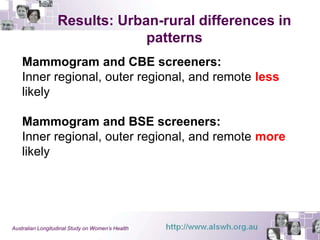
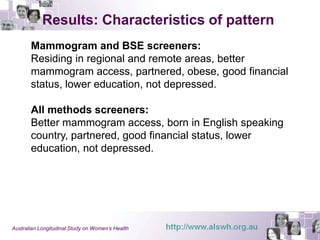
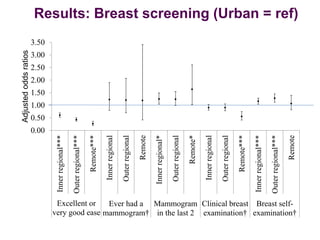
This document summarizes a study examining differences in breast cancer screening patterns between rural and urban Australian women aged 50-64 years. The study used survey data from over 11,000 women participating in the Australian Longitudinal Study on Women's Health. The study identified six distinct patterns of breast cancer screening and found rural women were less likely to undergo mammography and clinical breast examinations but more likely to do breast self-examinations compared to urban women. Characteristics like geographic location, access to services, and socioeconomic status were associated with different screening patterns.