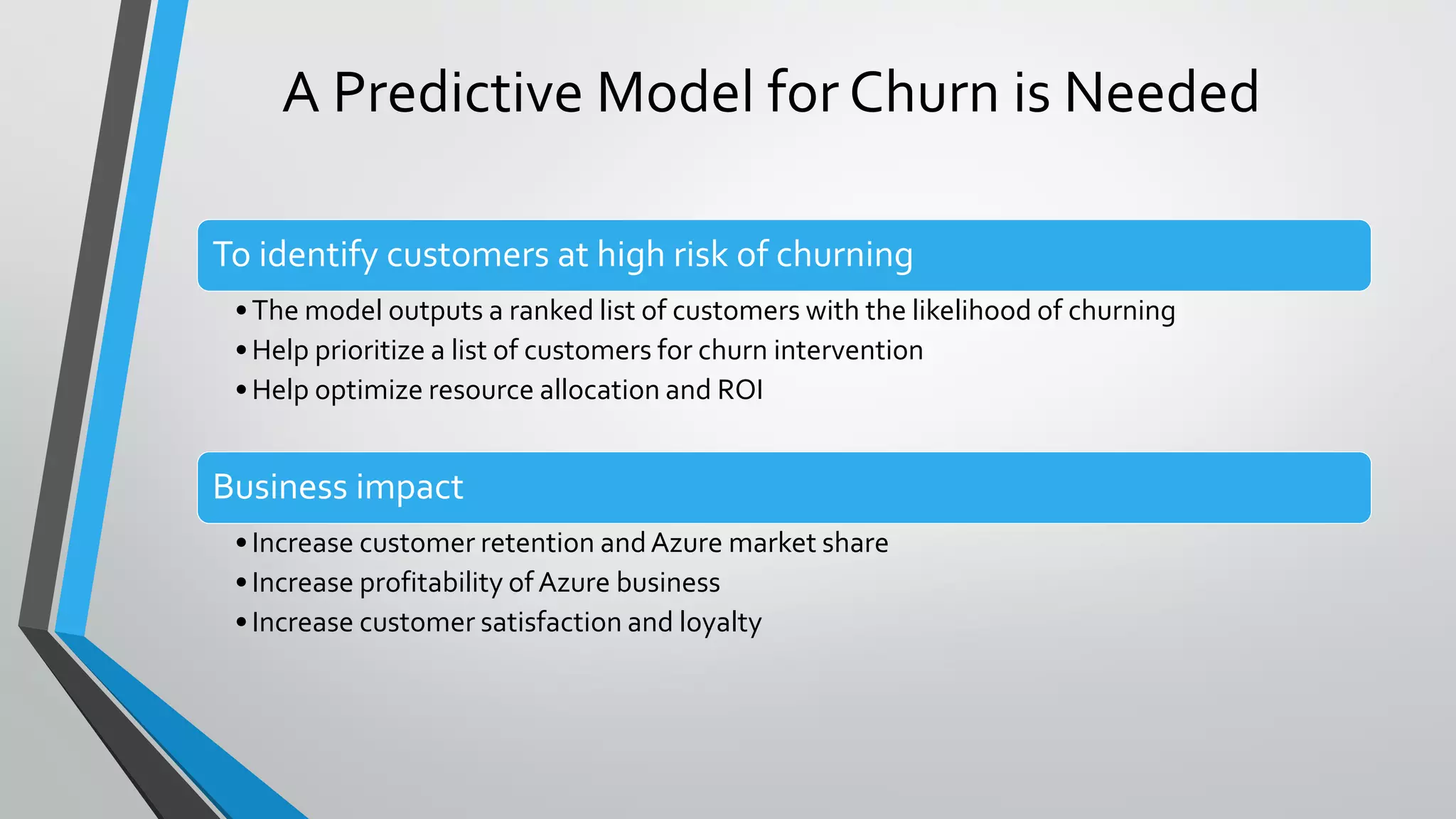
1) The document discusses using deep learning and LIME (Local Interpretable Model-agnostic Explanations) to improve Azure customer churn prediction and explain model predictions.
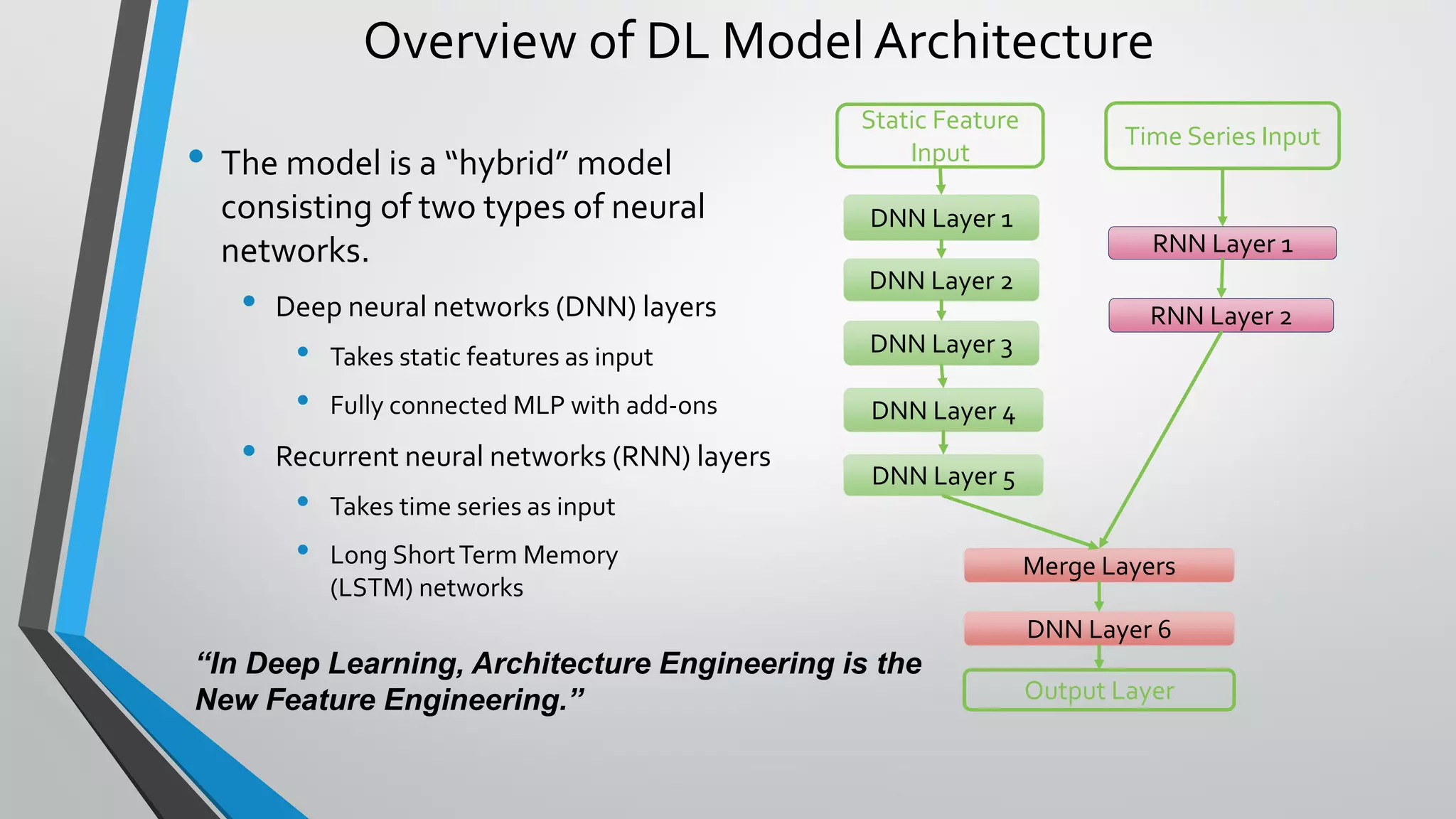
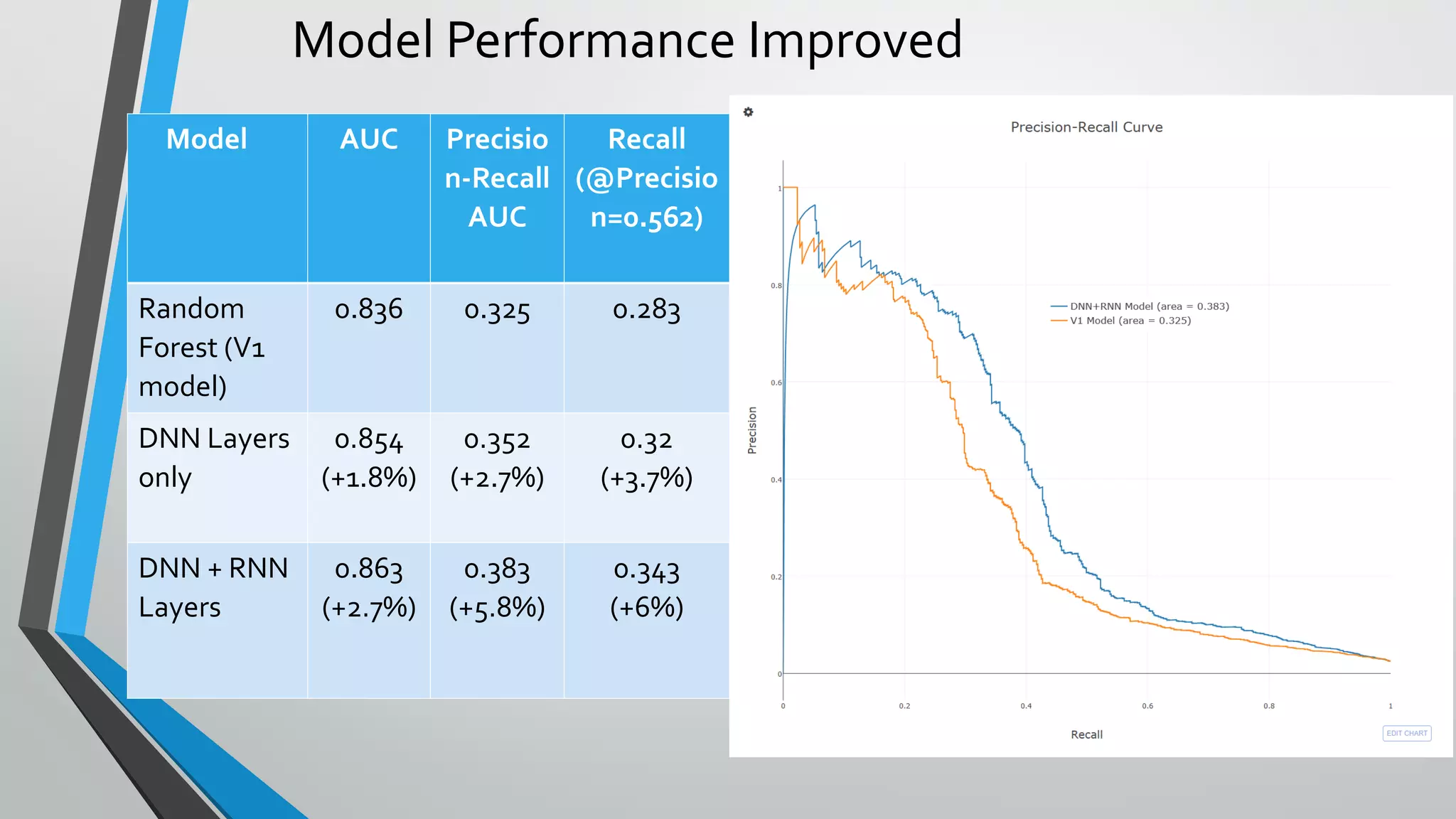
2) A deep learning model combining deep neural networks and recurrent neural networks improved churn prediction accuracy compared to the previous random forest model.
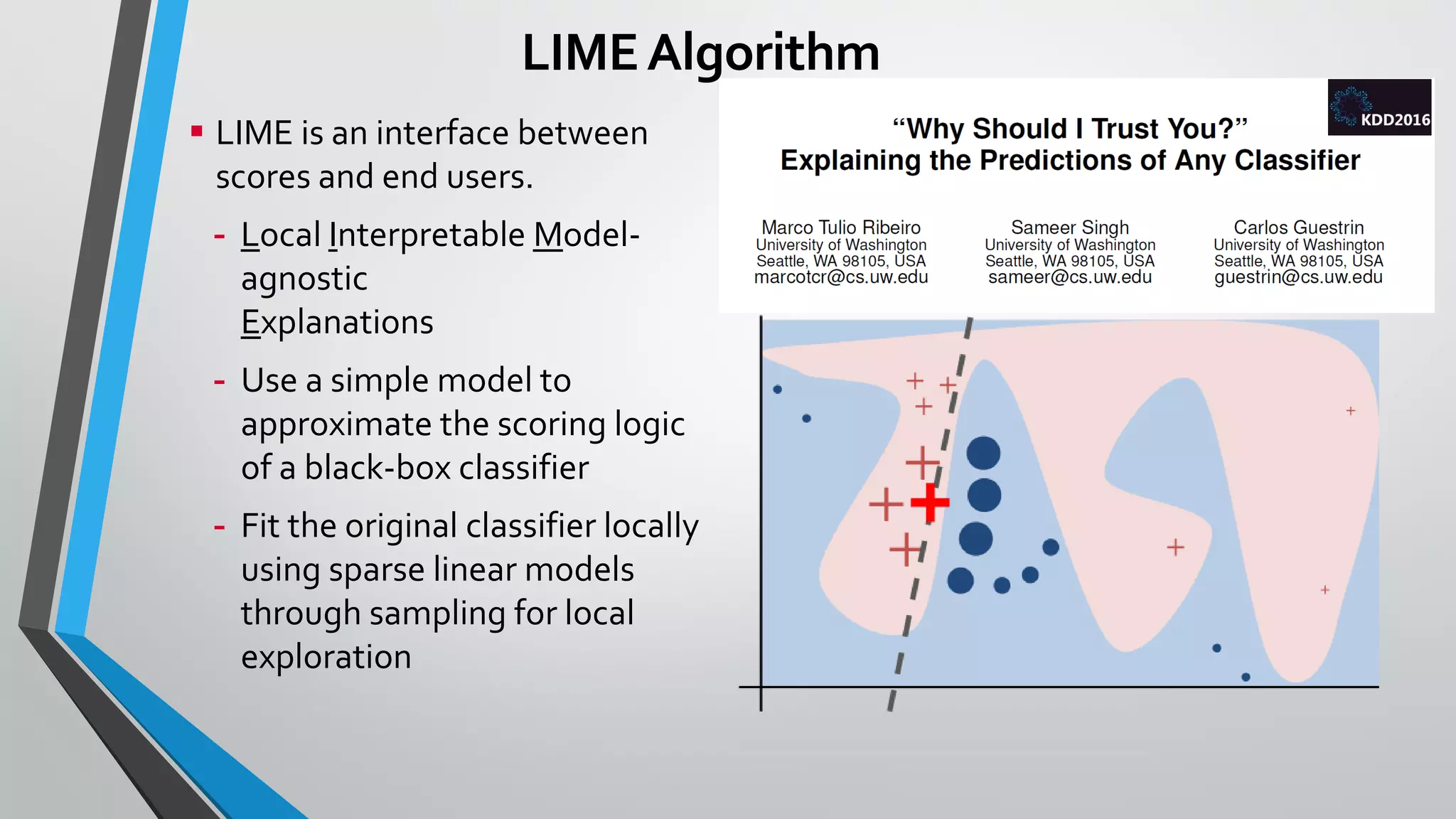
3) LIME is used to explain individual customer churn predictions by approximating the deep learning model locally and showing the most important features influencing the prediction. This helps users understand and trust the model's predictions.