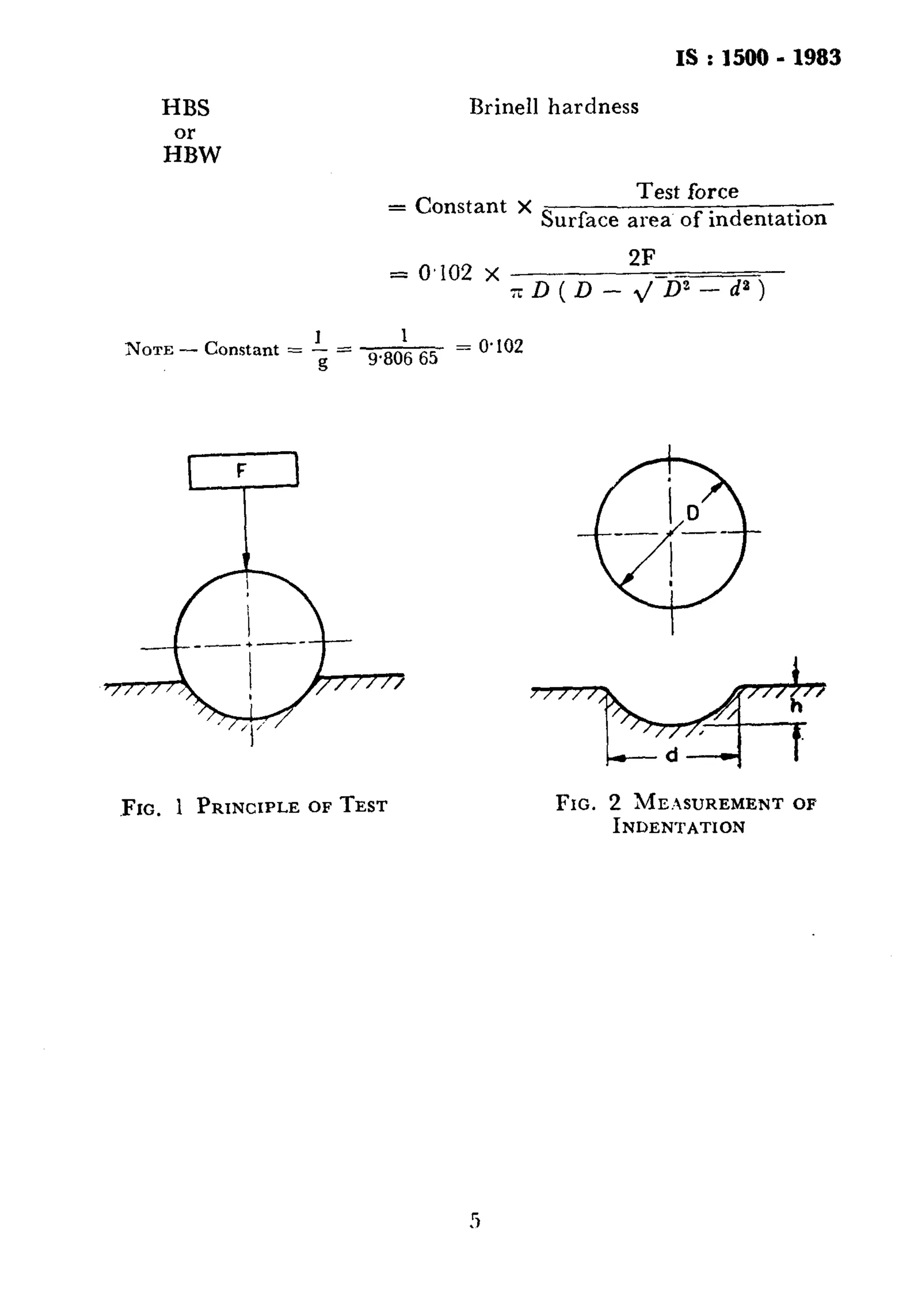
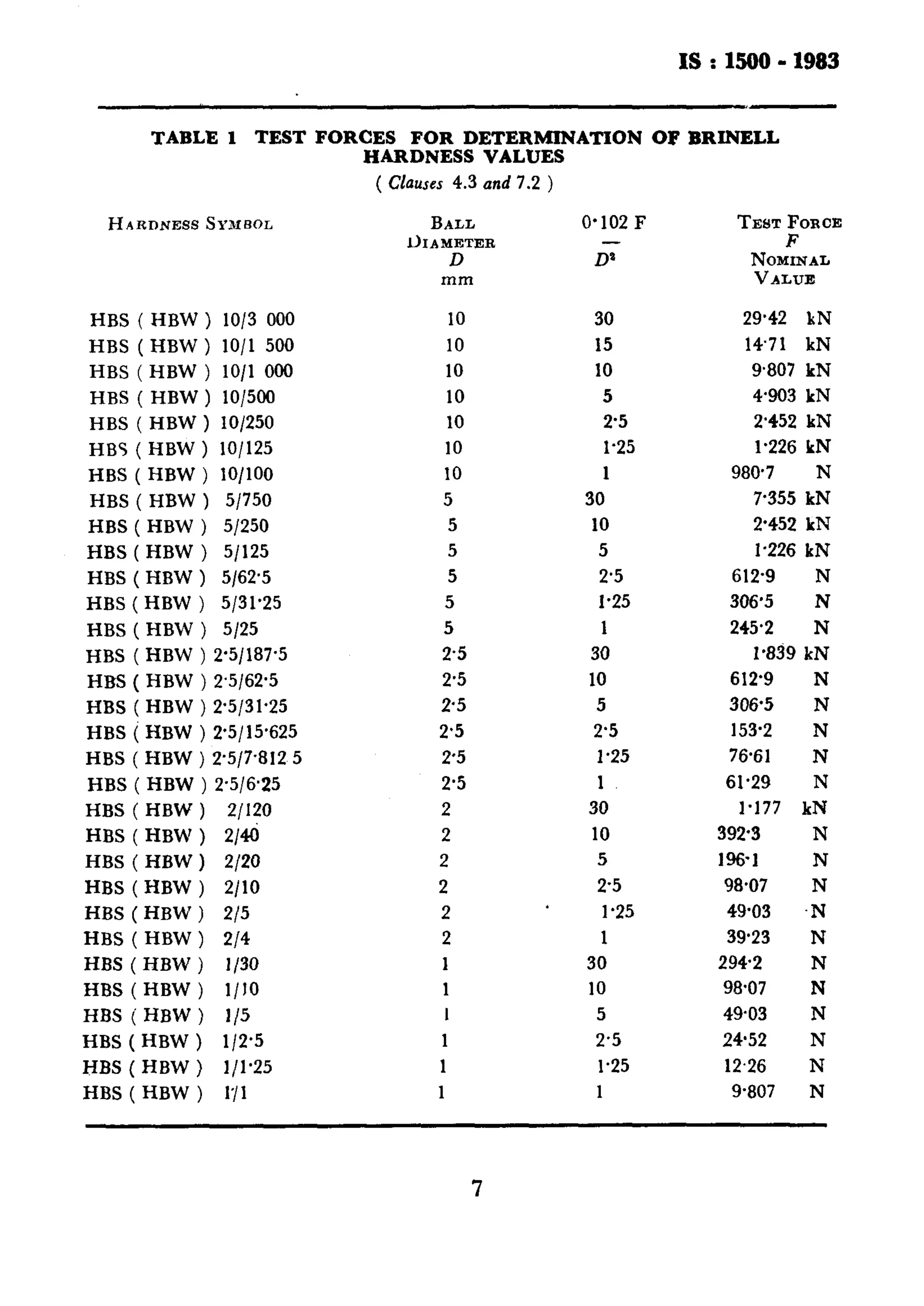
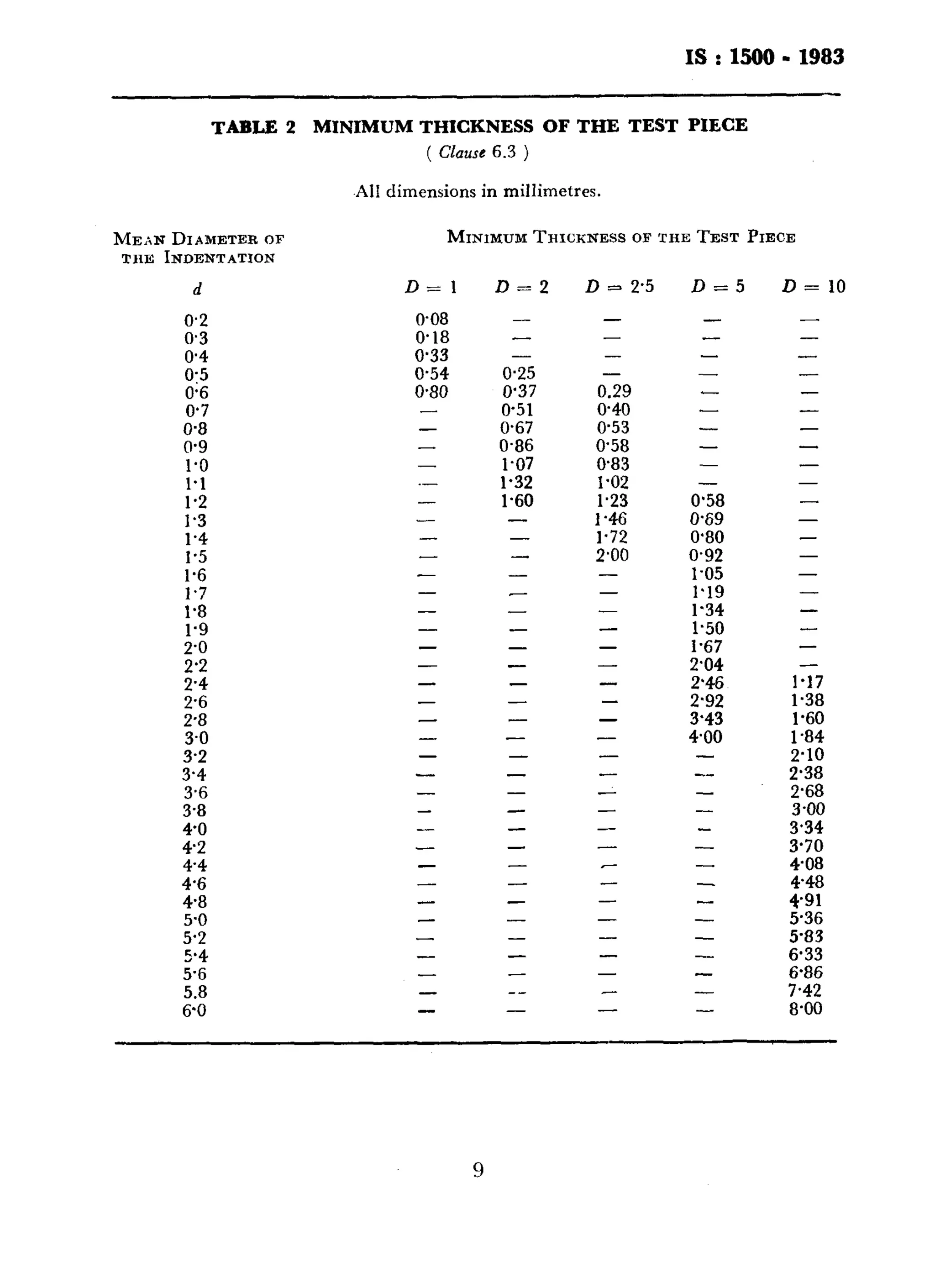
This document provides information on the Indian Standard method for the Brinell hardness test for metallic materials. It outlines the key aspects of the test including:
- The test uses a hardened steel or hard metal ball of a specified diameter that is pressed into the material's surface under a defined load.
- The Brinell hardness value is determined based on the diameter of the indentation left in the surface after removal of the load.
- The standard provides details on apparatus, test pieces, procedures, symbols and designations, and test forces to be used for different materials.