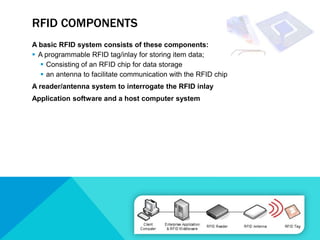
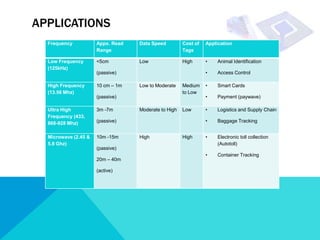
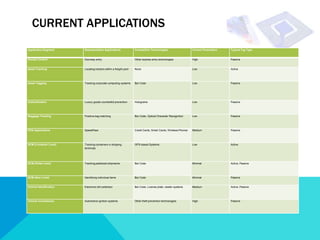
RFID technology allows for electronic identification and wireless tracking of objects using radio frequency signals. An RFID system consists of RFID tags attached to objects, RFID readers to interrogate tags, and software. There are three main types of tags: passive, semi-passive, and active. Current applications include access control, asset tracking, supply chain management, and electronic toll collection. While offering benefits over barcodes like contactless reading and rewritable data, RFID adoption has been limited by higher costs compared to barcodes and interoperability issues due to evolving standards. Further developments are expected in medical and library uses of RFID.