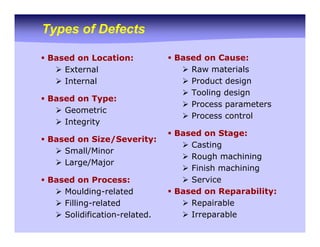
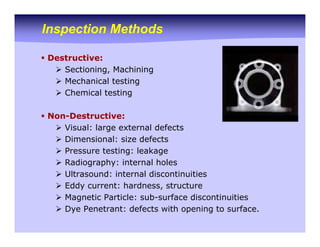
The document outlines various casting defects encountered in manufacturing, categorizing them based on location, type, size, cause, and stage of production. It also details inspection methods for these defects, both destructive and non-destructive, as well as analyses to identify and remedy the defects. Overall, it emphasizes the importance of quality control and the shift in responsibility for defect management towards manufacturers.

![Moulding-related Defects
ƒ Improper Closure
ƒ Across parting plane: flash
ƒ Along parting line: mismatch
FLASH
MISMATCH
[Atlas of Casting Defects, Institute of British Foundrymen]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/120048832-casting-defects-ppt-220717113759-73a3bf60/85/120048832-Casting-Defects-Ppt-pdf-4-320.jpg)
![Filling-related Defects
ƒ Incomplete Filling: cold shut, misrun.
ƒ Gaseous Entrapments: blow hole, gas porosity.
ƒ Solid Inclusions: sand inclusion, slag inclusion.
COLD SHUT MISRUN BLOW HOLE GAS POROSITY
[Atlas
of
Casting
Defects,
Institute
of
British
Foundrymen]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/120048832-casting-defects-ppt-220717113759-73a3bf60/85/120048832-Casting-Defects-Ppt-pdf-5-320.jpg)
![Solidification/Cooling-related Defects
ƒ Solidification Shrinkage: cavity, porosity, centerline, sink.
ƒ Hindered Cooling Contraction: hot tear, crack, distortion.
SHRINKAGE CAVITY POROSITY
SINK CORNER SHRINKAGE CRACK
[Atlas
of
Casting
Defects,
Institute
of
British
Foundrymen]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/120048832-casting-defects-ppt-220717113759-73a3bf60/85/120048832-Casting-Defects-Ppt-pdf-6-320.jpg)


